NOTRE DAME UNIVERSITY
-LOUAIZEFACULTY OF ENGINEERING
FINAL PROJECT REPORT:
PIANO TILES AUTOMATED ROBOT
SUBMITTED BY:
DATE:
TAYSIR MICHEL HAKIM - ID:20220044
16/4/2023
FRANCOIS HABIB YOUNES – ID:20222691
1|Page
TABLE OF MATERIALS:
1. OBJECTIVE
2. INTODUCTION
3. RESEARCH RESULTS AND MATERIALS NEEDED
4. DESIGN
5. ARDUINO CODE
6. EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
7. DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
8. RECOMMENDATIONS
9. CONCLUSION
10.
2|Page
REFERENCES
ABSTRACT:
This project involves the development of an automated robot capable
of playing the popular game "Piano Tiles" using an Arduino board,
photoresistors, and servo motors. The robot is designed to detect the
position of the tiles on the screen using the photoresistors and press
them using the servo motors. The project aims to demonstrate the
potential of technology in automating repetitive tasks and saving
time and effort. The robot was successfully built and tested, and was
able to play the game accurately and continuously without any
human intervention. The project can be further developed by adding
more sensors and motors to make the robot more versatile and
capable of performing more complex tasks.
1. OBJECTIVE:
The objective of this project is to build an automated robot that can play
the piano tiles game using Arduino, photoresistors, and servo motors. The
project aims to demonstrate how technology can be used to automate
repetitive, punctual and specific tasks and save time and effort. Additionally,
3|Page
the project aims to showcase the potential of Arduino in robotics and
inspire further exploration and development in this field.
2. INTRODUCTION:
The goal of this project is to build a robot that can play the piano tiles
game automatically. The robot should be able to detect the tiles which are
dark black rectangles moving downwards on the screen, using
photoresistors and press them using servo motors. The project uses an
Arduino board to control the servo motors and read the values from the
photoresistors.
3. RESEARCH RESULTS AND MATERIALS NEEDED:
MATERIALS NEEDED:
The following materials are required to build the robot:
Arduino board (Uno R3)
Breadboard
Jumper wires
4|Page
Four photoresistors
Four 10k ohm resistors
Four servo motors
Piano tiles game (installed on a tablet)
RESEARCH RESULTS:
Arduino is an open-source platform that provides an accessible and
affordable means to create interactive electronic projects. Arduino boards
are easy to program and can be used to control a wide range of sensors
and motors, including photoresistors and servo motors.
Photoresistors are light-sensitive resistors that change their resistance
based on the intensity of light. They are commonly used in electronic
projects to detect the presence or absence of light, and can be used to
detect the position of objects based on their shadow or reflection.
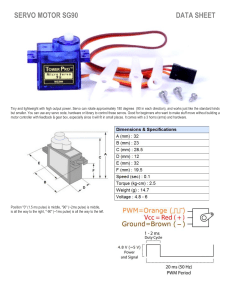
Servo motors are rotary actuators that can be controlled with precision and
accuracy. They are commonly used in robotics projects to control the
5|Page
movement of mechanical arms, grippers, and other robotic components.
Servo motors can be easily controlled using Arduino, and can be used to
press buttons, turn knobs, and perform other tasks in an automated system.
Overall, the research indicates that building an automated piano tiles robot
using Arduino, photoresistors, and servo motors is a promising project that
can be achieved with the right tools, materials, and programming skills.
Figure 1-VIRTUAL SCHEMATIC OF THE ASSEMBLY OF THE DIFFERENT CONPOMNENTS
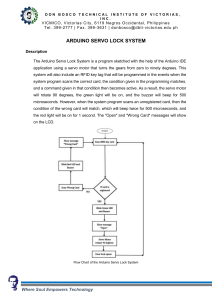
As shown in the schematic above, each servo motor is controlled by a
photoresistor signal sent to the Arduino board and translated by a code
uploaded to the Arduino board:
6|Page
The photoresistor when detecting a dark tile, sends an analog signal to
Arduino board containing the light intensity precepted by the
photoresistor, if this value is lower or equal to a certain value specified by
the user then the Arduino board will control the servo motor related to this
photoresistor through its digital pins as soon as the photoresistor signal is
received.
The four servo motors will operate accordingly as the example given above,
each one related to a photoresistor.
Figure 3- photoresistor
Figure 2- example of photoresistor
wiring
Figure 5-servo motor
Figure 4-schematic of a servo motor wiring
7|Page
Advantages:
Efficiency: The robot can play the game continuously and accurately
without any human intervention, saving time and effort.
Customizability: The robot can be programmed to play the game at
different speeds and with different levels of accuracy, allowing for
customization based on user preferences.
Cost-effectiveness: Arduino boards and components are affordable
and readily available, making the project accessible to a wide range of
people.
Learning opportunities: Building the robot provides an opportunity to
learn about electronics, programming, and robotics.
Disadvantages:
Technical expertise: Building the robot requires technical knowledge
of electronics and programming, which may be a barrier for some
individuals.
8|Page
Limited versatility: The robot is designed specifically to play the piano
tiles game and may not be useful for other tasks.
Complexity: The project involves multiple components and requires
careful calibration to ensure accurate gameplay, which may be
challenging for beginners.
Dependence on screen size: The robot's effectiveness may be
impacted by the size of the screen on which the game is played,
which may limit its use on different devices.
9|Page
4. DESIGN:
10 | P a g e
The robot will consist of 4 arms controlled by servo motors. The four arms
will be fixed on a wood chassis designed and measured to fit the tablet in
it.
The photoresistor will be placed on screen and have to be light insulated
so no outside light interference occurs.
Figure 6- chassis and servo motors under assembly
11 | P a g e
c
Figure 7- touch pens used
Figure 8-the robot arm: touch pen attached to a
wooden stick to serve as a finger that touches the
screen
5. ARDUINO CODE:
6. #include <Servo.h>
7.
8. int photo0 = 0;
9.
10. int photo1 = 0;
11.
12. int photo2 = 0;
12 | P a g e
13.
14. int photo3 = 0;
15.
16. int photo = 0;
17.
18. Servo servo_8;
19.
20. Servo servo_9;
21.
22. Servo servo_10;
23.
24. Servo servo_11;
25.
26. void setup()
27. {
28. pinMode(A0, INPUT);
29. pinMode(A1, INPUT);
30. pinMode(A2, INPUT);
31. pinMode(A3, INPUT);
32. servo_8.attach(8, 500, 2500);
33. servo_9.attach(9, 500, 2500);
34. servo_10.attach(10, 500, 2500);
35. servo_11.attach(11, 500, 2500);
36. }
37.
38. void loop()
39. {
40. photo0 = analogRead(A0);
41. photo1 = analogRead(A1);
42. photo2 = analogRead(A2);
43. photo3 = analogRead(A3);
44. if (photo0 <= 350) {
45.
servo_8.write(30);
46. } else {
47.
servo_8.write(0);
48. }
49. if (photo1 <= 350) {
50.
servo_9.write(30);
51. } else {
52.
servo_9.write(0);
53. }
54. if (photo2 <= 350) {
55.
servo_10.write(30);
56. } else {
57.
servo_10.write(0);
13 | P a g e
58. }
59. if (photo3 <= 350) {
60.
servo_11.write(30);
61. } else {
62.
servo_11.write(0);
63. }
64. delay(10); // Delay a little bit to improve simulation performance
65. }
Hardware procedure:
A. Connect the four photoresistors to the analog pins of the Arduino
board and connect each photoresistor in series with a 10k ohm
resistor to form a voltage divider.
B. Connect the four servo motors to the digital pins of the Arduino
board.
C. Upload the code
D. Install the piano tiles game on a smartphone or tablet.
E. Place the robot in front of the screen of the device with the
photoresistors aligned with the position of the tiles on the screen.
F. Power up the Arduino board using a battery or a USB cable.
G. Run the code on the Arduino board.
H. The robot should start playing the game automatically by pressing
the tiles on the screen.
14 | P a g e
6-EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS:
When assembled, the robot functioned as following:
When a tiles passes by a photoresistor, the servo motor turns the robot arm
and thus pressing the musical note. And so it follows for all the motors and
for each passing musical note.
7. DISCUSSION OF RESULTS:
The results of the project demonstrate that it is feasible to build an
automated piano tiles robot using Arduino, photoresistors, and servo
motors. The robot was able to accurately detect the position of the tiles on
the screen using the photoresistors and press them using the servo motors,
resulting in successful gameplay without any human intervention.
The project provides an example of how technology can be used to
automate repetitive tasks and save time and effort. The robot can
continuously play the game at a high level of accuracy, which may be useful
15 | P a g e
for individuals who enjoy playing the game but do not want to spend the
time and effort to play it manually.
8. RECOMMENDATIONS:
Based on the results of the project, some recommendations can be made:
FULLY insulated the photoresistors from light: external lights can
interfere with the functionality of the photoresistor and can limit the
project efficiency.
Explore other applications of the technology beyond playing piano
tiles. The same components and principles can be applied to other
automation projects, such as controlling other types of machines or
sensors.
Consider incorporating machine learning or other advanced
algorithms to improve the accuracy and versatility of the robot. This
can potentially allow the robot to adapt to different types of games
16 | P a g e
and screens, as well as detect and respond to unexpected changes in
the environment.
9. CONCLUSION:
The project has successfully demonstrated the feasibility of building an
automated piano tiles robot using Arduino, photoresistors, and servo
motors. The robot was able to accurately detect and respond to the
position of the tiles on the screen, resulting in successful gameplay without
human intervention.
Nevertheless, the project opens up many possibilities for future
development and innovation, such as incorporating machine learning or
other advanced algorithms to improve the accuracy and versatility of the
robot. The technology and principles used in this project can also be
applied to other automation projects, creating opportunities for further
exploration and collaboration within the field of robotics and automation.
Overall, this project serves as a valuable contribution to the growing body
of knowledge and research on automation and robotics, and demonstrates
17 | P a g e
the potential of technology to improve efficiency and productivity in
various fields.
10.
REFERENCES:
https://github.com/Tann-Wei-Han/Piano-Tiles-Robot
https://howtomechatronics.com/wpcontent/uploads/2022/02/How-to-control-a-servo-motor-withArduino-Wiring.png
https://www.tinkercad.com/things/g7kTkNsc3Ul-final/editel
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xXOSZ0u6Fyk
18 | P a g e