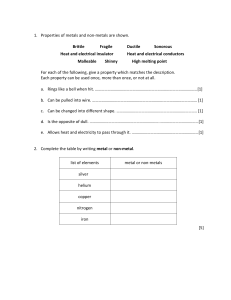
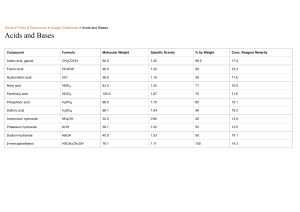
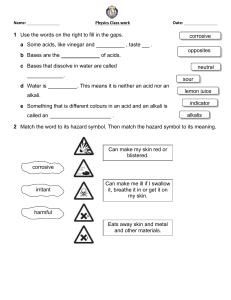
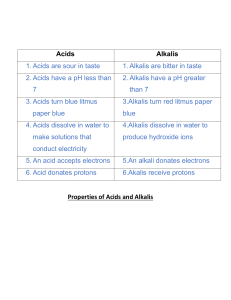
Unit 5 Acids, bases and salts ALKALIS AND BASES Pages 129-131 Ms. Rabiya Waheed CLASSROOM RULES STARTER https://youtu.be/zYGnq7-_L9w Students will: Identify the alkalis and bases. Describe the properties and uses of alkalis and bases • bases • alkali • neutralization • antacids Alkalis Alkalis are substances that dissolve in water to give solutions with a pH greater than 7. The solution contains an excess of hydroxide (OH-) ions. What will be the color of alkalis with litmus paper? Alkalis and bases The Venn diagram shows relation between alkalis and bases. All alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis Alkalis Alkalis are bases that is soluble in water. Alkalis are generally used in the laboratory as aqueous solution. Examples: Sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH). Potassium hydroxide solution (KOH). Calcium hydroxide solution Ca(OH)2 often known as limewater. Ammonium hydroxide solution NH4OH also known as ammonia solution. These solutions contain OH- ions, turn litmus paper blue and have pH greater than 7 Bases A base will neutralize an acid, and as a result salt and water is formed. This is called neutralization reaction. Alkalis and bases The alkalis will also neutralize acids as they belong to the base group with a difference that they are soluble in water Q. How are bases different from alkalis? Students will: Identify the alkalis and bases. Describe the properties and uses of alkalis and bases Properties of alkalis and bases Bases: neutralize acids to give salt and water only are the oxides and hydroxides of metals are mainly insoluble in water Alkalis are bases that dissolve in water, and feel soapy to skin turn litmus blue give solutions with a pH greater than 7. give solutions that contain OH- ions Properties of antacids Antacids are compounds that are used to neutralize acid digestion and include: Magnesium oxide and magnesium hydroxide Sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogencarbonate Calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate Alkalis-Formula and uses Name Formula Strong/weak Where found or used Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) NaOH Strong In oven cleaners; in making soap and paper. Potassium hydroxide (caustic potash) KOH Strong In making soft soaps and biodiesel Calcium hydroxide (limewater) Ca(OH)2 Strong To neutralize soil acidity and acidic gases produced by power stations; has limited solubility Ammonia solution (ammonium hydroxide) NH3 or NH4OH weak In cleaning fluids in the home; in making fertilizers. Bases- Formula and uses Name Formula Where found or used Calcium oxide CaO For neutralizing soil acidity and industrial waste; in making cement and concrete Magnesium oxide MgO In antacid indigestion tablets A solution of calcium hydroxide in water is alkaline. a. Which one of the pH below is alkaline pH 3 pH 6 pH7 pH11 b. Which of the following is common name for calcium hydroxide Cement limestone quicklime slaked lime c. Some farmers use calcium hydroxide to control soil acidity. Why is it important to control soil acidity? d. Calcium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. State the name of this type of chemical reaction e. What are the products formed as a result of this reaction? A solution of calcium hydroxide in water is alkaline. a. Which one of the pH below is alkaline pH 3 pH 6 pH7 pH11 b. Which of the following is common name for calcium hydroxide Cement limestone quicklime slaked lime c. Some farmers use calcium hydroxide to control soil acidity. Why is it important to control soil acidity? For the growth of plants. d. Calcium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. State the name of this type of chemical reaction Neutralization reaction e. What are the products formed as a result of this reaction? Salt (calcium chloride) and water Students will: Identify the alkalis and bases. Describe the properties and uses of alkalis and bases Alkalis and bases Properties of antacids Properties and uses of alkalis and bases