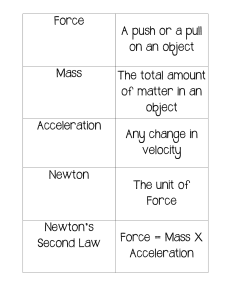
1/21/25, 2:42 AM Kinetic of Particles KINETIC OF PARTICLES KINETICS study of the relations existing between the forces acting on a body, the mass of the body, and the motion of the body Newton’s 1st Law An object remains at rest or moves in a straight line at constant speed unless acted upon by an external force Newton’s 3rd Law Mutual forces of action and reaction between two particles are equal, opposite, and collinear. Newton’s 2nd Law The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. F=ma FBD(Free-Body Diagram) COORDINATES SYSTEMS WORK AND ENERGY NORMAL AND TANGENTIAL Work is defined as the product of force and displacement components acting in the same direction. Tangential acceleration. Changes the speed of a particle. (at=dv/dt): Normal acceleration. Changes the direction of motion. (an=v^2/ρ) KD(Kinetic Diagram) RADIAL AND TRANVERSE https://whimsical.com/kinetic-of-particles-Px28LhndYGysfeMb6v8Xmo FORMULA Work U=F⋅ds Potential Energy (Gravity) Vg=W.y Potential Energy Elastic Ve=(1/2).ks^2 Kinetic Enery T=(1/2)mv^2 IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM (Momentum) The product of an object’s mass and velocity. L=mv (Impulse) The effect of a force acting over a period of time. I=F.Δt mv1+I = mv2 1/1