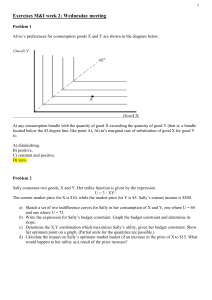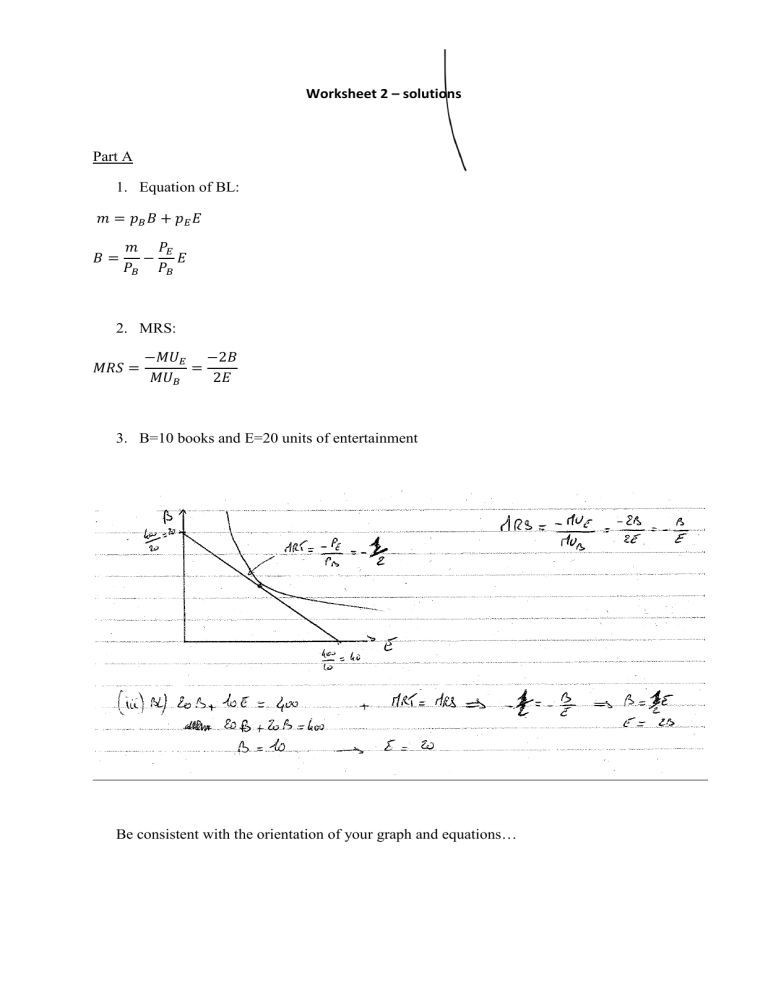
Worksheet 2 – solutions Part A 1. Equation of BL: 𝑚 = 𝑝𝐵 𝐵 + 𝑝𝐸 𝐸 𝐵= 𝑚 𝑃𝐸 − 𝐸 𝑃𝐵 𝑃𝐵 2. MRS: 𝑀𝑅𝑆 = −𝑀𝑈𝐸 −2𝐵 = 𝑀𝑈𝐵 2𝐸 3. B=10 books and E=20 units of entertainment Be consistent with the orientation of your graph and equations… Part B 1. Initial situation 𝑀𝑅𝑆 = − 𝑀𝑈𝐷 −𝐹 = 𝑀𝑈𝐹 𝐷 𝑀𝑅𝑇 = − 𝑝𝐷 −4 = 𝑃𝐹 5 4 Tangency condition: 𝐹 = 5 𝐷 Budget constraint: 160𝐷 + 200𝐹 = 8,000 𝐷∗ = 25; 𝐹 ∗ = 20 𝑈(25,20) = 500 2. Change in price of D Budget constraint: 250𝐷 + 200𝐹 = 𝑥 𝐷∗ = 𝑥 𝑥 ; 𝐹∗ = 500 400 3. Keep utility constant ∗ 𝑈(𝐷 , 𝐹 ∗) 𝑥2 = = 500 500 ∗ 400 𝑥 = √108 = 10,000 4. Compensated bundle 𝐷𝐶∗ = 𝑥 10,000 𝑥 10,000 = = 20; 𝐹 𝐶∗ = = = 25 500 500 400 500 5. Final optimal bundle 𝐷∗∗ = 𝑥 8,000 𝑥 8,000 = = 16; 𝐹 ∗∗ = = = 20 500 500 400 500 6. Conclusion We have decomposed the change in quantity demanded due to a price change into two effects (i) a substitution effect (change in prices: slope of the budget line, but utility is kept constant) and (ii) an income effect (change in purchasing power). Part C Optimality conditions: 1. 𝑝1 𝑞1 + 𝑝2 𝑞2 = 𝑌 2. 𝑀𝑅𝑆 = 𝑀𝑅𝑇 Using the tangency condition first: 𝑀𝑈1 = 𝜕𝑈 = 𝑎. 𝑞1𝑎−1 . 𝑞21−𝑎 𝜕𝑞1 𝑀𝑈2 = 𝜕𝑈 = (1 − 𝑎). 𝑞1𝑎 . 𝑞2−𝑎 𝜕𝑞2 𝑀𝑅𝑆 = 𝑀𝑈1 𝑎 𝑞2 = . 𝑀𝑈2 1 − 𝑎 𝑞1 𝑀𝑅𝑇 = 𝑀𝑅𝑆 = 𝑀𝑅𝑇 𝑝1 𝑝2 𝑎 𝑞2 𝑝1 . = 1 − 𝑎 𝑞1 𝑝2 ≡ (1 − 𝑎). 𝑞1 . 𝑝1 = 𝑎. 𝑞2 . 𝑝2 Second, we substitute using the budget line: BL: 𝑝2 𝑞2 = 𝑌 − 𝑝1 𝑞1 Quantity demanded for each good: 𝑞1 = 𝑞2 = 𝑎𝑌 𝑝1 (1 − 𝑎)𝑌 𝑝2 Note the steps! They will always be the same.