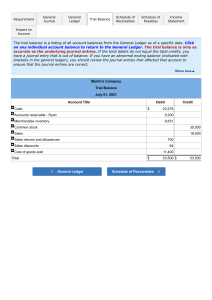
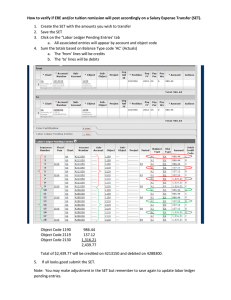
Grade 10 Accounting Scheme of work (2025) Term 1 1. The purpose of accounting. • Understand and explain the difference between bookkeeping and accounting. • State the purpose of measuring a business profit or loss. • Explain the role of accounting in providing information for monitoring progress and decision-making. 2. The double entry system of bookkeeping. • Explain the meaning of assets, liabilities and owners’ equity. • Explain and apply the accounting equation. • Outline the double entry system of bookkeeping. • Process accounting data using the double entry system 3. Books of prime entry • Explain the advantage of using various books of prime entry. • Explain the use of and process accounting data in the books of prime entry. • Post the ledger account entries from the books of prime entry. Explain, calculate and account for trade discount. 4. The cashbook. • Explain the dual function of a cashbook both as a book of prime entry and as a ledger account for bank and cash. • Understand the use and purpose of a bank statement. • Explain the use of record payment and receipts made by bank transfers and other electronic means. • Understand the purpose of and prepare a bank reconciliation statement to include bank errors, uncredited deposits and unpresented cheques. 5. Business documents. • Recognize and understand the invoice, debit note, credit note, statement of account, cheque and receipt • Complete proforma business documents • Understand the use of business documents as sources of information 6. The general journal • • • • Explain that the general journal is one of the books of prime entry. Explain the use of the journal Enter the transaction, including correction of errors that cannot be recorded in any special journal. Write relevant explanatory narrations for each entry. Term 2 1. The ledger. • Preparing ledger accounts • Post transactions to the ledger accounts • Balance ledger accounts as required and make transfers to financial statement. • Interpreted ledger accounts and their balances. 2. The trial balance. • Understand that the trial balance is a statement of ledger balances on a particular date • Outline the uses and limitations of trial balance • Prepare a trial balance from a given list of balances and amend a trial balance that contain errors. • Identify and explain those errors which do not affect the trial balance 3. Adjustments of ledger accounts. • Understand the importance of matching costs and revenues. • Prepare ledger accounts and journal entries to record accrued and prepaid expenses. • Prepare ledger accounts and journal entries to record accrued and prepaid incomes. 4. Capital and revenue expenditure. • Distinguish between and account for revenue and capital expenditure. • Distinguish between and account for capital receipts and revenue receipts. • Calculate and comment on the effect on profit of incorrect treatment. • Calculate and comment on the effect on assets valuations of incorrect treatment. 5. Accounting for depreciation and disposal of non-current assets. • Define depreciation • Explain the reasons for accounting for depreciation • Name and describe the straight-line method and balance reducing method. • Prepare ledger accounts and journal entries for the provision of depreciation. • Prepare ledger accounts and journal entries to record the sale of non-current assets, including the use of disposal accounts. Term 3 1. Correction of errors. • Correct errors by means of journal entries. • Explain the use of the suspense account as a temporary measure to balance the trial balance • Correct errors by means of suspense account. • Adjust profit or loss for an accounting period after the correction of errors. • Understand the effect of the correction of errors on the statement of financial position. 2. Control accounts. • Understand the purpose of the purchases ledger, sales ledger and control accounts. • Identify the books of prime entry as sources of information. • Prepare purchases ledger and sales ledger control accounts to include credit sales and purchases, reicepts and payments, cash discount returns and contra entries, opening and closing balances. 3. Financial statements. • Calculate the gross profit and profit (loss) for the year based on accounting principles. • Recognize that profit (or loss) for the year is the increase in the net assets during that year • Prepare simple columnar trading accounts when dealing with a business that has two departments. 4. Statement of financial position. • Understand that statement of financial position record assets and liabilities on a specified date. • Recognize and define the content of a statement of financial position non-current assets, intangible assets, current assets, current liabilities, non-current liabilities capital employed and capital owned. • Understand the inter-relationship of items in a statement of financial position. • Relate working capital to the liquidity of the business. • Understand the basis of the valuation of assets. • Distinguish between and show understanding of equity and capital employed. • Prepare simple inventory valuation statements. 5. Sole traders. • Explain the advantages and disadvantages of working as a sole trader. • Explain the importance of preparing income statements and statements of financial position. • Explain the difference between trading business and service business. • Prepare income statements for trading business and service business. • • • • Prepare statements of financial position for trading business and service business. Make adjustments for provision for depreciation using the straight line and reducing balance method. Make adjustments for irrecoverable debts and doubtful debts. Make adjustments for goods taken by business owners for private use.