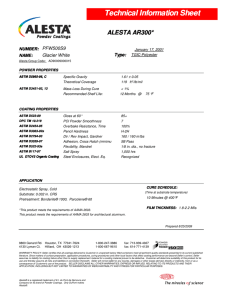
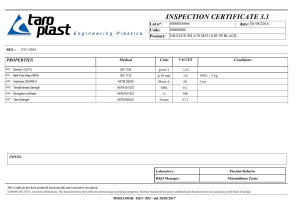
SSPC-Paint 38 March 1, 2012 Edtorial Revision September 13, 2013 SSPC: The Society for Protective Coatings Coating Standard No. 38 Single-Component Moisture-Cure Weatherable Aliphatic Polyurethane Topcoat, Performance-Based 1. Scope 3.4 ASTM STANDARDS:2 1.1 This standard contains performance requirements for a high-performance, single-component, moisture-curing UV-stable polyurethane topcoat (ASTM D 16, Type II polyurethane) for use on steel substrates. The coating is intended to be used as a topcoat that provides good color and gloss retention. D 16 D 523 * D 562 1.2 Coatings meeting the requirements of this standard are generally suitable for exposures in SSPC Environmental Zones 1A (interior, normally dry), 1B (exterior, normally dry), 2A (frequently wet by fresh water, excluding immersion), 2B (frequently wet by salt water, excluding immersion), 3B (chemical exposure, neutral) and 3C (chemical exposure, alkaline)1. D 1014 * D 1296 1.3 The coating is intended for application by brush, spray, or roller over a primer or intermediate coating. * D 1475 2. Description * D 1535 2.1 This single-package moisture-curing polyurethane coating is characterized by the presence of free polyisocyanate groups capable of reacting with atmospheric moisture in order to form a film. * D 1640 D 2244 2.2 WEATHERING LEVELS: This standard contains three levels of accelerated (A) and South Florida weathering (SF) performance described in Section 7.2. * D 2369 3. Referenced Standards * D 2371 3.1 The latest issue, revision, or amendment of the referenced standards in effect on the date of invitation to bid shall govern, unless otherwise specified. Standards marked with an asterisk (*) are referenced only in the Notes, which are not requirements of this standard. * D 2621 3.2 If there is a conflict between the requirements of any of the cited referenced standards and this standard, the requirements of this standard shall prevail. D 2794 * D 2697 D 4214 3.3 SSPC STANDARD: Guide 13 1 Guide for the Identification and Use of Industrial Coating Materials in Computerized Product Databases 2 SSPC Environmental Zones are defined in “About SSPC Standards and Guides” available online from <http://www.sspc.org>. 1 Standard Terminology for Paint, Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss Standard Test Method for Consistency of Paints Measuring Krebs Units (KU) Viscosity Using the Stormer-Type Viscometer Standard Practice for Conducting Exterior Exposure Tests of Paints and Coatings on Metal Substrates Standard Test Method for Odor of Volatile Solvents and Diluents Standard Test Method for Density of Liquid Coatings, Inks, and Related Products Standard Practice for Specifying Color by the Munsell System Standard Test Methods for Drying, Curing, or Film Formation of Organic Coatings at Room Temperature Standard Test Method for Calculation of Color Tolerances and Color Differences From Instrumentally Measured Color Coordinates Standard Test Method for Volatile Content of Coatings Standard Test Method for Pigment Content of Solvent-Reducible Paints Standard Test Method for Infrared Identification of Vehicle Solids from Solvent-Reducible Paints Standard Test Method for Volume Nonvolatile Matter in Clear or Pigmented Coatings Standard Test Method for Resistance of Organic Coatings to the Effects of Rapid Deformation (Impact) Standard Test Methods for Evaluating Degree of Chalking of Exterior Paint Films ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm. org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website. SSPC-Paint 38 March 1, 2012 Editorial Revision September 13, 2013 D 4541 D 4587 D 5402 G 154 5.2 APPLICATION PROPERTIES: All guidance provided by the manufacturer regarding thinning requirements and special application requirements shall be followed (see Note 11.3). The coating shall be easily applied by brush, roller, or spray in accordance with the manufacturer’s written instructions. The coating shall have no streaking, running, or sagging or other defects during application or while drying. Standard Test Method for Pull-Off Strength of Coatings Using Portable Adhesion Testers Standard Practice for Fluorescent UV-Condensation Exposures of Paint and Related Coatings Standard Practice for Assessing the Solvent Resistance of Organic Coatings Using Solvent Rubs Standard Practice for Operating Fluorescent Light Apparatus for UV Exposure of Nonmetallic Materials 6. Test Panel Preparation Triplicate test panels shall be prepared for each test. Prior to application of the topcoat to be tested, a compatible primer and intermediate coat recommended by the manufacturer of the topcoat to be tested shall be applied to the panels and cured in accordance with the manufacturer’s written instructions. The topcoat to be tested shall be applied according to the manufacturer’s written recommendations. 3.5 AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARDS INSTITUTE (ANSI) STANDARD:3 Z129.1 Hazardous Industrial Precautionary Labeling Chemicals – 7. Weathering Requirements 3.6 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF STATE HIGHWAY AND TRANSPORTATION OFFICIALS (AASHTO) STANDARD:4 TP 67-03 7.1 WEATHERING RESISTANCE: Two weathering test procedures are defined below. Performance levels are established using whites and light colors. It is left to the discretion of the specifier whether to accept Florida data from a similar color or to use UV-A data in lieu of South Florida weathering data. [NOTE: Commercial test sites in North America conforming to this requirement are located in southern Florida and Arizona.] Standard Method of Test for Analysis of Structural Steel Coatings for Isocyanate Content 4. Composition Requirements 4.1 RESIN REQUIREMENT: The resin used in the coating shall be a polyisocyanate-based product that cures through a chemical reaction with atmospheric moisture. Use of other resins or modifiers shall be minimal and limited to products necessary for formula ingredient compatibility and to improve recoating properties. Manufacturer’s formulations of single-component moisture-curing weatherable polyurethane topcoats normally contain levels of polyisocyanate in vehicle solids above 3.5% by weight, as determined by AASHTO TP 67-03. 7.1.1 Accelerated Weathering: Accelerated weathering shall be performed in accordance with ASTM D 4587, Cycle 2. Apparatus – Fluorescent UV/condensation apparatus complying with ASTM G 154. TABLE 1 TIME CORRESPONDING TO EACH PERFORMANCE LEVEL Performance Level 4.2 VOC CONTENT: See Note 11.1 for information on VOC content. 4.3 ANALYTICAL TEST DATA: If required, the coating manufacturer shall provide certificates of analysis for coating batches qualified by independent testing to meet this standard for use in verifying batch-to-batch consistency of material (see Note 11.2 and subsections) * 5. Requirements of Liquid Coating Hours to Noticeable Change* Cycles to Noticeable Change* Accelerated UVA/Condensation Level 1 500 to 1000 63 to 125 Level 2 1001 to 2000 126 to 250 Level 3 2001 or more 251 or more Noticeable change following Accelerated UV-A/Condensation testing is defined as a gloss reduction of 25% or more of the initial gloss value measured at a 60° angle or a color change greater than 3.0 ∆E* (see Section 7.2.1). TABLE 2 SOUTH FLORIDA WEATHERING PERFORMANCE 5.1 STORAGE STABILITY: The coating shall exhibit no curdling, gelling, gassing, or hard caking after being stored unmixed for a minimum of 180 days in a tightly sealed, unopened container at a temperature of 25 degrees C (77 degrees F). Performance Level Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 American National Standards Institute, 1819 L Street, NW, Suite 600, Washington, DC 20036. Standards available online from www.ansi. org 4 American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials, 444 North Capitol Street, NW, Suite 249, Washington DC 20001, 202-624-5800. Standards available online at https://bookstore.transportation.org 3 Months to Noticeable Change* 12 to 23 24 to 47 48 or more * Noticeable change following Florida exposure testing is defined as a gloss reduction of 35% or more of the initial gloss value measured at a 60° angle or a color change greater than 3.0 ∆E* (see Section 7.2.1). 2 SSPC-Paint 38 March 1, 2012 Edtorial Revision September 13, 2013 TABLE 3 SUMMARY OF PERFORMANCE TESTING RESULTS FOR COLOR AND GLOSS RETENTION Measurement Test/Evaluation Criteria Exposure Test † Performance Level Exposure Time Accelerated Weathering (A) (Section 7.1.1.) Level 1A 500 h Level 2A 1000 h Level 3A 2000 h South Florida Weathering (SF) (Section 7.1.2) ASTM D 1014 Level 1 SF 12 mo Level 2 SF 24 mo Level 3 SF 48 mo Color Retention ASTM D 2244 Maximum Gloss Reduction ASTM D 523 Color Change ≤3.0 ΔE C.I.E. 1976 L*A*B*† 25% from original reading Color Change ≤3.0 ΔE C.I.E. 1976 L*A*B*† 35% from original reading Smaller values of color change (less than 3.0 ∆E*) may be visible, but the noticeable change maximum of 3.0 ∆E* required by this standard is acceptable for most industrial and marine applications. The specifier has the option to require more stringent gloss and color retention. according to ASTM D 523. Table 3 summarizes the tests of Section 7 as well as the minimum acceptance criteria. See Note 11.4 regarding test results for darker colors. Procedure –Test according to ASTM D 4587 Cycle 2 procedure. This eight-hour duration comprises one test cycle. Continue cycle testing to achieve the exposure hours defined in the required performance levels (as shown in Table 1). 8. Laboratory Physical Tests of Applied Coatings Smaller values of color change (less than 3.0 ∆E*) may be visible, but the noticeable change maximum of 3.0 ∆E* required by this standard is acceptable for most industrial and marine applications. The specifier has the option to require more stringent gloss and color retention. 8.1 RECOATABILITY: Intercoat and substrate adhesion properties of the polyurethane topcoats shall be determined by measurement of adhesion values between: a) primer and the substrate, b) polyurethane topcoat and the primer or intermediate coat, and, if applicable c) the second coat of polyurethane topcoat and the same previously applied topcoat. Coating manufacturers shall provide acceptable window (time frame) ranges between applications of coats in a multi-coat system. Unless the purchaser specifically requests a variance, the maximum dry film thickness and the minimum curing time (with reported conditions for temperature and humidity) as stated on the manufacturer’s product data sheets will be used for coating application prior to adhesion testing. All testing shall be performed on a minimum of three steel test panels each with minimum dimensions of 75 x 150 x 6 mm (3 x 6 x ¼ inches). The panels shall be prepared to the minimum surface preparation recommendations of the coating manufacturer. 7.1.2 South Florida Weathering: South Florida weathering shall be performed in accordance with ASTM D 1014 (45˚ south exposure, washed with mild detergent before readings are taken). 7.2 Performance Levels: Tables 1 and 2 specify the amount of time the coating must perform before noticeable change in order to achieve the defined performance level. Polyurethane topcoats are available in a wide range of color and gloss. Procurement documents shall state the desired level of performance, exposure method (in accordance with Tables 1 and 2), color, and gloss. For example, a specifier may require Level 2SF Florida exposure, initial gloss greater than 80, matched to a specific color. A certain level of accelerated weathering does not necessarily correspond to a particular level of atmospheric weathering and they need to be specified independently. These are two independent complementary tests for measuring coating performance. If no level is specified, either Accelerated Level 3 or South Florida Level 3 data is acceptable. The coating manufacturer shall report the type of testing used to generate the data. 8.2 ADHESION 8.2.1 Primer Adhesion to Steel Substrate: Apply the primer to the steel panel and cure according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Test adhesion according to ASTM D 4541 and identify the type of adhesion tester used (Type II, III, IV, or V). The minimum adhesion acceptance value of the primer to the substrate shall be 4.1 MPa (or 600 psi in U.S. units). 7.2.1 Each replicate panel must meet the minimum acceptance criteria. Clear coatings must be tested over the intended basecoat. Initially, and at the end of the exposure period for each level, tristimulus color values shall be measured according to ASTM D 2244, and 60 degree gloss shall be measured 8.2.2 Polyurethane Topcoat Adhesion to the Primer: Apply topcoat to panels (previously primed as described in 8.2.1) and cure according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. 3 SSPC-Paint 38 March 1, 2012 Editorial Revision September 13, 2013 TABLE 4 ADDITIONAL REQUIRED PERFORMANCE PROPERTIES TEST Adhesion (to substrate, primer, intermediate coat, or previously applied topcoat) (Section 8.2 and subsections) ASTM METHOD RESULT (UNITS) MINIMUM ACCEPTABLE VALUE D 4541 MPa (psi) 4.1 (600) Direct Impact Resistance (Section 8.4) D 2794 kg-force per square centimeter (lb-force per square inch) 4.2 (60) Solvent (MEK) Resistance (Section 8.5) D 5402 Number of double-rubs 4 sets of 25 with no topcoat visible on cloth Evaluating degree of chalking in exterior paints (Section 8.6) D 4214 Photographic standard rating method 6, where 10 is no chalking* * At desired weathering level. 9. Labeling Test the intercoat adhesion between topcoat and primer or intermediate coat in accordance with ASTM D 4541 and identify the type of adhesion tester used. Intercoat adhesion is defined as the force required to separate the topcoat from the underlying coat. The minimum intercoat adhesion (both adhesive and cohesive) shall meet or exceed the cohesive strength of the coating. 9.1 Labeling shall conform to ANSI Z129.1 9.2 Technical data shall be provided for at least all data elements categorized as “essential” in SSPC-Guide 13. The specifier has the option to require additional data to satisfy quality assurance or local regulatory requirements. 8.2.3 Polyurethane Topcoat Adhesion to (Same) Previously Applied Topcoat: Apply a second coat of topcoat and cure according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Test the intercoat adhesion in accordance with ASTM D 4541 and identify the type of adhesion tester used. The minimum intercoat adhesion (both adhesive and cohesive) shall meet or exceed the cohesive strength of the coating. 10. Disclaimer 10.1 While every precaution is taken to ensure that all information furnished in SSPC standards and specifications is as accurate, complete, and useful as possible, SSPC cannot assume responsibility nor incur any obligation resulting from the use of any materials, coatings, or methods specified herein, or of the specification or standard itself. 8.3 Polyurethane topcoat cohesion (bond strength within a single layer of coating) shall be equal to or greater than the minimum acceptable intercoat adhesion 10.2 This specification does not attempt to address problems concerning safety and health associated with its use. The user of this specification, as well as the user of all products or practices described herein, is responsible for instituting appropriate health and safety practices and for ensuring compliance with all governmental regulations. 8.4 Direct Impact Resistance: The minimum impact resistance of the cured topcoat as applied to 3 test specimens shall be 4.2 kilograms of force (kg-force) per square centimeter (or 60 pounds of force per square inch [in-lb] in U.S. units) when measured in accordance with ASTM D 2794. 11. Notes 8.5 Solvent (MEK) Resistance: Using a test cloth saturated with MEK following procedures in ASTM D 5402, no topcoat shall be visible on the test cloth after four sets of 25 double-rubs. Notes are not requirements of this specification. 11.1 VOC CONTENT: Local regulations regarding VOC content, VOC emissions, and container labeling may vary depending on project location. For example, U.S Federal limits for VOCs in industrial maintenance coatings were published in 1998 and may be found at <http://www.epa.gov/ttn/atw/183e/ aim/aimpg.html#RULE>. These limits apply to the coating at the time of application, after thinning according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. 8.6 Resistance to Chalking: When evaluated in accordance with procedures in ASTM D 4214 Test Method A at the time period indicated for desired weathering level, maximum chalking value shall be a level of 6 using Reference Photograph No. 1. These properties are summarized in Table 4. 4 SSPC-Paint 38 March 1, 2012 Edtorial Revision September 13, 2013 However, many state and local governments and/or air quality management areas have more stringent VOC regulations than those in the federal rule. In the U.S., information on the VOC content of each container before mixing or thinning is found on the container label and in the manufacturer’s safety data sheet. The coating manufacturer’s product data sheet usually provides information on the total VOC content of a coating after mixing and any recommended thinning. material. The pass/fail criterion is that the measurement of the test sample shall fall within two standard deviations of the target value. The contracting parties must agree on a target value. 11.2.2 Quality Assurance Testing Procedures: Quality assurance tests include but are not limited to: infrared analysis (ASTM D 2621), viscosity (ASTM D 562), weight per gallon (ASTM D 1475), total solids (ASTM D 2369), volume solids (ASTM D 2697), dry time (ASTM D 1640), percent pigment (ASTM D 2371), gloss (ASTM D 523), color (ASTM D 1535, ASTM D 2244), odor (ASTM D 1296), and isocyanate content (AASHTO TP 67-03). 11.2 QUALITY ASSURANCE TESTS: Quality assurance tests are used to determine whether the supplied products are of the same type and quality as those originally tested. The selected tests should rapidly and accurately measure the physical and chemical characteristics of the coating necessary to verify that the supplied material is substantially the same as the previously accepted material. All of the quality assurance tests must be performed on the originally submitted qualification sample. The results of these tests are used to establish pass/ fail criteria for quality assurance testing of supplied products. 11.3 These coatings may be susceptible to pinholing if applied under adverse conditions such as high humidity. The degree of pinholing depends on formulation variables. Consult the coating manufacturer’s recommendations for formulation additives that may be used to address this problem. 11.4 Test results for color and gloss of deeper colors (i.e., having a Munsell value below 9) will vary significantly due to differences in pigment weathering properties, and may not meet the requirements of Section 7 without use of additional procedures such as clear coating. Alternatively, the specifier may accept a greater change in gloss and color for deeper colors. 11.2.1 Establishing Quality Assurance Acceptance Criteria: Many ASTM test methods contain precision and bias statements. Specification developers should be cognizant of the fact that these statements exist. Quality assurance test criteria should not be more stringent than the interlaboratory precision of the test methods used. The specifier may require additional technical data to satisfy QA or local regulatory requirements. Where precision and bias data are not available for a given test method, determine the standard deviation of a minimum of five measurements taken on the originally tested and certified The coating manufacturer should be contacted if the user desires color change of less than 2.0 ∆E* for a specific application. In order to achieve this requirement, additional procedures such as clear coating may be needed. Copyright © SSPC standards, guides, and technical reports are copyrighted world-wide by SSPC: The Society for Protective Coatings. Any photocopying, re-selling, or redistribution of these standards, guides, and technical reports by printed, electronic, or any other means is strictly prohibited without the express written consent of SSPC: The Society of Protective Coatings and a formal licensing agreement. 5