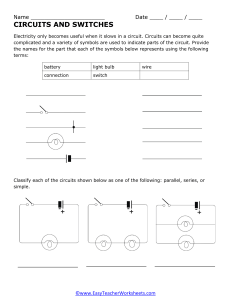
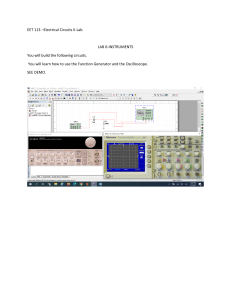
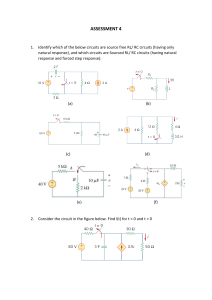
ECEN 218-001/002 Electrical Circuits Lab Laboratory Assignment #5 Introduction to laboratory Instruments Aryan Mehmood Mike Larsen Date experiment performed: 9/27/2023 Due date: 10/4/2023 Introduction: In this lab, we delved into the fundamental concepts of equivalent and linear circuits. We made use of familiar equipment from prior lab sessions, including the oscilloscope, function generator, DMM (Digital Multimeter), and our standard parts kit. The key objectives of this lab encompassed constructing uncomplicated circuits, conducting load line measurements, merging circuits, and manipulating voltage sources to acquire meaningful data. Implementation & Results: This lab comprised a series of 8 distinct experiments, each with its own level of complexity. To commence, the initial experiment entailed the creation of two distinct circuits as outlined in the lab manual. It was imperative that these circuits be constructed on a shared breadboard, as they would eventually be merged. Subsequently, the second task involved determining the load line for each of these circuits, a task easily accomplished through the utilization of a 10kΩ potentiometer. As previously stated, the subsequent experiment involved the integration of the individual circuits into a single entity. Experiments four, five, and six revolved around the measurement of V1, V2, and V0, with variations in the status of the voltage sources, both in the off and on states. The chart displaying our findings under these different conditions is presented below for reference. The second-to-last task involved employing the function generator as a voltage source and integrating a capacitor into the circuit. This modification was made to enable the measurement of waveforms in the ultimate activity. In the final task, we proceeded to measure and document the waveforms during the charging and discharging phases using a square wave with a 2-Vp (peak-to-peak) amplitude, employing the oscilloscope. Below, you can observe the complete cycles recorded from this particular exercise. Discussion: 1. . 2. 3. V0 = V1 + V2. The output voltage is equal to the sum of both the left and right sides of the circuit. 4. V1 = V0 - V2, and V2 = V0 - V1. 5. RT1 = 2kΩ, RT2 = 6kΩ 6. 7. VS1, V=IR, if there is more(or less) resistance, then there is more(or less) voltage since current never changes in this circuit. Conclusion: The primary objective of this lab was to enhance students' comprehension of equivalent circuits and the concept of superposition. In this lab, students were tasked with measuring two segments of an incomplete circuit, both individually and in their combined state. This hands-on approach aimed to provide students with practical experience in applying superposition to more intricate circuit scenarios. Furthermore, the lab required students to calculate total voltage, resistance, and load lines, and encouraged them to create equivalent circuits based on this data.