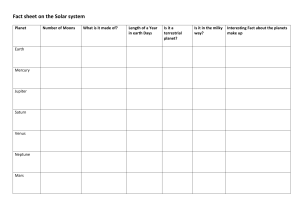
what is the solar system The solar system is a gravitationally bound system comprising the Sun and all the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. It is part of the Milky Way galaxy and is located in one of its spiral arms, called the Orion Arm All solar system planets Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune What is the Mercury est planet to the Sun. It is a small, rocky e covered in craters, similar to Earth's Moon. me temperature variations, ranging from 30°C during the day, due to its thin can't trap heat. It has a very short orbit, h days to complete one revolution around the slow rotation, taking about 59 Earth days to It has no moons and is often difficult to due to its proximity to the Sun. What is the Venus ond planet from the Sun, and it is often ister planet" due to its similar size, mass, n. Venus has a thick atmosphere primarily dioxide, with clouds of sulfuric acid, ce pressure about 90 times greater than net has extreme temperatures, with an temperature of around 465°C (869°F), cury, despite being farther from the Sun. What is the Earth net from the Sun and the only one known a diverse surface with oceans, land, and 71% of Earth’s surface is covered by land. Its atmosphere contains oxygen, ases, which support life. Earth has t, and a variety of ecosystems. It’s about and has a dynamic surface shaped by ectonics. What is the Mars planet from the Sun, often called the "Red its reddish appearance, caused by iron oxide e. Mars has a thin atmosphere, primarily on dioxide, and its surface features include deserts, and polar ice caps. It has two small d Deimos. Mars has a day length similar to 6 hours, but a year on Mars lasts 687 Earth of interest for potential past or present life, nt water and current seasonal methane What is the Jupiter anet from the Sun and the largest in our solar nt, primarily composed of hydrogen and d surface. Jupiter has a strong magnetic field s, including the four large Galilean moons: Io, and Callisto. It has a prominent storm, the ch has been raging for centuries. Jupiter's of clouds of ammonia and methane, and it has terns. It also has a very fast rotation, in just under 10 hours. What is the Saturn What is the Uranus nth planet from the Sun and an ice giant. It y of hydrogen, helium, and water, thane ices. Uranus has a unique feature: it with an axial tilt of about 98 degrees, extreme. The planet has a faint ring system ons, with the largest being Miranda, Ariel, and Oberon. Its blue color is due to osphere, which absorbs red light. Uranus th years to complete one orbit around the h and farthest planet from the Sun. It is a omposed of hydrogen, helium, and water eep blue color due to methane in its net is known for its strong winds, some of r system, and its Great Dark Spot, a ter's Great Red Spot. Neptune has 14 Triton being the largest, which orbits in n of the planet’s rotation. Neptune's year h years, and it takes 16 hours to complete What is the Neptune Evidence: •Definition: Tangible data, facts, or observations collected through research or experiments. •Purpose: To support or refute theories or claims. •Nature: Concrete and measurable, coming from experiments, samples, or observations. •Example: Fossil records and genetic data support the Theory of Evolution. Theory: •Definition: An explanation or framework for a phenomenon, developed through observation, reasoning, and experimentation. •Purpose: To explain how or why things happen and predict outcomes. •Nature: Abstract, evolving with new evidence, and can be refined or replaced. •Example: The Theory of Evolution explains species' changes over time through natural selection. References (the most used) By : Abdelrahman mohamed and Alaa eldin mohamed