Joint Pain Medication: Selection, Prescription & Communication
advertisement

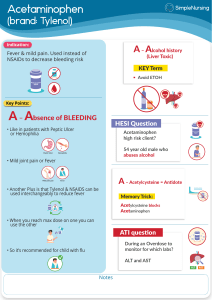
Selecting, Prescribing, and Communicating Medications for Joint Pain Relief Introduction • Overview of Joint Pain: • - Common causes (arthritis, injury, overuse) • - Impact on quality of life • Goals of Treatment: • - Pain relief • - Improving function • - Preventing further joint damage Non-Pharmacological Approaches (Before Medications) • - Rest and Activity Modification • - Physical Therapy and Exercise • - Heat and Cold Therapy • - Weight Management Pharmacological Management – NSAIDs • Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): • - Examples: Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Diclofenac • - Mechanism: Inhibits COX enzymes to reduce inflammation • - Indications: Mild to moderate pain, inflammation • - Side Effects: GI irritation, renal impairment • - Precautions: Use with caution in ulcers or Pharmacological Management – Acetaminophen • Acetaminophen (Paracetamol): • - Mechanism: Central inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis • - Indications: Mild pain without significant inflammation • - Advantages: Less GI side effects than NSAIDs • - Cautions: Risk of liver toxicity with high doses Pharmacological Management – Opioids • Opioid Analgesics: • - Examples: Tramadol, Oxycodone, Morphine • - Indications: Severe pain unresponsive to other analgesics • - Risks: Dependence, respiratory depression • - Prescribing Guidelines: Short-term use, lowest effective dose Pharmacological Management – Topical Analgesics • Topical NSAIDs and Capsaicin: • - Use Cases: Localized joint pain, minimizing systemic effects • - Advantages: Lower risk of systemic side effects • - Examples: Diclofenac gel, Capsaicin cream Intra-Articular Injections • Corticosteroid Injections: • - Indications: Inflammation in specific joints • - Mechanism: Potent anti-inflammatory effect • - Frequency: Limited to avoid cartilage damage • Hyaluronic Acid Injections: • - Role in Osteoarthritis: Lubrication and joint cushioning Communicating with Patients • Explaining Medication Choices: • - Tailor the explanation to the patient's condition and preferences • Discussing Potential Side Effects: • - Balance between benefits and risks • Instructing Proper Usage: • - Dosage, timing, and adherence importance • Setting Realistic Expectations: • - Pain relief levels and timelines Conclusion • Multimodal Approach: • - Combining non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatments • Patient-Centered Care: • - Individualized treatment plans • Follow-Up: • - Monitoring for efficacy and side effects