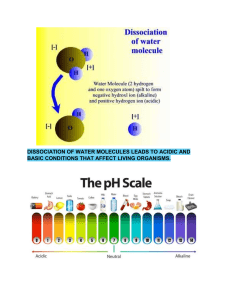
Glossary of Terms absorbed accumulate acid acid rain acidic adaptation addictive aerobic respiration air resistance alcohol alkaline alveoli amplitude amylase anaerobic respiration angle of incidence angle of reflection antagonistic muscles asthma atmosphere atmospheric pressure atom When a substance is taken in by something or moved across a barrier such as a cell membrane, it is said to have been absorbed. To increase in amount or concentration, especially in one place. Corrosive substance which has a pH lower than 7. Acidity is caused by a high concentration of hydrogen ions. Rain that contains dissolved acidic gases such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide. Having a pH less than 7. A feature of an organism's body which helps it to survive. Something that is addictive is habit-forming. It creates a dependency so that more of it is wanted. Respiration that requires oxygen. A force of friction produced when an object moves through the air. A depressant that can be found in wines, spirits and beers. Also known as ethanol. Having a pH greater than 7. Tiny air sacs in the lungs, where gas is exchanged during breathing. The maximum height of a wave from the middle of the wave to its the crest or trough. An enzyme found in yeast, which can break down starch into simple sugars. Respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen. Angle between the normal and the incident ray. The angle between the reflected ray and the normal (the imaginary line drawn at 90 degrees to the reflecting surface). A pair of muscles that act on a joint. As one contracts, the other one relaxes. A disease that affects the respiratory system. The layer of gases that surround the Earth. The important gases in the atmosphere are nitrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide. The weight of air resting on the Earth's surface. All elements are made of atoms. An atom consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. atomic number The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Also called the proton number. average speed Average speed = distance ÷ time over a known distance and time. For example, the average speed of the bus between Edinburgh and Glasgow was 30 m s-1. bacteria Single-celled microorganisms, some of which are pathogenic in humans, animals and plants. Singular is bacterium. balanced diet A diet that contains the correct amounts of all the necessary nutrients required for healthy growth and activity. An equation in which the symbols and formulae of the reactants and products are used to model a reaction. Also called a symbol equation, balanced symbol equation or chemical equation. balanced equation balanced force When the total force in opposite directions are equal in magnitude. For example, with a thrust of 15 N and a frictional force of 15 N, the body experiences balanced forces. base A substance with a pH higher than 7, and which has a high concentration of hydroxyl ions. Bases react with acids to form a salt and water (called neutralisation). Metal hydroxides, oxides and carbonates are all bases. base pair The pair of nitrogenous bases that connects the complementary strands of DNA. bile A substance produced in the liver. It emulsifies fats to prepare them for digestion. The range of plants and animals in the ecosystem. The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. The chemical link that holds molecules together. Hard, rigid tissue forming the skeleton in humans and other vertebrates. Soft tissue found inside bones that produces new blood cells. If something is brittle it is easily broken. biodiversity boiling point bond bone bone marrow brittle bronchi bronchioles bronchitis cancer capillaries carbohydrase carbohydrate carnivore catalyst The plural of 'bronchus'. The bronchi are the two major air tubes in the lungs. The many small, branching tubules into which the bronchi subdivide. Inflammation of the bronchi and bronchioles. Cancer is a disease caused by normal cells changing so that they grow in an uncontrolled way. The uncontrolled growth causes a lump called a tumour to form. Tiny blood vessels with walls one-cell thick where exchange of materials occurs. Enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates. Food belonging to the food group consisting of sugars, starch and cellulose. It is vital for energy in humans, and is stored as fats if eaten in excess. In plants, carbohydrates are important for photosynthesis. An animal that eats meat or flesh only. Changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction itself. cell Basic unit of life. Unicellular organisms only have one cell. Multicellular organisms have many cells. cell membrane A selectively permeable membrane surrounding the cell and controlling the entry and exit of materials. cell wall Outer structure which provides support and prevents the cell from bursting by the uptake of water by osmosis; plant, fungal and bacterial cell walls have a different structure and chemical composition. chloroplast The green chemical inside the chloroplasts of plant cells. It enables photosynthesis to take place. Contains the green pigment chlorophyll; the site of photosynthesis. chromatography Chromatography is used to separate different substances dissolved in a liquid. chromosome The structure made of DNA that codes for all the characteristics of an organism. cilia Tiny hair-like projections from a cell that usually allow it to move a substance past the cell (for example, in the bronchioles in the lungs). chlorophyll circulatory system combustion competition complete combustion compound compression conduction conductor conservation of energy Bodily system made up of the heart, blood vessels and blood that delivers nutrients and other essential materials to cells whilst removing waste products. The process of burning by heat. The interaction between organisms after the same limited resources. Burning in a plentiful supply of oxygen or air. Complete combustion of a hydrocarbon produces water vapour and carbon dioxide. A substance formed by the chemical union of two or more elements. Being squashed. The transfer of heat energy through a material - without the material itself moving. A material which allows charge to move easily through it. The principle that the total energy of a system stays the same, that energy cannot be created or destroyed (only stored or transferred). consumer An organism that obtains its energy by eating other organisms. continuous variation Variation that shows a wide range of intermediate values between two extremes; they can be measured. Become shorter. Able to damage metal, stonework, clothes and skin. Strong acids and alkalis are corrosive. contract corrosive cytoplasm deficiency deformation density diaphragm diet dietary fibre diffuse diffuse scattering diffusion digestion The living substance inside a cell (not including the nucleus). In the diet, a deficiency happens if there is too little of a particular nutrient. Changing shape and/or size as a result of forces being applied. The ratio of mass to volume. It is usually measured in grams per cubic centimetre or grams per cubic decimetre. A large sheet of muscle that separates the lungs from the abdominal cavity. The type and amount of food consumed by people. The part of food that cannot be digested. It is also called roughage. When particles spread out from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. When light is reflected off a surface in all directions. The movement of particles (molecules or ions) from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. The breakdown of large insoluble food molecules to smaller soluble ones. digestive system Organ system involved in breaking food down so that it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. discontinuous variation Differences between individuals in a characteristic that can only be put into different categories. Spread away and apart. Spreading out of the different wavelengths of light, caused by refraction of light as it passes through a prism. dispersed dispersion displace Take the place of another substance in a chemical reaction. For example, a metal can displace a less reactive metal from its oxide, removing oxide ions from the less reactive metal and becoming an oxide itself. distance Numerical description of how far apart two things are. For example, the distance from Edinburgh to Glasgow is approximately 50 miles. distance-time graph A graph with distance travelled plotted on the vertical axis against time taken on the horizontal axis. DNA double helix drug echo ecosystem effort egestion elastic elastic potential energy elements embryo endangered species Deoxyribonucleic acid. The chemical which chromosomes are made out of, carrying the genetic information of a living being. The shape of the DNA molecule with two strands twisted together in a spiral. A substance that can change chemical reactions in the body. A sound caused by the reflection of sound waves from a smooth surface back to the listener. A community of animals, plants and microorganisms, together with the habitat where they live. Force used to move a load over a distance. The process of passing out the remains of food that has not been digested, as faeces, through the anus. Elastic materials return to their original shape and size after being stretched or squashed. Energy stored in squashed, stretched or twisted materials. A substance made of one type of atom only. An organism in the early stages of development. Animals that are close to extinction because of their low numbers. endothermic Reaction in which energy is taken in from the surroundings. The surroundings then have less energy than they started with, so the temperature falls. energy resource energy transfers Useful supply or store of energy. Changes from one form of energy to another form of energy. environmental variation enzyme Differences between individuals of a species due to factors in their surroundings. A protein which catalyses or speeds up a chemical reaction. ethanol The alcohol which is produced as a result of fermentation of sugars by yeast. evaporation When a liquid changes state to a gas. excretion Process by which waste products from chemical reactions in an organism are removed. Breathe air out. Reaction in which energy is given out to the surroundings. Increase in length, for example, as a result of being pulled. A species that has completely died out. When something is taken away from or out of something else. Type of anaerobic respiration carried out by yeast. Capable of producing offspring. The fusion of a male and female gamete. The process of passing a mixture through filter paper - soluble substances pass through the filter as a 'filtrate' but insoluble substances stay in the filter as a 'residue'. exhale exothermic extension extinct extracting fermentation fertile fertilisation filtering filtrate finite resource fluid food chain food web Fluid that has passed through a filter. Resource that can only be used once and is in limited supply. For example, oil is a finite resource. A substance that can flow, such as a liquid or a gas. A sequence (usually shown as a diagram) of feeding relationships between organisms, showing who eats what and the movement of energy through trophic levels. Diagram of feeding relationships between organisms in an evnironment. force fossil fuel fractional distillation frequency frictional force fuel gamete gas exchange gene bank generator genes genetic engineering geothermal gestation gland global warming A push or a pull. The unit of force is the newton (N). Fuel which is finite and is made from plant and animal materials over millions of years, eg oil, coal and natural gas. In fractional distillation a mixture of several substances, such as crude oil, is distilled and the evaporated components are collected as they condense at different temperatures. The number of waves produced each second. The unit of frequency is hertz, 'Hz'. Force that resists one object moving through or over something. An example is air resistance on a car. Material that is used to produce heat, like coal, oil or gas. Sex cell. Oxygen passes through the capillary wall and into the tissues; carbon dioxide passes from the tissues into the blood. A store of genetic material such as sperm, embryos or seeds. Device that converts kinetic energy into electrical energy. The basic units of genetic material inherited from our parents. A gene is a section of DNA which controls part of a cell's chemistry - particularly protein production. Process which involves the artificial transfer of genetic information from one donor cell or organism to another. Energy from the heat of the Earth. The time during which a fertilised egg develops into a baby ready to be born. An organ or tissue that makes a substance for release, such as a hormone. The rise in the average temperature of the Earth's surface. gradient Another word for 'slope'. On a graph, the gradient is defined as being the change in the y value divided by the change in the x value, and defines how steep a line is. gravitational field strength Force per unit mass. Measured in newtons per kg (Nkg-1), eg the gravitational field strength of the Earth is 9.8Nkg-1. gravitational potential energy The energy stored by an object lifted up against the force of gravity. Also know as GPE. greenhouse gases The gases responsible for global warming - carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and CFCs. group A vertical column in the periodic table containing elements with similar chemical properties. heart disease A deadly disease that affects the heart. Hepatitis herbivore heredity HIV Hooke's Law hormone hydrocarbon incident ray Inflammation of the liver, which can be caused by alcohol, viruses or bacteria. An animal that feeds only on plants. To do with passing genes to an offspring from its parent or parents. Human immunodeficiency virus, a very serious disease which is at present incurable. Law describing that the extension of an object or material is directly proportional to the force applied. Chemical messengers produced in glands and carried by the blood to specific organs in the body. A compound that contains hydrogen and carbon only. Light ray moving towards a surface or boundary. incomplete combustion indicator infrared radiation inhale inherited variation insoluble insulator intercostal muscles internal energy kinetic energy lactic acid Burning when there is a limited supply of air or oxygen. A substance that has different colours, depending upon the pH of the solution it is in. Electromagnetic radiation emitted from a hot object. To breathe air in. Differences between individuals of a species due to their genetic information. Unable to dissolve in a particular solvent. For example, sand is insoluble in water. Material that does not allow charge or heat to pass through it easily Muscles between the ribs which raise the ribcage by contracting and lower it by relaxing. Energy stored in all materials, including energy due to the motion of particles and the chemical bonds between them. The energy that moving objects have. A toxic chemical produced during anaerobic respiration. large intestine The lower part of the alimentary canal (gut) where absorption of water and production of faeces happens. law of reflection In reflection at a surface, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. lens ligament A transparent tool that can change the direction of a ray of light. Tough material joining two bones together. light microscope Device that uses visible light and a series of lenses to produce an enlarged image of an object. limewater Calcium hydroxide solution. It turns milky in the presence of carbon dioxide. lipase lipid Enzyme that breaks down lipids (fats and oils). Fat or oils composed of fatty acids and glycerol. A type of indicator that can be red or blue. Red litmus turns blue in alkalis, and blue litmus turns red in acids. Force in a machine due to the mass, weight or movement of an object. A wave that moves in the same direction as the direction in which the particles are vibrating. litmus paper load longitudinal wave lungs malleable mass menstrual cycle menstruation metal The organs responsible for gas exchange in mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians. If a material is malleable it is capable of being hammered or pressed out of shape without being likely to break or return to the original shape. The amount of matter an object contains. Mass is measured in 'kg'. Recurring series of events in the human female reproductive system. Also called a 'period'. The loss of blood and tissue from the lining of the uterus through the vagina during the menstrual cycle. Shiny element that is a good conductor of electricity and heat, and which forms alkaline oxides. microorganism Another name for a microbe. It is microscopic and is an organism, such as a virus or bacteria. minerals Naturally occurring, inorganic chemical substances. Minerals are necessary for both plant and animal health. mitochondria Structures in the cytoplasm of all cells where respiration takes place (singular is mitochondrion). A collection of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. molecule moment mucus multicellular natural selection nervous system neutral neutralisation neutralise newton nicotine non-metal A turning effect of a force. Slimy white protein, which lines the respiratory tract and alimentary canal. Having more than one cell. The natural process whereby the best-adapted individuals survive longer and have more offspring, thereby spreading their characteristics through a population. 'Survival of the fittest'. The brain and nerves. When a substance is neither acidic nor alkaline, and has a pH of 7. The reaction between an acid and a base to form a salt plus water. To be made neutral by removing any acidic or alkaline nature. Unit of force named after British scientist Isaac Newton (1642-1727). Eg, the frictional force on the boat is 20,000 N. The addictive substance found in tobacco and tobacco smoke. Element that is a poor conductor of electricity and heat, and which forms acidic oxides. normal A resource that cannot be replaced when it is used up, such as oil, natural gas or coal. Acting at an angle of 90° to a surface or boundary. nuclear fuels Radioactive materials, usually uranium or plutonium, used in nuclear reactors. nucleus The nucleus controls what happens inside the cell. Chromosomes are structures found in the nucleus of most cells. The plural of nucleus is nuclei. An animal that eats both plants and meat. non-renewable omnivore organ organ system oscilloscope trace ovaries ovary (plant) oxidation A group of different tissues that work together to carry out a particular function, eg heart and lungs. A group of organs that work together to complete a specific function. The wave pattern seen on the screen of an oscilloscope. A pair of organs in the female reproductive system where ova (eggs) and hormones are produced. Part of the female reproductive tissue in plants, which contains the ovules. The gain of oxygen, or loss of electrons, by a substance during a chemical reaction. pascal Unit of pressure. Pascal (Pa), eg normal atmospheric pressure is 1.01x105 Pa. period A horizontal row in the periodic table. periodic table A tabular representation of all known elements in order based on atomic number, eg all the noble elements are found on the right of the periodic table. pH Scale of acidity or alkalinity. A pH (power of hydrogen) level below 7 is acidic, a pH level above 7 is alkaline. photo-sensitive material Substance that changes in some way when it absorbs light, for example leading to a chemical or electrical change. photosynthesis pitch pivot A chemical process used by plants and algae to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. The frequency of a sound. Sounds with a high pitch have a high frequency. A point around which something can rotate or turn. placenta pollen grain pollination population predator pressure The organ in the uterus of pregnant mammals that allows the transfer of nutrients and waste products between the mother and the fetus through the umbilical cord. The structure produced in the anthers of a flower that contains the male gamete. The fertilisation of flowers by passing on their pollen. All of the members of a single species that live within a geographical area. An animal that hunts, kills and eats other animals for food. Force exerted over an area. The greater the pressure, the greater the force exerted over the same area. prey primary consumer producer product protease Organisms that predators kill for food. The name given to an organism that eats a producer. A herbivore. A green plant that makes its own food by photosynthesis. A substance formed in a chemical reaction. Enzyme that breaks down proteins. protein Organic compound made up of amino acid molecules. One of the three main food groups, proteins are needed by the body for cell growth and repair. Time during which sexual maturity happens. puberty pyramid of numbers radioactive ray diagram reactants reaction force reactive reactivity series red blood cell reflect reflected ray A diagram that shows the relative numbers of organisms at each stage in a food chain. When unstable atoms give off particles that can be harmful to humans. Diagram that represents the direction and angle of travel of light. Substances present at the start of a chemical reaction. Force exerted in the opposite direction to an action force. The tendency of a substance to undergo a chemical reaction. A list of substances in order of their reactivity, usually from most reactive to least reactive. The blood cell which contains the pigment haemoglobin responsible for the transport of oxygen. Bounce off. Shiny surfaces, such as mirrors, reflect light well. Hard surfaces, such as walls, reflect sound well (producing echoes). Light ray leaving a surface or boundary. refraction Process by which a wave changes in speed and sometimes direction upon entering a denser or less dense medium. For example, a light ray changes direction when refracted by a lens. relative motion The change in position with time of one object compared to another object. renewable reproductive system Energy sources that are replenished and not exhausted, eg solar power. The organs and tissues involved in producing offspring. The material left over at the end of a process, often the material that is removed during purification of a substance. residue respiration respiratory system resultant force Chemical change that takes place inside living cells, which uses glucose and oxygen to produce the energy organisms need to live. Carbon dioxide is a byproduct of respiration. The organ system where air is taken into and out the body, and gas exchange happens. The single force that could replace all the forces acting on an object, found by adding these together. If all the forces are balanced, the resultant force is zero. retina The light sensitive area on the back of the eye. Light must be focussed on the retina in order to see clearly. secondary consumer An organism that obtains its energy by eating the primary consumer. seismic waves Shock waves travelling through the Earth, usually caused by an earthquake. selective breeding An artificial process in which organisms with desired characteristics are chosen as parents for the next generation. Separation method used to separate a solvent from a solution. simple distillation skeleton The support structure for an organism. In humans, it consists of bones inside the body. small intestine The part of the alimentary canal or gut, between the stomach and large intestine, where digestion and absorption happen. An activity where people burn tobacco and inhale smoke into their lungs. A device that converts light energy into electrical energy. A device that produces hot water from the Sun's energy. smoking solar cell solar panel soluble sonorous Able to dissolve in solvent. For example, sugar is soluble in water because it dissolves to form sugar solution. Able to make a ringing sound when hit. specialised A cell that has become differentiated to carry out a particular function, eg red blood cell. species Used in the classification of living organisms, referring to related organisms capable of interbreeding. A series of similar waves arranged in order of wavelength or frequency. Reflection in which light travelling towards a surface in one direction is all reflected in a single direction. spectrum specular reflection speed stomata surface area surface area synovial joint tar temperature tendon tension tertiary consumer thermal decomposition The distance travelled in a fixed time period, usually 1 second. Measured in m s-1. For example, the speed of the car was 10 m s-1. Tiny holes in the epidermis (skin) of a leaf - usually on the undersides of leaves. They control water loss and gas exchange by opening and closing. Singular is stoma. The area of the surface of an organism or membrane. The total area of an object, for example the area of a skydiver's body facing the air as they fall, or the area of a car tyre that touches the road. A freely moveable joint. Examples include the hip, shoulder, elbow and knee joints. Sticky substance found in tobacco smoke, which can cause cancer. How warm or cold something is. Tough material joining a muscle to a bone. Pulling force exerted by each end of an object such as a string or rope. An organism that obtains its energy by eating the secondary consumer. Type of reaction in which a compound breaks down to form two or more substances when it is heated. thermal equilibrium A situation where two objects are at the same temperature and there is no overall transfer of energy between them. time Term that describes the order and duration of events. For example, the Physics lesson was 50 minutes long. tissue toxic trachea translucent A group of similar cells that carry out the same function, eg muscle tissue. Substances that cause harm to people or the environment. The windpipe, the tube that leads from the mouth towards the lungs. Allows light to pass through but is not completely clear. transparent transverse turbine ultrasound unicellular universal indicator paper unreactive upthrust vacuole vacuum variation ventilation See-through. At 90 degrees. In transverse waves, the vibrations are at 90 degrees to the direction in which the waves travel. Revolving machine with blades that are turned by wind, water or steam. Turbines in a power station turn the generators. Sound with a frequency greater than 20,000 Hz (20 kHz). A single-celled organism. Paper stained with universal indicator, a chemical solution that produces many different colour changes corresponding to different pH levels. A substance is unreactive or inert if it does not easily take part in chemical reactions. Upwards force exerted by a liquid or gas on an object floating in it. A space within the cytoplasm of plant cells that contains cell sap. A volume that contains no matter. Difference between individuals; distance from the norm. Breathing in and out. villi Finger-like projections in the small intestine that provide a large surface area for the absorption of food. vitamins Organic substances which are essential in small amounts to regulate the metabolism and maintain the immune system. The length of a single wave, measured from one wave crest to the next. wavelength weight The force acting on an object due to the pull of gravity from a massive object like a planet. The force acts towards the centre of the planet and is measured in newtons (N). word equation An equation in which only the names of the reactants and products are used to model a reaction. work done The amount of energy it takes to do a task. Measured in joules (J). Eg, the work done in raising a mass through 10 m would be equal to the gain in potential energy of the mass. yeast A unicellular fungus used in the brewing and baking industries.