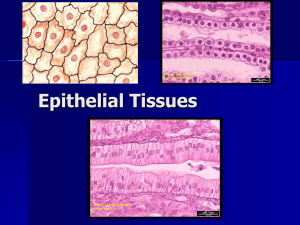
Histology I Ferdinand Gomez Department of Medical Education Objectives • Describe the basic mechanisms of tissue staining and compare and contrast different types of staining • Name and list the structural and functional characteristics of various epithelia as applied to the gastric pits, intestinal glands and the filtration slit diaphragm • Contrast serous and mucous secretion • Recognize the structural and functional classification of the exocrine glands Histological Methods: Tissue preparation • Fixation-permanent preserve specimen • Postfixation • Section staining • TEM vs SEM Stain: Hematoxylin & Eosin • Nuclei: blue • Pink/red: cytoplasm • Pink: collagen Stain: Periodic Acid-Schiff • Deep red/magenta: G cells • Pink: brush borders Stain: Weigert’s • Elastic fibers • Blue/black: elastic fibers • Pink: residual Stain: Mallory-Azan • Hyaline: deep blue • RBC: red Stain: Wright’s • Blood cells • Cell: bluish/purple (nucleus) • Cell: bluish/gray (cytoplasm) • Red/pink: RBCs Stain: Silver & Gold • Blue-black: fibers & neurofibrils • Colorless background Epithelial Tissue Occurs in the body as: Covering, lining, glandular epithelium Functions include: Protection, absorption, filtration, secretion Epithelial Tissue Characteristics Composed of close packed cells Tiny amount of extra-cellular material in between Form continuous sheets Avascular Domains: apical, lateral, base Figure 04.co Epithelial Classification Number of layers: • Simple (single cell) layer for absorption, filtration, & thin barrier • Stratified (two or more) layers common in high abrasion areas Epithelial Classification Shape: • Squamous • Cuboidal • Columnar • Nuclear shape conforms to cell shape Simple Epithelium Squamous Cells laterally flattened Located in areas of filtration/rapid diffusion Simple Epithelium Endothelium Provides frictionless lining Blood vessels, heart chambers Simple Epithelium Mesothelium Epithelium found lining walls and organs Simple Epithelium Cuboidal Spherical nuclei Absorption and secretion Kidney tubules, secretory ducts Simple Epithelium Columnar Single layer of tall cells aligned in rows Some have cilia Absorption & secretion Simple Epithelium Pseudostratified Columnar Cells vary in height Absorption & secretion Filtration Slit Diaphragm Intestinal glands (Crypts) Stratified Epithelium Squamous Most widespread (in areas of wear and tear) Superficial cells less viable than deep cells Keratinized vs. Non-keratinized Stratified Epithelium Cuboidal Larger gland ducts Sweat glands Mammary glands Stratified Epithelium Columnar Rare tissue Forms large gland ducts Male urethra Stratified Epithelium Transitional Basal cells are cuboidal/columnar Apical cells vary in shape according to distension of organ Glandular Epithelium Secretion Type • Secretion type: serous, mucus, mixed Exocrine Glands Classification: Modes of Secretion Merocrine Holocrine Apocrine Ceruminous www.anatomyatlases.org/.../Images/plate142.jpg Mammary Thank you!