Trigonometric Identities Lesson: Simplify & Find Trig Values
advertisement

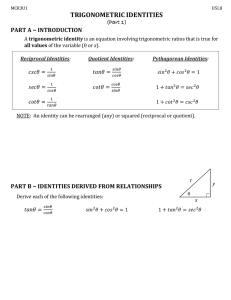
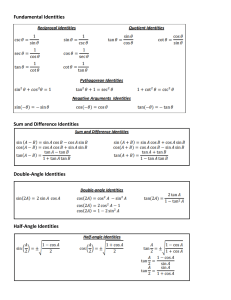
Lesson 5-1 Trigonometric Identities Students will be able to: ❖ Identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trig values ❖ Use basic trigonometric identities to simplify and rewrite trigonometric expressions Warm up: Identity in math: When the left side is equal to the right side for all values of a variable. An example: 2 · 𝑏 = 𝑏 · 2 Brainstorm some more: Notes: We know: Reciprocal Identities 1 1 𝑠𝑖𝑛(θ) = 𝑐𝑠𝑐(θ) 𝑐𝑠𝑐(θ) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛(θ) 1 1 1 1 Quotient Identities 𝑠𝑖𝑛(θ) 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) = 𝑠𝑒𝑐(θ) 𝑠𝑒𝑐(θ) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) = 𝑐𝑜𝑡(θ) 𝑐𝑜𝑡(θ) = 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) 𝑐𝑜𝑡(θ) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛(θ) Pythagorean Identities 2 2 2 2 2 𝑡𝑎𝑛 (θ) + 1 = 𝑠𝑒𝑐 (θ) 2 𝑠𝑖𝑛 (θ) + 𝑐𝑜𝑠 (θ) = 1 𝑐𝑜𝑡 (θ) + 1 = 𝑐𝑠𝑐 (θ) Cofunction Identities π 𝑠𝑖𝑛(θ) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠( 2 − θ) π 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛( 2 − θ) π 𝑐𝑠𝑐(θ) = 𝑠𝑒𝑐( 2 − θ) 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) = 𝑐𝑜𝑡( 2 − θ) π 𝑐𝑜𝑡(θ) = 𝑡𝑎𝑛( 2 − θ) Odd-Even Identities 𝑠𝑖𝑛(− θ) = − 𝑠𝑖𝑛(θ) 𝑐𝑠𝑐(− θ) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠(− θ) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) 𝑠𝑒𝑐(− θ) = 𝑠𝑒𝑐(θ) 𝑡𝑎𝑛(− θ) = 𝑐𝑜𝑡(− θ) = 𝑠𝑒𝑐(θ) = 𝑐𝑠𝑐( 2 − θ) − 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) π π − 𝑐𝑠𝑐(θ) − 𝑐𝑜𝑡(θ) Example 1: Use Reciprocal and Quotient Identities (pg. 312) If 𝑐𝑠𝑐(θ) = 7 , find 𝑠𝑖𝑛(θ) 4 If 𝑐𝑜𝑡(𝑥) = Practice: 5 If 𝑠𝑒𝑐(𝑥) = 3 , find 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥) Example 2: Use Pythagorean Identities (pg. 313) If 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) = − 8 and 𝑠𝑖𝑛(θ) > 0, find 𝑠𝑖𝑛(θ) and 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) Practice: Find 𝑐𝑠𝑐(θ) and 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) if 𝑐𝑜𝑡(θ) = − 3 and 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) < 0 1 Find 𝑐𝑜𝑡(𝑥) and 𝑠𝑒𝑐(𝑥) if 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑥) = 6 , 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥) > 0 5 , find 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥) 3 Example 3: Use Cofunction and Odd-Even Identities (pg. 314) π If 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) = 1. 28, find 𝑐𝑜𝑡(θ − 2 ) Practice: If 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑥) = π − 0. 37, find 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥 − 2 ). Example 4: Rewriting Using Only Sine and Cosine (pg. 315) Simplify 𝑐𝑠𝑐(θ)𝑠𝑒𝑐(θ) − 𝑐𝑜𝑡(θ) Practice: Simplify 𝑠𝑒𝑐(𝑥) − 𝑡𝑎𝑛(𝑥)𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑥) Homework pg 317: Find the value of each expression using the given information 5 1) If 𝑐𝑜𝑡(θ) = 7 , find 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) 1 5) If 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥) = 6 , 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑥) = 35 , find 𝑐𝑜𝑡(𝑥) 6 9) 𝑠𝑒𝑐(θ) 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) given that 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) = − 5, 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) > 0 8 13) 𝑐𝑜𝑠(θ) and tan(θ) given that 𝑐𝑠𝑐(θ) = 3 , 𝑡𝑎𝑛(θ) > 0 17) If 𝑐𝑠𝑐(θ) = π − 1. 24 find 𝑠𝑒𝑐(θ − 2 ) Simplify the expressions 23) 𝑐𝑠𝑐(𝑥) − 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥)𝑐𝑜𝑡(𝑥) 24) 𝑠𝑒𝑐(𝑥)𝑐𝑜𝑡(𝑥) − 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑥)