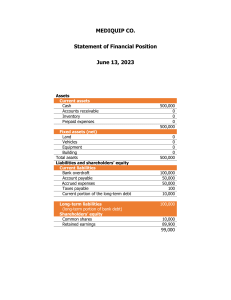
FINAL REVIEW COMM 210 Segregation of duties – what does this mean? Why is it so important in cash? If two people are involved, the task is “segregated”. This means theft is harder to do as you need 2 people in on it. “collusion”. The more people involved up to A CERTAIN POINT is preferable. Cost must never > benefit. At least one other person should review work done regularly (once a year at least) Accounting equation (assets=liabilities + equity). If I give you 2/3, can you calc the 3rd? Who has Responsibilities for preparing FS? The company’s management. Accrual accounting – when we recognize revenue/expense and how to account for payables. Which kind of expenses are accrued? You’ve done it in your assignment; Prepaid, AP, AR, Depreciation, basically all the entries that do not contain cash. AJE’s, therefore timing, is what drives these entries. Know how to book a payable accrual AJE for expense. Why do we have accrual accounting, why is it so important? How/why do we record a payable, and how do we derecognize it once paid? If it’s not accrual it’s cash. Meaning timing does not matter and it skews our FS. Loans – What do term, maturity, and principal mean? How do we account for payment of interest and principal repayment via Journal entries? You’ve done it in your assignment; loan to dad. Term is how long you have to pay it back, maturity is the date it all must be due, and principal is how much you were given. In the assignment, there were no maturity or term dates. You only dealt with principal that you were expected to pay. Know these ratios to analyze – Quick, current, Earnings per share, and return on sales. Be prepared to know the formula, calculate it, and explain results of findings. Return on sales = NI/Net sales; tells you how much margin you kept. The higher the better as the more sales you keep in equity, the more money you can pay SH’s in dividends, the more debt you can pay, etc. Current ratio = Current Assets/Current Liabilities. This tells you how fast you can pay short term debt in a year. Anything >1 is good. Quick ratio = Cash + AR + Short term investments/ Current liabilities. How fast can you pay debts NOWW!!. Anything over is EXCEPTIONAL. EPS = NI/total CS issued gives $ earned maximum per share on a dividend. Know how to prepare a multi-step income statement out of a trial balance provided. Revenue – COGS = Gross margin. Operating expenses are subtotaled then deducted to equal earnings before taxes. Taxes are calculated and removed to = Net income Amortization – how to calc using the 3 methods. What are they? Straight line, units of production, Double declining method. SL = ($ cost – Residual value)/ Useful life. UoP = $ Cost/total units estimated to produce. Rate per unit* total units made per year. DDM = straight line rate per year * 2. Cannot depreciate past Residual. Inventory - Calc WA, FIFO COGS and Inventory ending and COGS. FIFO use the first purchase cost per unit first in sales. WA = total inventory value/total units Make sure you understand the pros/cons for financing with DEBT or EQUITY. ESPECIALLY if you have 51% (control) of the company. o Be prepared to analyze (meaning discussing impact to net income) using either debt or equity. Which method effects net income? How? o Earnings per share = Net income/(opening common shares + issued common shares, if option taken) See debt vs equity Q Know components of CF statements. Operating is biggest (NI+Depreciation + losses – gains +/- balance sheet changes aside from PPE.) Investing includes + proceeds – purchases PPE or notes payable/receivable. Financing are items to do with + share issuances and – redemption and – dividends. Add the 3 changes (net cashflow) to opening Cash balances = ending cash as per BS Bank reconciliation – you will not be required to prepare one, however know how to identify/ record required entries for reconciling items. Which bank rec items don’t we record for? See Q uploaded