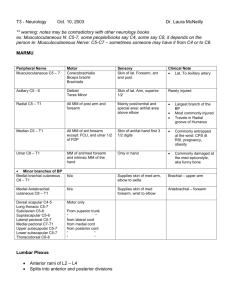
Regions of Lower Limb Compartments of Thigh • Three Compartments – Medial (adductor) • Act mainly at the hip joint – Anterior (extensor) • Hip Flexors • Knee Extensors – Posterior (flexor) • Hip Extension • Knee Flexion Femoral Triangle • Boundaries – Inguinal ligament – Medial border of sartorius muscle – Lateral border of adductor longus muscle • Floor – Iliopsoas – pectineus Femoral Triangle • Contents – Femoral Nerve – Femoral Artery – Femoral Vein – Lymphatics – NAVL Femoral Triangle • Femoral Artery Superficial in Femoral Triangle – Femoral pulse – Femoral catheterization – Coronary angiography • Femoral Sheath – Continuation of iliopsoas fascia and transversalis fascia – Encloses proximal femoral artery and vein Femoral Hernia • Femoral Ring – Located at base of femoral canal and is a weak area of abdominal wall and site of femoral hernia – Hernia initially presents as tender mass in femoral triangle – Can pass into subcutaneous tissue via saphenous opening – Strangulation and necrosis can occur as a result of compression against sharp, medial edge of femoral ring – Usually more rounded than inguinal hernias – More common in females Muscles of Anterior Compartment • Iliopsoas – Proximal Attachment • T12-L5 vertebrae and iliac fossa – Distal Attachment • Lesser trochanter of femur – Innervation • Iliacus: Femoral nerve (L2, L3) • Psoas Major: Anterior rami of lumbar nerves (L1, L2, L3) – Actions • Flexes thigh at hip joint; if thigh is fixed, flexes trunk on the thigh Muscles of Anterior Compartment • Pectineus – Proximal Attachment • Superior ramus of pubis – Distal Attachment • Pectineal line of femur, inferior to lesser trochanter – Innervation • Femoral Nerve (L2, L3), may receive branch of obturator nerve – Actions • Adducts and flexes thigh and assists with medial rotation of the thigh Muscles of Anterior Compartment • Sartorius – Proximal Attachment • Anterior superior iliac spine – Distal Attachment • Proximal part of medial surface of tibia (pes anserinus) – Innervation • Femoral Nerve (L2, L3) – Actions • Flexes, weakly abducts and laterally rotates thigh at hip joint; flexes leg at knee joint (weaver’s muscle) Muscles of Anterior Compartment • Rectus Femoris – Proximal Attachment • Anterior inferior iliac spine and ilium superior to acetabulum – Distal Attachment • Base of patella via common quadriceps tendon and indirectly to tibial tuberosity to via patellar ligament – Innervation • Femoral Nerve (L2, L3, L4) – Actions • Aids iliopsoas in thigh flexion and extends leg at knee joint • Most important muscle for knee extension, especially when force required i.e. standing from sitting or squatting, climbing stairs, running jumping • ~ 3 x’s stronger than hamstrings • Also important in stabilizing knee joint Muscles of Anterior Compartment • Vastus Lateralis – Proximal Attachment • Greater trochanter and lateral lip of linea aspera – Distal Attachment • Base of patella via common quadriceps tendon and indirectly to tibial tuberosity to via patellar ligament – Innervation • Femoral Nerve (L2, L3, L4) – Actions • extends leg at knee joint Muscles of Anterior Compartment • Vastus Medialis – Proximal Attachment • Intertrochanteric line and medial lip of linea aspera – Distal Attachment • Base of patella via common quadriceps tendon and indirectly to tibial tuberosity to via patellar ligament – Innervation • Femoral Nerve (L2, L3, L4) – Actions • extends leg at knee joint Muscles of Anterior Compartment • Vastus Intermedius – Proximal Attachment • Anterior and lateral surfaces of shaft of femur – Distal Attachment • Base of patella via common quadriceps tendon and indirectly to tibial tuberosity to via patellar ligament – Innervation • Femoral Nerve (L2, L3, L4) – Actions • extends leg at knee joint Muscles of Medial Compartment • Adductor Longus – Proximal Attachment • Body of pubis inferior to pubic crest – Distal Attachment • Middle 1/3 of linea aspera – Innervation • Anterior division of obturator nerve (L2, L3, L4) – Actions • Adducts thigh Muscles of Medial Compartment • Adductor Brevis – Proximal Attachment • Body and inferior ramus of pubis – Distal Attachment • Pectineal line and proximal linea aspera – Innervation • Anterior division of obturator nerve (L2, L3, L4) – Actions • Adducts thigh and to some extent flexes it Muscles of Medial Compartment • Adductor Magnus – Proximal Attachment • Adductor Part: inferior ischiopubic ramus • Hamstring Part: ischial Tuberosity – Distal Attachment • Adductor Part: Gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera and medial supracondylar line • Hamstring Part: adductor tubercle – Innervation • Adductor Part: posterior division of obturator nerve (L2, L3, L4) • Hamstring Part: tibial part of sciatic nerve (L4) – Actions • Adducts Thigh • Flexes Thigh (adductor portion) • Extends Thigh (Hamstring portion) Muscles of Medial Compartment • Gracilis – Proximal Attachment • Body and inferior ramus of pubis – Distal Attachment • Proximal part of medial surface of tibia (pes anserinus) – Innervation • Obturator nerve (L2, L3) – Actions • Adducts Thigh, flexes leg, helps stabilize knee and acts as synergist with other adductors • Gracilis Transplants Muscles of Medial Compartment • Obturator Externus – Proximal Attachment • External surface of obturator membrane and surrounding bone – Distal Attachment • Trochanteric fossa of femur – Innervation • Obturator nerve (L3, L4) – Actions • Laterally rotates thigh; steadies head of femur in acetabulum Muscles of Anterior and Medial Compartment Muscles of Anterior and Medial Compartment Muscles of Posterior Compartment • Semitendinosus – Proximal Attachment • Ischial tuberosity – Distal Attachment • Proximal part of medial surface of tibia (pes anserinus) – Innervation • Tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5, S1, S2) – Actions • Extends thigh, flexes leg and rotates it medially when leg is flexed • When thigh and leg are fixed, these muscles can extend trunk Muscles of Posterior Compartment • Semimembranosus – Proximal Attachment • Ischial tuberosity – Distal Attachment • posterior part of medial condyle of tibia – Innervation • Tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5, S1, S2) – Actions • Extends thigh, flexes leg and rotates it medially when leg is flexed • When thigh and leg are fixed, these muscles can extend trunk Muscles of Posterior Compartment • Biceps Femoris – Proximal Attachment • Long Head: ischial tuberosity • Short Head: linea aspera and lateral supracondylar ridge of femur – Distal Attachment • Lateral side of head of fibula – Innervation • Long Head: Tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5, S1, S2) • Short Head: Common Fibular division of sciatic nerve (L5, S1, S2) – Actions • Extends thigh, flexes leg and rotates it laterally when leg is flexed • When thigh and leg are fixed, long head can extend trunk Arteries of Thigh • Femoral – Deep Artery of Thigh (Profunda femoris) • Lateral Circumflex (ascending, transverse and descending) • Medial Circumflex • Perforating Arteries Arteries of Thigh • Obturator – Anterior Branch – Posterior Branch Nerves of Thigh • Femoral (L2-L4) – Anterior cutaneous nerve branches – Motor nerves to muscles of anterior compartment – Saphenous nerve Gray’s Anatomy for Students, 2 nd Edition, Drake, Vogl and Mitchell Nerves of Thigh • Obturator (L2-L4) – Posterior Branch • Obturator externus • Adductor brevis • Adductor portion of adductor magnus – Anterior Branch • Adductor longus • Gracilus • Adductor brevis • Cutaneous branches to skin on medial thigh Gray’s Anatomy for Students, 2nd Edition, Drake, Vogl and Mitchell Nerves of Thigh • Sciatic (L4-S3) – Tibial Nerve • Biceps femoris (long head) • Semitendinosus • Semimembranosus – Common Fibular Nerve • Biceps femoris (short head) Gray’s Anatomy for Students, 2 nd Edition, Drake, Vogl and Mitchell Cross Section of Thigh