Methanol Production from Syngas: Renewable Energy Innovations
advertisement

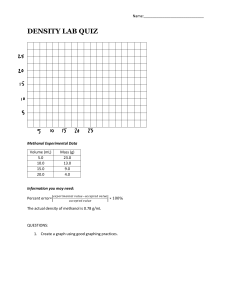
METHANOL PRODUCTION FROM SYNGASS INNOVATIONS IN RENEWABLE ENERGY A SUSTAINABLE FUEL FOR THE FUTURE PRESENTED BY: GROUP NO 02 WAJIH UL HASSAN (UW-23-CHE-BSC-002) SYED MUNTAZIR MEHDI (UW-23-CHE-BSC-016) INTRODUCTION What is Methanol? •A simple alcohol with the chemical formula CH3OH . •Chemical with numerous applications. Innovation in the Methanol Production: •Utilizing renewable energy sources. •Carbon capture and utilization (CCU). Traditional Methanol Production: •Fossil fuels (natural gas, coal). •The high carbon footprint. The Need for Change: •Transition to renewable energy sources. •To reduce greenhouse gas emissions. APPLICATIONS OF METHANOL IMPORTANCE OF METHANOL PRODUCTION Versatile Chemical Building Block: Methanol is a key ingredient in producing various products like formaldehyde, acetic acid, and MTBE, used in plastics, paints, and gasoline. Potential Transportation Fuel: Methanol can be used as a clean-burning alternative fuel in vehicles, reducing emissions. Carbon Capture Utilization: Methanol production from captured carbon dioxide can help mitigate climate change by utilizing a greenhouse gas. Energy Storage: Methanol can be produced from renewable sources and used as a liquid energy carrier, storing energy from wind or solar power. TRADITIONAL METHANOL PRODUCTION FROM COAL Coal Gasification: The coal is converted into synthesis gas (a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2)). Water-Gas Shift Reaction: CO reacts with steam to produce more H2 and CO2. Methanol Synthesis: CO and H2 react in the presence of catalyst to form methanol. Fig .01 Methanol production plant KEY REACTIONS IN COAL-TO-METHANOL PRODUCTION Coal Gasification: C + H2O → CO + H2 Water-Gas Shift Reaction: CO + H2O → CO2 + H2 Methanol Synthesis: CO + 2H2 → CH3OH CO2 + 3H2 → CH3OH + H2O Fig.02: Reaction for coal gasification FLOW DIAGRAM : Fig .03: Manufacturing process of methanol from coal gasification FUTURE OF METHANOL PRODUCTION Shifting to Renewable Sources: Utilizing renewable energy sources (e.g., solar, wind) for hydrogen production. Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU): Capturing CO2 emissions and using it as a feedstock for methanol synthesis. Sustainable Methanol Production: Reducing environmental impact and promoting a circular economy. GROWING DEMAND FOR SUSTAINABLE FUELS The increasing demand for sustainable fuels in various sectors, such as transportation and shipping, is driving the development and deployment of renewable methanol production technologies. Fig .04: Growing demand for sustainable fuels CHALLENGES OF COAL-TO-METHANOL PRODUCTION CONCLUSION Methanol is a versatile chemical with diverse applications in various industries and if talk about challenges we have environmental concerns, policy support, cost competitiveness but methanol will continue to play a significant role in the global economy because it is a key player in the chemical industries. REFERENCES 1. Sehested, J., Nielsen, J. H., Dybkjær, I., Grunwaldt, J.-D., Dahl, S., & Rostrup-Nielsen, J. R. (2004). Methanol synthesis rate. Journal of Catalysis, 221(1-2), 139-146. doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2003.09.017 2. Grahambell, M. H. (2008). Methanol Synthesis: Catalysts, Mechanisms, and Engineering.Wiley-VCH. 3. Satterfield, C. N. (1991). Heterogeneous Catalysis in Industrial Practice. McGraw-Hill. 4. Mills, G. A., & Steffgen, F. W. (1974). Catalytic synthesis of methanol. Catalysis Reviews: Science and Engineering, 8(1), 159-210. 5. R. A. Van Santen, G. J. K. Acres, J. A. Moulijn, P. W. N. M. van Leeuwen (Eds.), Catalysis: An Integrated Approach, 2nd ed., 1999, pp. 75-102. THANK YOU! Any comment? Any suggestion? Any Question?