Entrepreneurship Overview: Definitions, Risks, and Resources
advertisement

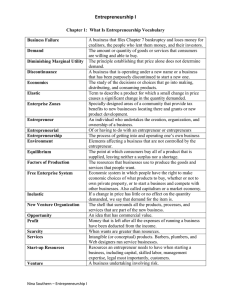
Monday October 28, 2024 Topic: An Overview of Entrepreneurship Week: 1 Introduction Entrepreneurship is one of the four (4) pillars of free enterprise society namely, land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship is the process of creating a new enterprise. The word “entrepreneur” is derived from a 17th century French word, Entreprendre which was defined a person who undertook the risk of a new enterprise. The entrepreneur also is one who undertakes to organize, manage, and assume the risks of a business. Evolution of Entrepreneurship The recognition of entrepreneurs date back to 18th century in France when a French economist, Richard Cantillon associated the “risk bearing” activity in the economy with the entrepreneur. Richard Cantillon popularized the concept of entrepreneurship in economics. At this same period in England, the industrial evolution was evolving with the entrepreneur playing a visible role in risk taking and the transformation of resources. The association of entrepreneurship and economics has long been the accepted norm. Until the 1950s, majority of the definitions and references to entrepreneurship came from economists. For instance, Richard Cantillon (1725), the renowned French economist, Jean Baptiste Say (1803), and a 20th century economic genius, Joseph Schumpeter (1934), all wrote about entrepreneurship and its impact on economic development. The word “entrepreneurship” became synonymous or closely linked with free enterprises and capitalism. Also, it was generally recognized that entrepreneurs serve as agents of change, provide creative and innovative ideas for business enterprises, and help businesses grow and become profitable. Whatever the specific activity they engage in, entrepreneurs in the 21st century are considered to be the heroes of free enterprise. Many of them have used innovation and creativity to build multimillion dollar enterprises, create new products and services, and assume the risks associated with these ventures. Definitions of Entrepreneurship Entrepreneurship can be defined as the process of creating and managing a business to achieve desired objectives. Entrepreneurship can be defined as the dynamic process of creating incremental wealth. This wealth is created by individuals who assume the major risks of setting up a business in terms of equity/sourcing for funds, time, and/or career commitment of providing value for product or service. The product or service itself may or may not be new or unique but value must somehow be infused by the entrepreneur by securing and allocating the necessary skills and resources. Entrepreneurship can be defined as the process by which an individual uses the factors of production that is, land, labor, and capital along with his own entrepreneurial skill to transform a business opportunity into a reality or profitable venture. Key Concepts in Entrepreneurship The key concepts in entrepreneurship include: 1. Entrepreneur, 2. Intrapreneurship, 3. Intrapreneurs, and 4. Management 1. Entrepreneur An entrepreneur is an individual who undertakes the risk of creating a new enterprise. He/she has the ability to see and evaluate business opportunities, assemble the necessary resources to take advantage of the opportunities, and take a personal stake in the success or failure of the enterprise. 2. Intrapreneurship Intrapreneurship refers to employees’ initiatives in organizations to undertake something new without being asked to do so. 3. Intrapreneurs Intrapreneurs refers to employees within an organization that create an innovative idea and nurture or champion it over a period of time. Intrapreneurs work inside the organization while entrepreneurs work outside the organization. Intrapreneurs focuses on innovation and creativity and transforms an idea into a profitable venture while operating within a business firm. 4. Management Management can be defined as the process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the efforts of organizational members and the use of organizational resources in order to achieve stated organizational goals. Risks of Entrepreneurship Risk is the inability to predict in an exact form the outcome of an action. Entrepreneurs face the following types of risks when creating a new enterprise. These risks include: 1. Business risk, 2. Financial risk, 3. Career risk, 4. Family and social risk, and 5. Psychological risk. 1. Business Risk This is the risk of business failure. In America, over 30% of all independent small businesses fail during the first two years of their startup or operation and 8% of every ten businesses within ten years. 2. Financial Risk This is the risk of losing financial investments or resources. 3. Career Risk This is the risk of leaving a secured job for a venture with a highly uncertain future. 4. Family and Social Risks Starting and running a young business require over 80 hours of work weekly. This leaves little time for family and friends. Demands of entrepreneurship often strain marriages and friendships. 5. Psychological Risk This is the risk of a deep sense of personal failure if the business does not beat the odds and succeed. Factors Influencing Entrepreneurship Realizing a lot of risks that entrepreneurs face coupled with the time and energy required for success, one wonders why people are still interested to take the entrepreneurial plunge. Entrepreneurs launch businesses because of one or more entrepreneurial motivations. Some of these motivations include: 1. Desire for Personal Autonomy/Desire to Work Independently Many young graduates do not like to take up paid employment. They desire long before they finished their tertiary education of setting up their own business. A very good example of such young and successful entrepreneur is Barrister Jimoh Ibrahim of Global Fleet who never worked for any organization before venturing into business. 2. Job Dissatisfaction Many employees are not satisfied with their jobs either due to poor remuneration package or job conditions. Due to these situations, an employee that is entrepreneurially inclined and has the necessary resources may decide to venture into small scale business. 3. Loss of Paid Employment When some employees lose their employment and can’t secure another comparable employment in good time, they may not have any alternative option rather than setting up their own small scale business. It is said that necessity is the mother of inventions. In entrepreneurship, we can say loss of paid employment is the mother of venturing. 4. The Desire to Identify Unexplored Opportunities An entrepreneur may stumble into unexplored opportunities that he has the resources to exploit. This bright opportunity may engineer him to set up a small business of his own in order to exploit the opportunity. 5. Continuity of Family Business due to Inheritance Some people go into this type of business as a result of the compelling need to run the family business, 6. Success recorded by a friend or colleague from running his own business can serve as a motivating factor for one to establish his own business, 7. Desire to own a personal business after retirement from paid employment, 8. Greater expectation of return on investment from venturing into an entrepreneurship business, and 9. An investor may stumble into a unique business idea that has an enviable and sustainable market potentials. Resources of Entrepreneurship The resources of entrepreneurship are the assets which the business makes use of. These resources include: 1. Tangible resources, and 2. Intangible resources. 1. Tangible Resources These are resources or assets that can be quantified and observed. These resources include: i. Natural resources, ii. Human resources, iii. Capital, iv. Physical assets, and v. Infrastructural facilities. i. Natural Resources The productive capacity of an entrepreneur can be partly explained by the natural resource endowments such as land, climate, and water that the entrepreneur is blessed with. The entrepreneur that is investing into sawmill in the Southern part of Nigeria is able to add value to the trees in the bush because of the climatic condition which is rainforest. The rainforest is naturally blessed with good timbers. ii. Human Resources Labor is the human effort either physical or mental that is exerted in the production of goods and services. It is through the use of labor and other resources that the natural resources are exploited and converted into other more valuable goods and services. The drive, direction, and desire to get the resources of business activated and committed to production of goods and services is at the discretion of human mind and interest. iii. Capital Capital can be described as all the man-made items that workers use in production and distribution or man-made items used for the creation of further wealth. The capital resources of a business can be classified into fixed and current capital. Fixed capital include buildings, machinery, equipment, and vehicles while current capital include stock in goods, cash at hand, etc. iv. Physical Assets Physical assets such as buildings, machineries, plants, raw materials, etc. are needed by an entrepreneur to pursue his or her dreams. v. Infrastructural Facilities The success of entrepreneurship depends on the quality, effectiveness, and efficiency of infrastructural facilities available within the environment it operates. A nation that is blessed with good roads, telecommunication facilities, power, water, and transportation system will have entrepreneurs striving better than a nation that is deprived of all these. 2. Intangible Resources These are resources of the firm that are difficult to quantify and examine physically. The intangible resources of entrepreneurship include: i. Government Policies The enabling environment created by the government through its policies and laws will impact heavily on entrepreneurship development. ii. Entrepreneur’s Reputation and Goodwill The integrity, reputation, and goodwill of the entrepreneur is a great resource that can impact on the success or otherwise of the business venture. iii. iv. v. Entrepreneur’s skills, knowledge, and reasoning ability, Decision making abilities of the workforce, and Technology. Characteristics of Entrepreneurs Every success bound entrepreneurs must possess the following attributes: 1. Mental ability, 2. Clear objectives, 3. Business secrecy, 4. Human relations ability, 5. Communication ability, and 6. Technical knowledge. 1. Mental Ability Mental ability consists of intelligence and creative thinking. 2. Clear Objectives An entrepreneur should have a clear objective as to the exact nature of the goods to be produced and subsidiary activities to be undertaken. 3. Business Secrecy An entrepreneur must be able to guard business secrets. 4. Human Relations Ability The most important personality traits contributing to the success of an entrepreneur are emotional stability, personal relations, consideration, and tactfulness. An entrepreneur must build and maintain good relations with his customers if he want them to keep patronizing his business. 5. Communication Ability An entrepreneur who can effectively communicate with customers, employees, suppliers, and creditors will be more likely to succeed than the entrepreneur who cannot. 6. Technical Knowledge An entrepreneur must have a reasonable level of technical knowledge. He should possess adequate knowledge of the tools, procedures, and techniques used in carrying out different operations in his organization. He should be familiar with tasks assigned to staff who work under him.