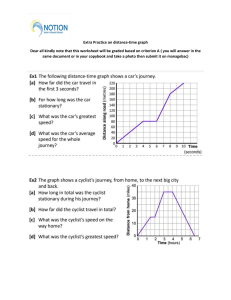
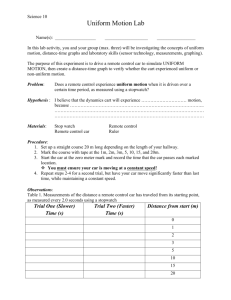
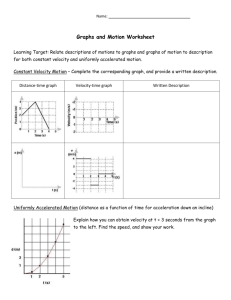
GOOD MORNING!!! ROSILEND M. ROMANILLOS Physics Teacher SCIENCE 7 - PHYSICS Third Quarter ROSILEND M. ROMANILLOS Physics Teacher PRAYERS CHECKING OF ATTENDANCE Group Activity . FOUR PICTURE IN A WORD Guess the word by analyzing the given picture. In this ac tivity, you'll be shown 4 photos in a grid, all of which share a word in common. Your goal is to figure out the common word. You are provided a paper where you write the word, within one minute all must show answer, for every correct answer a group will get a score of 5 points. 4 pic’s one word A. B. C 4 pic’s one word A. B. distance C time speed exploring distance-time relationship Objectives: 1. Define distance and time. 2. Explain the relationship between distance and time. 3. Analyze data to understand the distance-time relationship. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Arrange the scramble letter to form a word using the given clue. Write and show your answer after the time given end. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: DEEPS Clues: Measure of how fast an object is moving. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: SPEED Clues: Measure of how fast an object is moving. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: EAEVAGR DPSEE Clues: The total distance traveled by the object. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: AVERAGE SPEED Clues: The total distance traveled by the object. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: TCLVEOIY Clues: Speed in a particular direction. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: VELOCITY Clues: Speed in a particular direction. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: VELOCITY Clues: Speed in a particular direction. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: VAGREAE VEOIYTCL Clues: The ratio of displacement and time. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: AVERAGE VELOCITY Clues: The ratio of displacement and time. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: ECANTDSI Clues: The total length of the path traveled by an object, regardless of direction. UNLOCKING DIFFICULTY Term: DISTANCE Clues: The total length of the path traveled by an object, regardless of direction. RUBRICS GROUP TASK: (10 minutes) Seven group will be given activity sheet. Then perform the activity , you will be given 10 minutes to do and observed the activity and answer the guide questions. In your group choose a leader, timer, secretary and a reporter. Then after the given time share the results to the class. GROUP TASK: (10 minutes) Experiment: Distance-Time Relationship (Group Activity: 10 minutes Students do the activity following the procedure in worksheet. TABLE: DISTANCE - TIME DISTAMCE (CM) 30 60 90 TIME(S) AVERAGE (S) Presentation of the group output.(10minutes) Guided Questions: 1. What is the relationship between distance and time? 2. How does the distance traveled affect the time taken? 3. What happens to the time taken as the distance increases? 4. What does the slope of the distancetime graph represent? An object’s motion is usually described in terms of how fast or how slow it is moving. Is it possible for two objects to have an equal magnitude of speed and velocity? Speed is a measure of how fast something is moving. It is the rate at which distance is covered. The word rate is a clue that something is being divided by time. Speed is defined as the distance covered per unit time. Speed is also a scalar quantity. Velocity is a vector quantity. It describes how fast and in which way (speed + direction) an object is moving. It can be negative or positive depending on the direction of motion Line graph consists of x and y-axis, each representing a distinct variable. In this case/lesson, one axis will represent values for distance, and the other for time. Slope describes the steepness of a graph. It shows the change in the y and x coordinates of plotted points in the graph. It is usually represented by the mathematical expression slope of line (m) is equal to rise over run wherein the rise is the change in the y-coordinates and the run is the change in the x- coordinates. Distance-Time Graphs A distance-time graph is a graphical representation of how far a body has travelled in a specified amount of time. It is used to depict the relationship between distance and time, where distance is plotted on the Y-axis and time is plotted on the X-axis. Let’s first learn the importance of distance-time graphs. The graphs shown are distance-time graphs for various types of body motion. When a body is steady or stationary, When a body is moving at a uniform speed, When a body is moving nonuniformly with increasing speed, and When a body is moving nonuniformly with decreasing speed. If the distance-time graph is a straight line then the motion is uniform. If the distance-time graph of a body is given, its speed can be calculated using the slope of the graph. The slope of the straight-line graph is the same irrespective of the interval which is chosen. This implies that the speed of an object under uniform motion remains constant. EVALUATION: Choose and write the letter of the correct answer. 1. What does a distance-time graph represent? A) The speed of an object over time B) The distance traveled by an object over time C) The acceleration of an object over time D) The velocity of an object over time 2. What does the vertical axis represent on a distance-time graph? A. Speed of the object B. Velocity of the object C. Distance of the object D. Total time travelled by the object 3. What does a horizontal line in the distance-time graph indicate? A. No movement B. Constant speed C. Object is accelerating D. Object is decelerating 4. What does a line on a graph that is curving upwards mean in a distance-time graph? A. The object is not moving. B. The speed of the object is increasing C. The object has a constant speed. D. The speed of the object is decreasing 5. Which of the following options represents the distance-time graph of a stationary object? ASSIGNMENT: Study the graph and answer the following questions: 1. Calculate the speed of the car during the fast 10 seconds. 2. How long dis the car stop? 3. What is the speed of the car on its journey from C to D? 4. On which part of the journey did the car travel faster? 5. What is the average speed of the car for the whole journey? THANK YOU