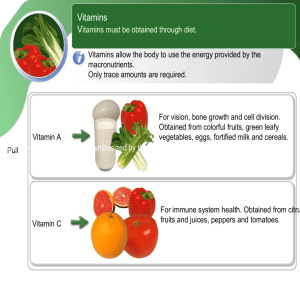
HUMAN NUTRITION AND DIET BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES Biological molecules are large molecules necessary for life , that are built from smaller organic molecules . There are four major classes of biological macromolecules. These are ; 1. Carbohydrate 2. Lipids 3.Protein 4. Nucleic acid (DNA) CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrate is made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Types of Carbohydrates 1.Monosaccharide ; This sugar contains a single ring. They are the simplest sugar e.g glucose ,fructose and galactose. They have a general formula of C6 H12 O6 Sub-unit – Glucose GLUCOSE 2. Disaccharide (Reducing sugar) ; These contain two carbon rings in their molecules and are represented with the formula C12 H22 011 e.g (i) Maltose = glucose and glucose (ii) Sucrose = glucose and fructose (iii) Lactose = glucose and glactose 3. Polysaccharide ; are made of long chains of monomers (simple sugar) held together by chemical bond . The general formula is (C6 H10 O5)n e.g starch, cellulose , glycogen .Polysaccharide are not soluble in water IMPORTANCE OF CARBOHYDRATES Provides energy FATS AND OILS Fats and oils are known as lipids .They contain high proportion of carbon, hydrogen but very little oxygen. Fats are solid .When fats are liquid they are known as oils. A molecule of fat or oil is made up of three molecules of fatty acid and one molecule of glycerol e.g olive oil, cold liver oil , waxes , melon oil, butter e.t.c Sub-unit- Fatty acid and glycerol IMPORTANCE OF FATS AND OIL 1. Formation of cell membrane and nuclear membrane 2. Provides more energy than carbohydrates 3. Serves as solvent for some vitamins 4. It protects vital organs 5. It smoothens the skin PROTEINS Protein is composed of carbon , hydrogen , oxygen , nitrogen and sometimes phosphorus and sulphur .Their molecules are made up of long chains of simpler chemicals called amino acids . There are about 20 different amino acids in animal protein and each type has its amino acid arranged in a special sequence e.g enzymes , muscle, haemoglobin, cell membranes, meat ,fish , beans ,groundnut ,soyabeans e.t.c Break down of protein during digestion takes place in the following stages Protein – Peptones – Polypeptides – Amino acid Sub unit – Amino acids Importance of protein 1. For body building 2. For growth 3. For repair of damaged tissues 4. For the supply of the necessary amino acids 5. For formation of hormones , enzymes, antibodies and forming of fibrinogen necessary for blood clotting PROTEIN SHAPE There are thousands of different proteins in the human body and other organisms. Different sequence of amino acids give different shapes to protein molecules. For example: - Enzymes have an area in them known as the active site, This is important as this is the place where another molecule fits into the enzyme in order for a reaction to take place - If the shape of the active site does not match the shape of the molecule that fits into it, the reaction will not take place - Every enzyme has a different shaped active site - Antibodies are proteins produced by certain types of white blood cell to attach to antigens on the surface if the pathogens - The shape of the antibody must match the shape of the antigen so that it can attach to it and signal it for destruction - In this way every protein has a unique 3- D shaped that enables it to carry out its function STRUCTURE OF DNA A DNA is made up of long chains of nucleotides , formed into two strands(double helix) . Each nucleotide is made up of ; 1) Deoxyribose – a 5-carbon sugar molecule 2) Phosphate group 3) An organic base which is either Adenine (A), Thymine (T) , Guanine (G) or Cytosine (C).Cross-links between the strands are formed by pair of bases The bases always pair up in the same way : Adenine (A) with Thymine (T) and Guanine (G) with Cytosine (C) Draw the above structure STRUCTURE OF DNA The size of the DNA molecules makes sure that A always pair with T and C with G. They are complementary strands . The double strands is twisted to make a helix . Scientist that are involved in the discovery of DNA ; 1. Crick and Watson 2. Rosalind Franklin ROLE OF mRNA IN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS mRNA carries a copy of the gene /DNA/ base pair sequence mRNA travel from the nucleus to the cytoplasm/ribosome . The order of amino acids depends on the sequence of bases in mRNA MINERAL SALT Mineral salts are required for metabolic activities within the body. They are taken in minute quantity through the food we eat. Lack of these mineral salts will result in nutritional deficiency.Mineral salt include Calcium , Phosphorus , Magnesium , Potassium, Suphur , Sodium , Chlorine , Iron , Iodine , Msgaaese e.t.c THE SOURCE, FUNCTION AND DEFICIENCY SYMPTOMS OF SOME MINERAL SALTS Mineral Calcium Phosphorus Iron Sodium and Chlorine Iodine VITAMINS Sources Milk, Cheese, Egg, Fish Functions - Bone and teeth formation and development - For blood clotting - Normal functioning of heart , Nervous system and muscles Milk , Cheese , Egg , - For strong development of Fish and Wheat teeth and bones - Forms part of DNA and RNA - For respiration Eggs , Liver , - Formation of haemoglobin kidneys , Beans , in red blood cells Vegetables Table salt , Fish , - Transmission of nervous Friuts impulses - Maintenance of osmotic balance of the cells Seafoods - Required by the thyroid gland to make thyroxine Deficiency Symptoms -Rickets - Tooth decay - Osteomalacia - Ricket - Tooth decay - Osteomalacia - Anaemia - Dehydration - Muscle cramp - Goitre Vitamins are inorganic compounds and they are biocatalyst i.e they promote chemical reactions in the body . Groups of vitamins : i. Fat soluble vitamins e.g Vitamins A,D,E and K Ii. Water soluble vitamins e.g Vitamins B- Complex and Vitamin C Vitamins required by humans Vitamin Vitamin A (Retinol ) Vitamin B1 (Thamine) Vitamin B2 ( Riboflavin) Vitamin B3 (Niacin ) Source Liver, eggs, fish , milk , palm oil , fresh vegetables Yeast , unpolished rice , milk, beans , palmwine Function - For proper vision of the eye - Required for normal growth Deficiency Symptoms - Night blindness - Skin becomes flaky - needed for synthesis of coenzymes - involved in cellular respiration - Formation of co-enzymes involved in cellular respiration - Beriberi ( a condition due to loss of appetite , weight, tiredness and paralysis) - Cracking of the skin around the corners of nose , mouth and eyes - Pellagra ( Scally pigmented skin , sore mouth and tongue , nervous disorder ) - Disorder of nervous system and gut Yeast, Soyabeans , egg , milk , green vegetables Yeast , beans , milk - needed for cellular , palmwine , yam , respiration vegetables Vitamin B5 ( Pantothenic ) Yeast, egg , rice bran - Formation of co-enzymes involved in cellular respiration Vitamin B6 ( Pyridoxine ) Yeast , egg , cereal Vitamin B12 Kidney, liver , fish , milk - Formation of enzymes - Anaemia involved in synthesis of amino- - Diarrhoea acids -Formation of red blood cells - Pernicious aneamia ( Cyanocobalamin) Vitamin C Fresh fruits e.g (Ascorbic acid ) orange and green vegetables Vitamin D Fish , milk , egg, (Calciferol ) liver , formed in the skin by sunlight - aids wound healing - helps to resist infection - Scurvy - needed for strong bone and teeth formation and development - Ricket - softening of bones in adult Vitamin E (tecopherol) Vitamin K Green vegetables , egge , butter , liver Fresh green vegetables , liver - promotion of fertility in animals - aids clotting of blood -Sterility and premature abortion -Haemorrhages i.e inability of blood to clot in time WATER Water is composed of two elements: Hydrogen and oxygen. IMPORTANCE OF WATER 1. Aids excretion 2. Acts as solvent for soluble substances in digestion 3. It is necessary for the digestion of food 4. It can be used for the maintenance of body temperature 5. Acts as a medium of transportation for nutrients 6. It helps to maintain the osmotic content of the body tissues ROUGHAGES Roughages consists of indigestible fibre materials derived from vegetables, fruit, carbohydrates and proteins IMPORTANCE OF ROUGHAGES 1. Stimulates bowel movement / peristalsis 2. Reduces blodd cholesterol / bowel cancer / Gall stones 3. They do not contribute to weight gain / High blood sugar 4. It releases glucose slowly 5. It prevents constipation / Add digestion FOOD TEST TEST FOR VITAMIN C BALANCED DIET Balanced diet is a diet containing all nutrients/components in correct proportions to maintain health and appropriate energy requirements.Balanced diet requirements varies according to age/sex/ lifestyle/pregnancy. IMPORTANCE OF BAKANCED DIET 1. It encourages growth and normal development of the body 2. It increases resistant to diseases 3. It provides energy required for normal activities 4. Balanced diet prevents malnutrition / deficiency disease Lack of some food substance e.g protein in a diet can cause a nutritional disease called kwashiorkor in children and Marasmus as a result of early weaning is characterized by: a. Retarded growth b. Loss of weight c. Diarrhoea d. Fatigue e. Muscle wasting f. Pale body g. Change in the colour of the hair , the hair becomes reddish brown Don’t draw