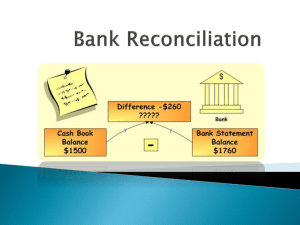
Bank Reconciliation 1. Timing differences (e.g., unpresented cheques, deposits not yet credited). 2. Errors (e.g., mistakes in recording transactions in the Cash Book or by the bank). • Ensures the accuracy of financial records. • Detects and resolves any discrepancies. • Verifies the company’s actual available bank balance. • • Unpresented cheques Uncredited deposits • Errors 1. Direct Bank Transfer: Automatic transfer of money from a firm's account to creditors or employees. 2. Bank Overdraft: When a firm's withdrawals exceed its deposits, creating a debt owed to the bank. 3. Direct Debit: An agreement allowing a creditor to withdraw varying amounts from a firm’s account. 4. Standing Order: Agreement for a creditor to withdraw fixed sums at regular intervals. 5. Drawer: The person writing a cheque. 6. Payee: The person to whom the cheque is paid. • Unpresented Cheque: A cheque issued but not yet cleared. • Bank Lodgement: A cheque received but not yet cleared. • Dishonoured Cheque: A cheque that is not honoured by the bank. 1. Update the Cash Book: o Check for transactions in the bank statement that are missing in the cash book. 2. Prepare the Bank Reconciliation Statement: o Reconcile the differences between the Cash Book and Bank Statement balances. • Debit: Represents money leaving your account. • Credit: Represents money entering your account. 1. Identify and update missing transactions in the Cash Book. 2. Reconcile the remaining balance using an agreed format to confirm time delays and rule out errors. • Provided example highlights differences due to: o Bank charges o Bank interest o Unrecorded transactions