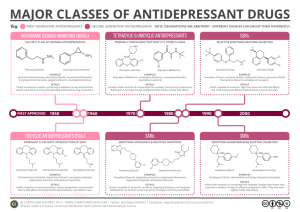
Psychotherapeutic Meds Workshop Wednesday, April 24, 2024 10:14 AM • (Missed the 1st question) • What symptoms do cholinergic receptors effect? ○ Parasympathetic NS ○ Agonists = stimulate ○ More rest & digest • What do anticholinergic meds do? ○ Dry up secretions ○ More excitability ○ Sympathetic NS stimulation • What type of symptoms w/ anticholinergic meds? - block parasympathetic ○ Dried up secretion ○ Cant see, pee, spit, poop ○ Think about systems and how they are affected CNS - dilated pupils, anxious, excitability CV - increased HR & BP, palpitations, dysrhythmias , flushing/redness d/t increased blood flow GI - dry mouth, constipation, decreased saliva GU - decreased urine output, Vision - blurred vision, glaucoma (blocks fluid from coming out of eye) MS - hyperthermia d/t increased muscle contraction ○ Contraindications: Glaucoma Renal dysfunction Arrhythmias HTN Hyperthyroidism - Grave's disease Dementia - associated w/ ACh in the brain BPH - reduced outflow --> potential obstruction • What are sympathomimetics, and what are S/E? ○ Mimic sympathetic NS Work on adrenergic receptors - alpha & beta [Look up for review] Alpha 1 - vasoconstriction, Beta 1 - inotropic (heart squeeze), ○ S/E: Antidepressant - SSRI/SNRI/MAOI/TCA DRUG CLASS: SSRI - Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors How does it work? Blocks the reuptake of serotonin What are some important S/E of this drug class? CNS: Headache, drowsiness, dizziness, insomnia, nervousness, anxiety, sedation GI: N/V/D, dry mouth, anorexia, constipation, weight loss GU: painful menstruation, cystitis, sexual dysfunction, urgency, impotence Mental Health Page 1 GU: painful menstruation, cystitis, sexual dysfunction, urgency, impotence Respiratory: cough, dyspnea, URI, pharyngitis Serotonin Syndrome: confusion, agitation, disorientation, hallucinations, delirium, seizures, tachycardia, labile BP, diaphoresis, fever, hyperreflexia, tremors, N/V/D, abdominal pain, coma. What are some nursing indication for this drug class? Suicide precautions Drink adequate fluids Dry mouth - sugar free candies/beverages Report sexual difficulties Sertraline - administer in PM Paroxetine - administer in PM Examples: Fluoxetine, Sertraline, Paroxetine, citalopram, escitalopram DRUG CLASS: SNRI - Serotonin- NE Reuptake Inhibitors How does it work? Decrease reuptake of serotonin & NE and weakly dopamine What are some important S/E of this drug class? Nausea, constipation, dizziness, headache, higher HR, hyperhidrosis/diaphoresis, erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, tachycardia, vomiting, palpitations Serotonin Syndrome: confusion, agitation, disorientation, hallucinations, delirium, seizures, tachycardia, labile BP, diaphoresis, fever, hyperreflexia, tremors, N/V/D, abdominal pain, coma. Boxed warning: increase risk of suicidal thoughts & behaviors What are some nursing indication for this drug class? Examples: Desvenlafaxine, duloxetine, levomilnacipran, milnacipran, venlafaxine (Effexor) DRUG CLASS: SNRI - TCA - Tricyclic Antidepressants How does it work? Block activity of NE & serotonin or increasing the sensitivity of postsynaptic receptor sites Relieve symptoms of hopelessness, helplessness, anhedonia, inappropriate guilt, SI, daily mood variations What are some nursing indication for this drug class? Examples: Mental Health Page 2 Examples: Amitriptyline, amoxapine, doxepin, imiparmine, desipramine, nortriptyline, DRUG CLASS: MAOI - Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors How does it work? Block activity of NE & serotonin or increasing the sensitivity of postsynaptic receptor sites Relieve symptoms of hopelessness, helplessness, anhedonia, inappropriate guilt, SI, daily mood variations What are some nursing indication for this drug class? Examples: Amitriptyline, amoxapine, doxepin, imiparmine, desipramine, nortriptyline, • Which classes of antidepressants are most safe, and which are considered least safe? Why? ○ Most Safe: SSRI/SNRI ○ Least Safe: MAOI/TCA MAOI - hypertensive crisis - tyramine TCA - OD can be fatal • What are important points for all antidepressants? ○ Suicide risk Black box warning - adolescents/children ○ Takes a few weeks to see effects ○ Don't stop abruptly SI Withdrawal symptoms • What are symptoms of W/D? ○ Headache, N/V, agitation, labile mood, vertigo, malaise, nightmares • Which of antidepressant drug classes has food restrictions and why? ○ MAOI - Tyramine --> Hypertensive crisis MAO is an enzyme that breaks down tyramine • Your pt is taking an MAOI, Write a list of food that they cannot eat these foods in a language your pt can understand? ANYTHING AGED □ Alcohol □ Aged Cheese □ Pepperoni/Sausage (cured meats) □ Soy sauce / teriyaki / □ Tofu □ Fermented foods □ Nava beans □ Saurkraut □ Yogurt □ Coffee □ Chocolate □ Aged fruits - avocado, bananas, citrus fruits • Which antidepressant drug classes puts pts most at risk for cardiac complications? ○ TCA • 3 main S/E pts complaining about when taking antidepressants Mental Health Page 3 • 3 main S/E pts complaining about when taking antidepressants ○ Insomnia ○ Sexual dysfunction ○ Weight gain/Loss Sleep / Sex / Slim • 5HT = Serotonin ○ Found in GI tract, CNS, platelet ○ Metabolized by MAO in liver Interacts w/ MAOI • Which block reuptake of Serotonin? ○ SSRI / SNRI / TCA • What is serotonin syndrome? ○ Build up of serotonin ○ Usually occurs w/in 24H of use ○ Pt w/ serotonin syndrome - stop meds DRUG ALERT – SEROTONIN SYNDROME Serotonin syndrome occurs when there is an inadequate washout period between taking MAOIs & SSRIs or when MAOIs are combined with meperidine. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include: • Change in mental status state: confusion & agitation Neuromuscular excitement: muscle rigidity, weakness, sluggish pupils, shivering, tremors, myoclonic jerks, collapse, and muscle paralysis Autonomic abnormalities: hyperthermia, tachycardia, tachypnea, hypersalivation, and diaphoresis • • • • • • Greatest concern for MAOI (what adverse effect is most concerning)? ○ Build up of tyramine --> hypertensive crisis • How is fluoxetine (Prozac) different from other SSRIs? ○ Takes longer for symptom relief ○ Longer half life (7 days) - longer for drug to leave body • What can you recommend if an SSRI is making a PT drowsy? ○ Take medication at night • What can you recommend if a pt is experiencing dry mouth due to meds? ○ Sugar free candies/beverages • Memorize drugs that are taken on empty stomach What classes fall w/in anxiolytic category? • Benzodiazepines - anxiety, W/D, ○ Work on GABA - acts same as alcohol • Antidepressants • Buspirone • Beta-blockers - decreased symptoms • Antipsychotics Benzodiazepines • Antidote - flumazenil IV What eye condition is contraindication for benzo administration? • Glaucoma - benzos block outflow. Seizure protocol - pt starts convulsing, what medicine do you anticipate giving and which route? • Lorazepam (Ativan) - IV • 3rd line - barbituates Pt stopped taking Ativan 2 days after being on it for 6 weeks rx for anxiety. What is primary Mental Health Page 4 • Pt stopped taking Ativan 2 days after being on it for 6 weeks rx for anxiety. What is primary concern? • Withdrawal Mental Health Page 5