What are Governments
advertisement

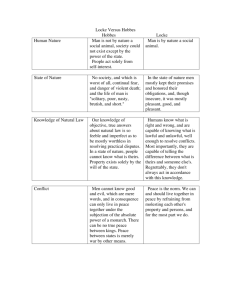
WHAT ARE GOVERNMENTS FOR? What are governments? 19th Century: night watchman states › Provide law and order, defense, protect property 20th Century: Police state and welfare states › Welfare state: from Bismarck to US However, Western Europe focuses on health equality, US focuses on equality of opportunity and education Welfare states have grown into regulatory states because governments have become large and inefficient Reformation and Enlightenment Church being questioned-as was divine right Martin Luther-focused on individual rights and right to worship God directly Locke vs Hobbes Thomas Hobbes believed the state’s only job is to stop disorder, protect against war; actually encouraged democratic thought while defending royal absolutism John Locke believed the state’s job is to protect property, commerce and economic growth Locke vs. Hobbes Adapted from www.jim.com/hobbes.htm Issue Locke: Second Treatise on Government Hobbes: Leviathan Human nature and natural law Man is by nature a social animal and they Man is not by nature a social have an ability to know right and wrong and animal, society only exists what is theirs and someone else’s through the state and property only exists through the state The State of Nature Men were honest, and while insecure it was peaceful, good and pleasant No society, man lives in continual fear of death; life is solitary, poor, short The Social Contract We give up our right to ourselves exact retribution for crimes in return for impartial justice If you shut up and do as your told, you have right not to be killed Violation of Social Contract If a ruler seeks absolute power, he is in a state of war with citizens and they have a right to kill the ruler No right to rebel; ruler’s define good and evil Role of the State The only role of the state is to ensure that justice is being done Whatever the state does is just by definition Jean Jacques Rousseau The Social Contract Freedom of Thought and Action All citizens could and should join in the making of laws agreed on by the basis of the general will Other functions of governments 1. Community and nation building teaching common language, heritage, values, symbols, myths, identity 2. Security and order Internal security and external Other functions 3. Protecting property and other rights Without protections of property, people won’t work to create sustained economic growth 4. Promoting economic efficeincy and growth to prevent economic failure Provide public goods (national defense, clean air, parks) Externalities---natural monopolies Other functions 5. Social justice Create level playing field through redistribution 6. Protect the weak Children Aged Disabled Animals Environment Critics of governments Anarchists Communitarians Believe governments destroy communities Libertarians Individualists Governments violate basic rights of people Other criticisms of government Creates economic inefficiency---government has too much involvement in the economy Government is good for private gain---common in poor societies where politics is the path to wealth Government protects vested interests---the larger the government, harder to change Alternatives Markets Libertarians argue that less government is more government Voluntary Coordination Anarchists would like to see the office holders closer to the people and more opportunities for people to participate in decision making