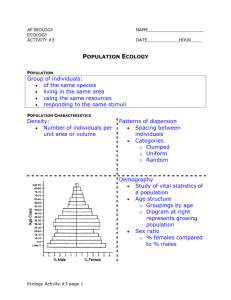
9/21/23 POPULATION DISTRIBUTION, GROWTH AND DENSITY POPULATION ¡ Refers to a group of organisms of the same kind or species living in the same place at the same time ¡ A population may increase or decrease due to birth, death, immigration and migration Daile M eek S. M em breve Biology Departm ent, College of science 1 2 POPULATION GROWTH POPULATION CHARACTERISTICS ¡ Is the change in a population over time, and can be quantified as the change in the number of individuals of any species in a population using ‘per unit time’ for measurement ¡ In demographics, population growth rate (PGR) is the rate at which the number of individuals in a population increases in a given time period as a fraction of the initial population. 3 Natality Mortality Sex ratio Age distribution Growth rates Special distribution 4 1 9/21/23 NATALITY OR BIRTH RATE MORTALITY OR DEATH RATE ¡ Refers ¡ The number of deaths per year. to the number of individuals added to the population through reproduction. ¡ It is usually discussed in terms of the number of individuals who die per one thousand individuals in the population per year ¡ It is the number of individuals born per one thousand individuals in the population per year. 5 6 POPULATION AGE DISTRIBUTION POPULATION CHARACTERISTICS ¡ The individuals of different age groups in a population. ¡ Age distribution ¡ Models that incorporate age structure allow better prediction of population growth, plus the ability to associate this growth with the level of economic development in a region. ¡ Population growth rate ¡ Bodenhelmer (1938) recognizes three ecological ages as: ¡ Population density 7 ¡ Pre-reproductive Reproductive ¡ Post reproductive ¡ 8 2 9/21/23 https://image.slideserve.com/228323/population-pyramids-for-the-four-demographic-transitionphases-l.jpg 9 https://cdn.thinglink.me/api/image/786025515705171970/1240/10/scaletowidth 10 POPULATION GROWTH CURVE ¡ Biotic potential is biological ability to produce offspring ¡ Sex ratios and age distribution directly affect the rate of reproduction within a population. Population | Department of Health website (doh.gov.ph) 11 12 3 9/21/23 TYPICAL POPULATION GROWTH CURVE TYPICAL POPULATION GROWTH CURVE ¡ Deceleration phase ¡ occurs when the population growth rate begins to slow. ¡ Lag phase is the period of time immediately following the establishment of a population, when the population remains small and fairly constant ¡ The number entering the population by reproduction remains high but the number leaving by death increases and the population growth rate begins to slow ¡ Stable Equilibrium Phase ¡ Exponential growth phase: period of time when a population is growing rapidly ¡ ¡ Period of time when a population stops growing and maintains itself at a reasonably stable level Birth rate > death rate ¡ Birth rate ~death rate The Population Growth Curve - Population Ecology - EVOLUTION AND ECOLOGY - CONCEPTS IN BIOLOGY (schoolbag.info) 13 The Population Growth Curve - Population Ecology - EVOLUTION AND ECOLOGY - CONCEPTS IN BIOLOGY (schoolbag.info) 14 CARRYING CAPACITY POPULATION GROWTH LIMITING FACTORS ¡ The number of individuals of a species that can survive in that area ¡ Density-dependent over time ¡ Linked to population size ¡ Four broad categories of factors that determine the carrying capacity ¡ Diseases for a population ¡ Lack of food 1. Availability of raw materials ¡ Density-independent 2. Availability of energy 3. Accumulation of waste products and mean of disposal ¡ Droughts, floods, habitat destruction 4. Interactions among organisms 15 16 4 9/21/23 POPULATION DENSITY • Is the number of individuals per unit area • High population density needs more resources (competition) h ttp s :/ / w w w .a ffo rd a b le c e b u .c o m / p ic tu re s / a rtic le s / p h ilip p in e s / T o ta l-P o p u la tio n -o f-th e -P h ilip p in e s -2 0 2 2 .jp g h ttp s :/ / p s a .g o v .p h / s ite s / d e fa u lt/ file s / b e ta file s / p o p u la tio n -a n d -h o u s in g / x F ig u re ,P 2 0 1 _ 2 0 1 3 _ re v ,P 2 0 ,P 2 8 1 ,P 2 9 .p n g .p a g e s p e e d .ic .o 7 7 Z E o Y d l4 .w e b p 17 18 FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH ECOLOGICAL FOOTPRINT • The impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resources • Calculates the amount of land and water we need to provide everything we use in life • To be ecologically sustainable, each person should consum e no m ore than 1.8 ha of land 19 SOCIAL FACTORS ¡ Religious ¡ Cultural ¡ Women education ECONOMICS FACTORS ¡ In less developed countries, the economic benefits of children are extremely important ¡ In the developed world, large numbers of children are an economic drain https://i.pinimg.com/736x/95/7a/de/957adeffa95e9a0d87940214d86fb793--sustainable-tourism-carbon-footprint.jpg 20 5 9/21/23 FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH FAMILY PLANNING POLITICAL FACTORS ¡ Governments can reward or punish high fertility rates: ¡ China’s one-child policy decreased the country’s fertility rate paid maternity, child tax deduction from 6 to 1.8 in two decades (very controversial). ¡ Policies to encourage more children (low birth rate country) ¡ Family planning strategies 21 22 THANK YOU FOR LISTENING. MAKE YOUR OWN FOOTPRINT Footprint Calculator - Measure your Impact - Global Footprint Network Draw in a letter size paper 23 24 6