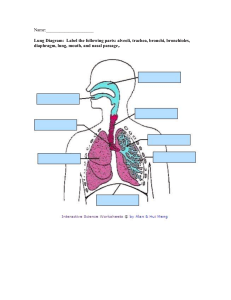
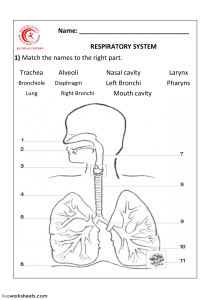
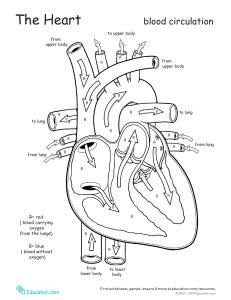
Chapter 16: LUNG & THORAIC Upper Airway: ❖ Nose ❖ Mouth ❖ Pharynx (throat): ➢ oropharynx (back of mouth) ➢ nasopharynx (back of nose) ❖ Larynx (voice-box) Lower Airway: ❖ Trachea (wind-pipe) ❖ Lungs ➢ RIGHT Lung: 3 lobes ▪ Higher than left bc of liver ▪ Right bronchus risk of aspiration & unintended intubation bc of higher up ➢ LEFT Lung: 2 lobes ▪ Narrower bc of heart ❖ Bronchi ❖ Bronchioles ❖ Alveoli *Bifurcation into the right & left lung happens at the CARINA (cough reflex) *GAS EXCHANGE happens in the ALVEOLI * TOP of LUNG called APEX : BOTTOM called BASE Pleurae: ❖ Visceral Pleura ➢ Lines the outer surface of lungs ❖ Parietal Pleura ➢ Lines thoraic wall, mediastinum & diaphragm Respirations: ❖ MAIN trigger for BREATHING: increased CO2 in the blood ➢ Occurs in brainstem: pons & medulla oblongata ➢ INHALATION occurs by: ▪ Diaphragm flattens creating vacuum pressure (NEGATIVE PRESSURE) pulling air in ➢ EXHALATION is: ▪ PASSIVE: muscle relax pushing air out Lung Sounds: Normal Lung Sound ❖ VESICULAR: ➢ Soft, low pitched ➢ Heard over finer airways near where gas exchange occurs in alveoli field ➢ Heard over lung periphery (over most of lungs) ❖ BRONCHOVESICULAR: ➢ Intermediate ➢ Heard over the Bronchi ➢ Inspiratory & expiratory equal ➢ Heard over front 1st & 2nd Intercostal Space (ICS) between Scapula ❖ BRONCHIAL: ➢ Loud, high pitched ➢ Heard over Trachea & Larynx *Larger Airways, breath sounds: louder & coarser *Smaller Airways, Breath sounds: softer & finer *Auscultate by listening TOP to BOTTOM, placed stethoscope directly on SKIN Adventitous Lung Sound ❖ RHONCHI: ➢ Low pitched ➢ Like snoring bc secretions moving around in the airways ➢ *Can clear with coughing in the morning when pts just wake up ➢ Heard in pt with pneumonia, edema, chronic bronchiits ❖ COARSE CRACKLES: ➢ Low pitched ➢ Fluid in Alveoli (smaller airways) ➢ Heard on inspiration mostly ➢ Sounds like velcro opening ➢ Heard in pts with edema, fluid, COPD ❖ WHEEZES: ➢ High pitched: air is squeezing thru a narrow airway ➢ Expiratory wheeze indicates mild to moderate Asthma ➢ Expiratory & inspiratory indicate severe Asthma ➢ Heard in pts with Asthma, Bronchitis & Emphysema ❖ STRIDOR: ➢ Loud, high pitched ➢ Heard over Trachea & Larynx due to spasm ➢ Due to aspiration of foreign object or epiglottis (medical emergency) ❖ PLEURAL FRICTION RUB: ➢ Loud, low pitched grating sound (like squeaky door) ➢ Heard in Lower Anterolateral thorax ➢ Pts with pleuritis *To assess Bronchophony, have pt say “99” while auscultating, if sound is loud & clear, this means (+) bronchophony. Pneumonia is present 96-99% of (+) pts Common Respiratory Conditions ❖ ASTHMA ➢ Hyper-sensitivity to allergens ➢ Low pitched wheeze due to narrow airway causing bronchospasm ➢ Diminished BS ➢ Percussion: occasional hyperresonance ❖ ATELECTASIS ➢ Collapsed section of alveoli ➢ Dyspnea ➢ Decreased or absent BS ➢ Confirmed by chest x-ray ❖ BRONCHITIS ➢ Inflammation of Bronchi ➢ Can be from infection or chronic COPD ➢ Confirmed by chest x-ray ➢ Percussion: resonance ❖ PNEUMOTHORAX ➢ Air in thoraic space caused by trauma ➢ Absent BS over effective area ➢ Dyspnea ➢ Confirmed by chest x-ray ❖ PLEURAL EFFUSION ➢ Fluid overload ➢ Decreased BS ❖ CONGESTED HEART FAILURE (CHF) ➢ Fluid overload, high BP ➢ Pink Frothy secretions ➢ Dyspnea, edema, weight gain Reference Lines: ANTERIOR (front) ❖ MIDSTERNAL LINE ➢ Runs vertically (top to bottom) center of sternum ❖ MIDCLAVICAL LINE ➢ Runs vertically from each clavical between sternoclavicular & acromioclavicular joints ❖ ANTERIOR (front) AXILLARY LINE ➢ Vertically (top to bottom) of anterior (front) axillary fold Reference Line: POSTERIOR (back) ❖ VERTEBRAL LINE ➢ Runs vertically down center of spinal cord process ❖ MIDSCCAPULAR LINE ➢ Runs parallel to vertebral line thru middle of each scapula