MEC 20001
Handong Global University
Prof. Sawoong Kang
Homework 1 (Friday, April 12, 2024)
You can write answers in Korean or English. (Full Score: 90 points)
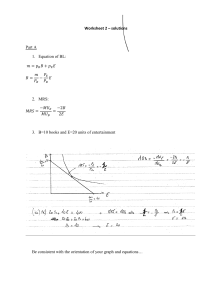
1. (10) Under what assumptions two indifference curves of the same consumer cannot intersect with each
other? Explain by using a graph.
2. (15) Sandy’s preference is represented by the following utility function.
(𝑿 − 𝟑)(𝒀 − 𝟐) 𝐢𝐟 𝑿 ≥ 𝟑 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝒀 ≥ 𝟐
𝑼={
𝟎
𝐢𝐟 𝑿 < 𝟑 𝐨𝐫 𝒀 < 𝟐
Her income is 20. The prices are: 𝑷𝑿 = 𝟐, 𝑷𝒀 = 𝟏.
A. (8) Show that her MRS is diminishing along the indifference curve.
B. (7) Find the optimal consumption bundle and the maximum utility.
3. (10) Hanna’s utility function is given by 𝑼 = 𝟏𝟎𝟎√𝑿 + 𝒀. Her income is 𝟏𝟎𝟎. And 𝑷𝒀 = 𝟏.
A. (5) Find the optimal consumption bundle when 𝑷𝑿 = 𝟓.
B. (5) Find the optimal consumption bundle when 𝑷𝑿 = 𝟓𝟎.
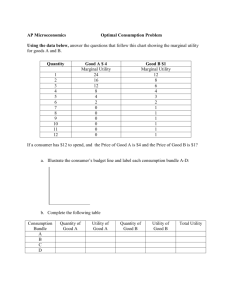
4. (20) Kevin’s utility function is given by 𝑈 = min (2𝑋, 𝑌). The prices are: 𝑃𝑋 = 𝑃, 𝑃𝑌 = 1. The income
is given by 20.
(10) Derive and graph his demand curve for good 𝑋.
A.
B. (10) Compute the price elasticity of demand when 𝑷 = 𝟖.
1
2
5. (10) Michael’s utility is given by 𝑈 = 𝑋 3 𝑌 3 . His income is 𝑀. And the price of good 𝑋 is 2 and the
price of good 𝑌 is denoted by 2. Derive and graph the ICC (income consumption curve).
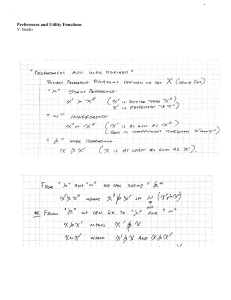
6. (10) Mary’s utility function is given by 𝑼 = 𝑿 + 𝟐𝒀. Her income is 𝟐𝟎. The prices are: 𝑷𝑿 = 𝟒,
𝑷𝒀 = 𝟐.
A. (3) Find her optimal consumption bundle.
B. (7) Now suppose that the price of good 𝒀 has risen to 𝑷′𝒀 = 𝟒.
i.
(3) Find her new optimal consumption bundle.
ii.
(4) Decompose the total price effect into substitution effect and income effect.
1
MEC 20001
Handong Global University
Prof. Sawoong Kang
7. (15) A representative consumer’s utility is given by 𝑼 = 𝑿𝒀. His income is 𝟐𝟒𝟎. And the prices are:
𝑷𝑿 = 𝟐, 𝑷𝒀 = 𝟏.
A. (3) Find the optimal consumption bundle and the maximum utility.
B. (8) Now the government levies a 𝟓𝟎% tax on the consumption of good 𝑿.
i.
(4) Find the optimal consumption bundle and the maximum utility.
ii.
(4) Compute the tax revenue from this tax.
C. (4) Now the government levies a lump-sum tax of the same amount as that you have obtained in
(ii) of part (B). Find the optimal consumption bundle and the maximum utility.
2