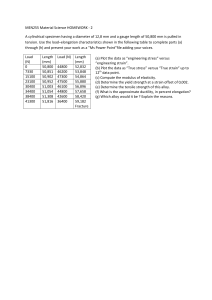
Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani Work Integrated Learning Programmes Division First Semester 2022 -2023 Comprehensive Examination (EC-3 Regular) Course No. Course Title Nature of Exam Weightage Duration Date of Exam Note to Students: 1. 2. 3. 4. : ENGG ZC232 : Engineering Materials : Open Book : 40% : 2 ½ Hours : 26/11/2021 (FN) No. of Pages =3 No. of Questions = 8 Total marks = 40 Marks Please follow all the Instructions to Candidates given on the cover page of the answer book. All parts of a question should be answered consecutively. Each answer should start from a fresh page. Assumptions made if any, should be stated clearly at the beginning of your answer. Please answer precisely to the point and do not drag around. Q.1. (a) Explain the main reason why aluminum and its alloys are widely used in motor vehicles? What are the advantages of using aluminum alloys compared to conventional steel materials for the production of parts and vehicle assemblies? [2.5 M] (b) What is specific strength? Why fibers have very high specific strength? [2.5 M] Q.2. (a) Compare the linear densities for the (1 0 0), (1 1/2 1) and (1/2 1/2 1) directions for the Iron (Fe) crystal structure below 723 °C with help of diagrams. [2.5 M] (b) Determine the miller indices for the unit cells shown in the figure below. [2.5 M] Q.3. (a) Sketch an isomorphous phase diagram of AB alloy and determine the weight fraction of liquid in an alloy of 73% B, if α of 82 % of B and liquid of 57 % B are in equilibrium. What would be the degree of freedom in such a case? [3 M] (b) Explain briefly the concept of true stress and strain against engineering stress and strain with a help of stress-strain diagram. [2 M] Q.4. (a) Mention the enabling materials properties for each labelled item in the figure given below. [2.5 M] (b) Briefly describe the importance of temperature, corrosion, fatigue, and strain rate behaviour of materials in engineering design applications. [2.5 M] Q.5. State the treatment processes must be performed on eutectoid steel to obtain transformation from: [2 M] (a) Martensite to Pearlite (b) Pearlite to Bainite, and (c) Austinite to Ferrite Q.6. (a) Sketch and explain the iron-iron carbide equilibrium diagram, and show their salient feature. Indicate the significance of this diagram for the heat treatment of steel. [4 M] (b) For a brass alloy, the stress at which plastic deformation begins is 345 MPa, and the modulus of elasticity is 103 GPa. [4 M] i. What maximum load may be applied to a specimen with a cross-sectional area of 130 mm2 without plastic deformation? ii. If the original specimen length is 76 mm, what is the maximum length to stretch it without causing plastic deformation? Q.7. Draw the tensile stress-strain diagram of the following materials in Table below and locate the yield and ultimate stress value. Also compare and make a ranking on the following mechanical properties, Toughness, Hardness, Ductility, Ultimate Tensile Strength and Plasticity of these materials. [5 M] S.No. Materials 1 2 3 4 5 Pure Copper Steel Pure Aluminum Magnesium Diamond Q.8. Explain the following BRIEFLY to the point: S.No. 1. 2. 3. Fatigue Define it Discuss the mechanism of fatigue failure Suggest methods to improve the fatigue life of materials [5 M] Creep Define it Discuss the mechanism of creep failure Suggest methods to improve the creep life of materials ***********