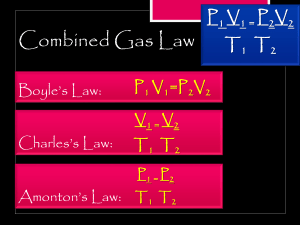
Name _____________________________________________ Date ____________________ Class ____________________ 12,13,15 The Gas Laws In your textbook, read about the basic concepts of the three gas laws. Use each of the terms below to complete the passage. Each term may be used more than once. pressure temperature volume Boyle’s law relates (1) ________________________ and (2) ________________________ if (3) ________________________ and amount of gas are held constant. Charles’s law relates (4) ______________________ and (5) _____________________ if (6) ___________________ and amount of gas are held constant. Gay-Lussac’s law relates (7) ______________________ and (8) ______________________ if (9) ______________________ and amount of gas are held constant. In your textbook, read about the effects of changing conditions on a sample of gas. For each question below, write increases, decreases, or stays the same. __________________ 10. The room temperature increases from 20°C to 24°C. What happens to the pressure inside a cylinder of oxygen contained in the room? __________________ 11. What happens to the pressure of the gas in an inflated expandable balloon if the temperature is increased? __________________ 12. An aerosol can of air freshener is sprayed into a room. What happens to the pressure of the gas if its temperature stays constant? __________________ 13. The volume of air in human lungs increases before it is exhaled. What happens to the temperature of the air in the lungs to cause this change, assuming pressure stays constant? __________________ 14. A leftover hamburger patty is sealed in a plastic bag and placed in the refrigerator. What happens to the volume of the air in the bag? __________________ 15. What happens to the pressure of a gas in a lightbulb a few minutes after the light is turned on? ***Additional Gas Law Questions/Problems at the end of the document. Please write out your solutions on paper. Chemistry: Matter and Change 18 Study Guide Name _____________________________________________ Date ____________________ Class ____________________ 13 The Combined Gas Law Fill in the following table. State what gas law is derived from the combined gas law when the variable listed in the first column stays constant and the variables in the second column change. Derivations from the Combined Gas Law Stays constant Change Becomes this law Volume Temperature, pressure 16. Temperature Pressure, volume 17. Pressure Temperature, volume 18. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 19. The variable that stays constant when using the combined gas law is a. amount of gas. b. pressure. c. temperature. d. volume. Answer the following questions. 20. What is standard temperature and pressure (STP)? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________ 21. A sample of carbon dioxide is at 273 K and 244 kPa. What will its volume be at 400 kPa? __________________ 22. A sample of oxygen occupies 10.0 L at 4.00 atm pressure. At what temperature will the pressure equal 3.00 atm if the final volume is 8.00 L? __________________ 23. At what pressure will a sample of gas occupy a 5.0 L container at 25°C if it occupies 3.2 L at 1.3 atm pressure and 20°C? Energy In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true; if the statement is false, change the italicized word or phrase to make it true. ___________________ 1. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. ___________________ 2. The law of conservation of energy states that energy can be created and destroyed. ___________________ 3. Chemical potential energy is energy stored in a substance because of its composition. ___________________ 4. Heat is a form of energy that flows from a warmer object to a cooler object. ___________________ 5. The specific heat of a substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of that substance by one degree Celsius. ___________________ 6. Kinetic energy is energy of motion. Chemistry: Matter and Change 19 Study Guide Name _____________________________________________ Date ____________________ Class ____________________ 13 Answer the following question. Show all your work. 7. If the temperature of a 500.0-g sample of liquid water is raised 2.00°C, how much heat is absorbed by the water? The specific heat of liquid water is 4.184 J/(g°C). 8. _____________________ is an insulated device used to measure the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical or physical process. 9. Sweating makes you feel cooler because, as it evaporates, the water on your skin (absorbs, releases) _____________________________ heat from your body. 10. When a gas condenses to a liquid, heat is (absorbed, released) __________________________ to the surroundings. 11. Chemistry: Matter and Change 20 Study Guide Name _____________________________________________ Date ____________________ Class ____________________ 13 12. What phase change occurs from A to B? 13. What phase is represented by C? 14. At what temperature and Pressure is the Triple Point? 15. What is the Triple Point? Additional Gas Law Problems (Please write out your solutions on paper) 1. In your own words, describe Charles’ Law and write the formula. 2. Using Charles’ Law: A 6 L sample of nitrogen is warmed from 350K to 359K. Find its new volume if the pressure remains constant. 3. Using Charles’ Law: An empty water bottle is left outside and by the morning a vacuum is created causing the bottle to cave in. Could this be caused by temperature increase or decrease? Chemistry: Matter and Change 21 Study Guide Name _____________________________________________ Date ____________________ Class ____________________ 13 4. In your own words, describe Gay-Lussac’s Law? 5. Using Gay-Lussac’s Law: Determine the pressure change when a constant volume of gas at 1.00 atm is heated from 293K to 303K. 6. Using Gay-Lussac’s Law: A sample of nitrogen inside a rigid, metal container is at 293K and a pressure of 3.00atm. When it is placed inside an oven whose temperature is 323K, what is the pressure of the nitrogen after its temperature is increased? 7. What is the formula for Boyle’s Law? What happens to a gas’s volume when you increase the pressure? 8. Boyle’s Law: If a gas occupies 3.60 liters at a pressure of 1.00 atm, what will be its volume at a pressure of 2.50 atm? 9. Boyle’s Law: 6.0L of a gas is at a pressure of 8.00 atm. What is the volume of the gas at 2.00 atm? Chemistry: Matter and Change 22 Study Guide Name _____________________________________________ Date ____________________ Class ____________________ 13 10. Combined Gas Law: What is the formula? 11. A helium balloon with an internal pressure of 1.00 atm and a volume of 4.50 L at 20.0 oC is released. What volume will the balloon occupy at an altitude where the pressure is 0.600 atm and the temperature is –20.0oC? 12. An airtight container with a volume of 4.25 x 104 L, an internal pressure of 1.00 atm, and an internal temperature of 15.0o C is washed off the deck of a ship and sinks to a depth where the pressure is 175 atm and the temperature is 3.00o C. What will the volume of the gas inside be when the container breaks under the pressure at this depth? Chemistry: Matter and Change 23 Study Guide Name _____________________________________________ Date ____________________ Class ____________________ 13 Chemistry: Matter and Change 24 Study Guide