Understanding the OSI Model: A Presentation
advertisement

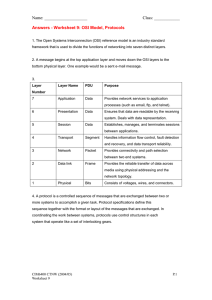
Understanding the OSI Model Professor Messer Domain 1.1 Understanding the OSI Model What is the OSI Model? • Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model, a model used within IT do describe the process data takes as it traverses our networks It’s a guide • Don’t get wrapped up in the details This is not the OSI protocol suite • Most of the OSI protocols didn’t catch on There are unique protocols at each layer You’ll often refer to this model for the rest of your career All People Seem To Need Data Processing OSI MODEL LAYERS LAYER 7 LAYER 6 LAYER 5 LAYER 4 LAYER 3 LAYER 2 LAYER 1 APPLICATION PRESENTATION SESSION TRANSPORT NETWORK DATA LINK PHYSICAL Page | 1 Understanding the OSI Model Layer 1 – Physical • • This is they physics of the network o Signaling, cabling, connectors o This layer is not about protocols o This layer deals with anything that is physical including switches, hubs, cables, routers, anything physical can be found at the physical layer “You have a physical layer problem” o Fix your cabling, punch-downs, etc. o Run loopback tests, test/replace cables, swap adapter cards Layer 2 – Data Link • • • The basic network “language” o The foundation of communication at the data link layer, the layer used for 2 devices to communicate Data Link Control (DLC) Protocols o This layer can also be called the Media Access Control Address (MAC address) because it is commonly associated with the adapter cards and network cards within our device. We refer to the physical address as a MAC address or a DLC. The Switching Layer o Since the network switches we use our network determine how to forward traffic on the destination MAC address, we refer to this as the Switching Layer. Page | 2 Understanding the OSI Model Layer 3 – Network Layer • • • The “routing” layer o We often refer to this layer as the routing layer because this is the layer where routers look at the destination IP address to determine how to forward traffic and know what the next hop might be for traffic traversing the network Internet Protocol (IP) Addresses o This layer also handles IP addresses or Internet Protocol Addresses Fragmenting frames to traverse different networks o This layer can also fragment data into smaller pieces to send to another network, especially if it’s sent across a network that may require smaller frames than our local network o Any time we are referring to a problem having to due with IP addresses, routing or fragmenting, we are referring to the network layer Page | 3 Understanding the OSI Model Layer 4 – Transport • • The “post office” layer o Referring to the ability to transport data from one device to another device o This is responsible for getting your “letter” or information from one part of a network to another Protocols o Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) o User Datagram Protocol (UDP) o These 2 protocols are commonly responsible for getting all of our information within our IP packets from one device to another, this involves taking apart a large piece of data into pieces and sending them across the network. Page | 4 Understanding the OSI Model Layer 5 – Session • • Communications Management between devices o This layer provides communication management from point A to point B o This layer also stops, starts and restarts communications between devices Control Protocols, tunneling protocols o If an application is using some type of application protocol or tunneling information, it is most likely on layer 5 Layer 6 – Presentation • • • Character encoding o This layer is responsible for putting all this data into a format we will see with our human eyes. o It put it in a format we can understand Application encryption Often combined with the application layer Page | 5 Understanding the OSI Model Layer 7 – Application • This is the layer we see o Anytime we are interacting with an application, we are working at layer 7 o Common applications that operate at layer 7 are HTTP/HTTPS, FTP, DNS, POP3 and thousands of other layer 7 applications Page | 6 Understanding the OSI Model LAYER 7 APPLICATION – Your eyes, what you see on your screen LAYER 6 The application you see PRESENTATION – Application encryption (SSL/TLS) LAYER 5 SSL Encryption SESSION – Control Protocols, Tunneling Protocols LAYER 4 LAYER 3 LAYER 2 LAYER 1 Link the presentation layer to the transport layer TRANSPORT – TCP Segment, UDP Datagram TCP Encapsulation NETWORK – IP Addresses, Router, Packet IP Encapsulation DATA LINK – Frame, MAC addresses, Extended Unique Identifier (EUI-48, EUI-64), Switch Ethernet PHYSICAL - Cables, fiber, the signals themselves Electrical Signals Page | 7