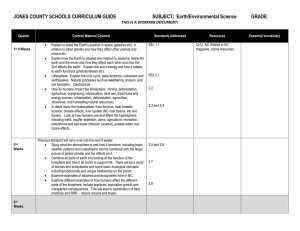
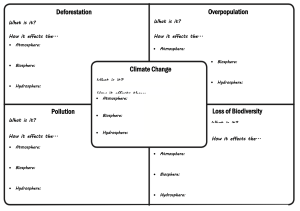
Introduction to Environmental Science and Engineering Environmental Science and Engineering Environmental Science studies how natural systems function and how humans impact them. Environmental Engineering applies scientific principles to develop solutions for environmental issues. This combines various disciplines: such as biology, chemistry, physics, and engineering to solve real-world environmental problems. Environmental Science Examines Earth's natural processes, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and lithosphere. Studies the impact of human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change. Helps develop strategies for conservation, sustainability, and resource management. Environmental Engineering Design solutions for pollution control, water treatment, and waste management. Develop renewable energy technologies like solar and wind power. Focuses on sustainable infrastructure, such as green buildings and smart cities. Addresses ongoing global challenges like climate change, pollution, and resource depletion Why is this field Ensures there is clean air, water, and sustainable resources for future generations important? Supports technological innovation for a greener and more sustainable world Understanding Earth’s Systems Earth’s systems Earth’s environment is made up of four major systems: Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, Biosphere, and Lithosphere. These systems interact with each other, influencing climate, ecosystems, and human activities. Understanding these interactions helps us develop solutions for environmental challenges. Earth’s systems: Atmosphere The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding Earth, essential for life. It protects us from harmful solar radiation and maintains the planet’s temperature. Human activities, like burning fossil fuels, have increased greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. Oxygen and Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Earth’s systems: Hydrosphere The hydrosphere includes all of Earth’s water bodies: oceans, rivers, lakes, groundwater, and glaciers. The water cycle moves water through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. Pollution from industries, agriculture, and plastic waste threatens clean water sources. Earth’s systems: Lithosphere The lithosphere is Earth’s solid outermost layer, including rocks, soil, and landforms. It provides natural resources, such as minerals, fossil fuels, and fertile soil for agriculture. Overuse of land through mining, deforestation, and urbanization leads to soil degradation and erosion. Earth’s systems: Biosphere The biosphere consists of all living organisms on Earth, from microbes to plants and animals. Ecosystems provide essential services, such as oxygen production, food, and climate regulation. Human activities, like deforestation and habitat destruction, are causing biodiversity loss. Human Impact on Earth’s Systems Industrialization and urbanization have increased pollution, deforestation, and climate change. Activities such as burning fossil fuels and waste dumping disrupt natural processes. Sustainability and Carrying Capacity Sustainability means meeting present needs without compromising future generations. Earth’s carrying capacity is the maximum population it can support without depletion of resources. Sustainable development balances economic growth, environmental protection, and social well-being. Major Environmental Issues Overview Global temperatures have risen by 1.1°C since pre-industrial times due to greenhouse gas emissions (IPCC, 2021). The world generates 2.01 billion metric tons of solid waste annually, with only 19% recycled (World Bank, 2022). Over 1 million species face extinction due to human activities (UN Biodiversity Report, 2019).