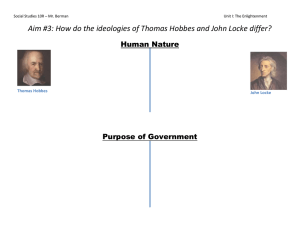
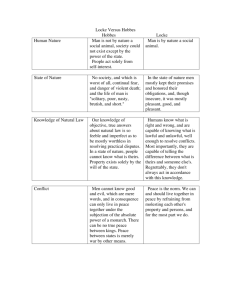
Front: What is Political Culture? Back: Political Culture refers to the set of attitudes, beliefs, and values that shape how people understand and interact with government and politics. Front: What role does Political Culture play? Back: It influences how people form political opinions, engage in political processes, and interact with government institutions. Front: What is Absolutism? Back: Absolutism is a political system where a single ruler holds all power, often justified by divine right, with no checks on their authority. Front: How did the Enlightenment Period impact views of authority? Back: The Enlightenment promoted ideas of reason and individual rights, challenging traditional authority and promoting the idea that government should be based on consent and rationality. Front: What is Classical Liberalism? Back: Classical Liberalism is a political ideology that emphasizes individual freedom, limited government, and free markets. Front: What are the core ideas of Classical Liberalism? Back: ● ● ● Political: Democracy, individual rights. Moral: Natural rights to life, liberty, and property. Economic: Free markets, limited government intervention. Front: How does Absolutism differ from Classical Liberalism? Back: Absolutism centralizes power in a single ruler with no limits, while Classical Liberalism advocates for limited government, individual rights, and democratic principles. Front: Who was Thomas Hobbes? Back: Thomas Hobbes was a philosopher who argued for an absolute monarchy and believed that in the state of nature, life would be "solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, and short." Front: Who was John Locke? Back: John Locke was a philosopher who believed in natural rights (life, liberty, property) and argued that government should be based on the consent of the governed. Front: What is the Social Contract? Back: The Social Contract is a theory that people consent to surrender some freedoms to a government in exchange for protection of their remaining rights. Front: How did Hobbes’ view of the Social Contract differ from Locke’s? Back: Hobbes believed in a powerful ruler with little to no right for rebellion, while Locke believed the government must protect individual rights and could be overthrown if it failed. Front: What are the principles of Limited Government? Back: Limited Government principles include restricted government power, separation of powers, checks and balances, and protection of individual rights. Front: How are Classical Liberal Principles reflected in the U.S. Government? Back: The U.S. Constitution embodies these principles through checks and balances, separation of powers, and protection of individual liberties in the Bill of Rights.