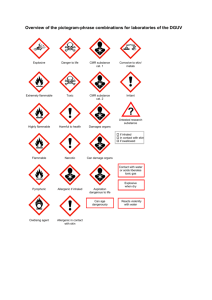
Material Safety Data Sheet N-Butane, (No Odourant) Date Issued: January 25th, 2010 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION Product Name: Material Use: Manufacturer: Emergency Tel: Fax Number: N-Butane Commonly used as a gasoline blending component and liquefied gas fuel; raw material for making maleic anhydride, ethylene, acetic acid, synthetic rubber and high octane liquid fuels; as a propellant in aerosols; as a refrigerant; and as a food additive. Spectra Energy Transmission Address: Bag Service 6180 1-800-663-9931 Mile 53 Alaska Highway 1-250-262-3422 WHMIS Class: UN/PIN Number: TDG: Class: Shipping Name: Chemical Identity: Fort St. John, BC V1J 4H7 Class A- Compressed Gas Class B1 – Flammable Gas 1011/1075 2.1 Butane Saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon / alkane / paraffin / n-alkane / butane isomer C4H10 (Structural Formula: CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3) Chemical Formula: 58.122 g/mol Molecular Weight: 106-97-8 CAS Number: Trade Names/Synonyms: Butyl hydride, Diethyl, Methylethylmethane, Butane (non-specific name), Liquefied butane Poison Control Centre British Columbia Poison Control Centre 1 (800) 567-8911 Numbers: Consult local telephone directory for emergency numbers 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION Appearance: Odour: Flammability: TLV (ACGIH): Potential Health Effects: Potential Environmental Effects: Routes of Exposure: Acute Inhalation: Colourless gas/liquid Typically odourless. At high concentrations, n-butane has a characteristic natural gas or petroleum-like odour. Extremely flammable gas or liquid at temperatures below 11 oC. Can form explosive mixtures in air at room temperature. 1,000ppm Refer to Section 11 Refer to Section 12 At low concentrations n-butane is essentially nontoxic. At high concentrations, it can cause depression of the central nervous system (CNS) with symptoms such as headache, nausea, dizziness, drowsiness and confusion. It is expected to cause unconsciousness (narcosis) due to CNS depression at approximately 17,000 ppm (1.7%). (Note that n-butane is extremely flammable). No symptoms except drowsiness were experienced by 3-6 volunteers during a 10-minute exposure to 10,000 ppm (1%). n-Butane gas concentrations can become so high that oxygen is displaced, especially in confined spaces. Life-threatening asphyxiation (suffocation) may result. n-Butane displaces oxygen to 18% in air when present at 14% (14,0000 ppm). Eye Contact: Skin Contact: Chronic Inhalation: Ingestion: Skin Absorption: n-Butane and some other closely related aliphatic hydrocarbons (propane and isobutane) are weak cardiac sensitizers in humans following inhalation exposures to high concentrations. Cardiac sensitizers may cause the sudden onset of an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) and, in some cases, sudden death. The asphyxiant effects of n-butane may enhance cardiac sensitization. Exposure to rapidly expanding gas or vaporizing liquid may cause frostbite (cold burns) and permanent eye damage. Exposure to rapidly expanding gas or vaporizing liquid may cause frostbite (cold burns). None available Material cannot usually be swallowed due to its primary physical state as a gas. None expected 3. COMPOSITION / INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS Component Concentration N-Butane Propane 95 – 100% 0 – 3% CAS No. 75-28-5 74-98-6 Exposure Limit (ACGIH TLV) 1,000 ppm 1,000 ppm LD50/LC50 (Species and route) LC50 (rat) – 680,000 mg/m3/ 2hr Not Applicable 4. FIRST AID MEASURES Inhalation: Eye Contact: This product is flammable. Take proper precautions to ensure your own safety before attempting rescue. Remove victim to fresh air. Commence CPR if breathing has stopped and summon medical attention immediately. Oxygen may be beneficial if administered by a person trained in its use. Liquid: Quickly remove victim from source of contamination. Immediately and briefly flush with lukewarm, gently flowing water until the chemical is removed. Do not attempt to re-warm. Cover both eyes Skin Contact: Ingestion: with a sterile dressing. DO NOT allow the victim to drink alcohol or smoke. Quickly transport victim to an emergency care facility. Gas: No effects anticipated Liquid: Quickly remove victim from source of contamination. Immediately and briefly, flush with lukewarm, gently flowing water until the chemical is removed. Do not attempt to re-warm the affected area on site. DO NOT rub or apply dry heat. Gently remove clothing or jewellery that may restrict circulation. Loosely cover the affected area with a sterile dressing. DO NOT allow victim to drink alcohol or smoke. Quickly transport victim to an emergency care facility. Gas: No effects anticipated Not applicable route of exposure for gases. 5. FIRE FIGHTING MEASURES Flashpoint: Lower Flammable (Explosive) Limit: Upper Flammable (Explosive) Limit: Auto-ignition Temperature: Flammability Classification: Combustion Products: Sensitivity to Mechanical Impact: Sensitivity to Static Charge: Extinguishing Media: Special Procedures: -60 - -83oC 1.6% 8.4% 287oC Extremely flammable gas or material. Can form explosive mixtures in air at room temperature. Oxides of carbon and other products of incomplete combustion. Stable material Not applicable. Can be readily ignited by a spark resulting from nearby mechanical impact. Can be ignited readily by an electrostatic charge of sufficient energy. Dry chemical powder and high-expansion foam. This product presents an extreme fire hazard. Liquid very quickly evaporates, even at low temperatures, and forms vapour, which can catch fire and burn with explosive force. Invisible vapour spreads easily and can be set on fire by many sources such as pilot lights, welding equipment, and electrical motors and switches. Heat from a fire can cause a rapid build-up of pressure inside cylinders, which may cause explosive rupture. Use water spray to cool exposed cylinders or tanks. If a leak or spill has not ignited, use water spray to disperse the vapours. Extinguish small residual fires with dry chemical powder or water spray. Try to cover liquid spills with foam. Evacuate area and fight fire from a safe distance or protected location. Use full protective equipment and SCBA. Use gas detectors in confined spaces. 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES Accidental Release Measures: Waste Disposal Method: Eliminate all sources of ignition in vicinity of released gas. Stop the source of the leak or release if possible to do so safely. Keep the public away. Notify the appropriate authorities immediately. Warn occupants of downwind areas. Disperse vapours with hose streams using fog nozzles. Monitor low areas, as butane is heavier than air and can settle into low areas. Prevent vapour and /or liquid from entering into sewers, basements or confined spaces. Dispose to an approved hazardous waste site. Where appropriate, incineration or vent to a burning flare may be an option in emergency situations. Check with applicable jurisdictions for specific regulatory and disposal requirements. 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE Handling: Follow handling regulations for flammable materials. Use ppe as directed in Section 8. Keep away from sources of heat and ignition, flammable materials, and oxidizers. Do not weld, cut, or heat. Use only with adequate ventilation and avoid breathing vapours. Ground and bond all lines and equipment and use intrinsically safe electrical equipment. To be handled by appropriately trained personnel only. Follow approved operating procedures. Storage Follow storage regulations, including NFPA for flammable materials. Store in a fire-proof building that is cool, dry, well ventilated, clearly identified, well illuminated, clear of obstruction and accessible only to trained and authorized personnel. Use a non-sparking ventilation system, explosion=proof equipment, and intrinsically safe electrical equipment. Inspect all incoming containers to ensure they are in good condition. sure no sources of ignition present in storage areas Store material out of direct sunlight and away from flammable and incompatible materials. Consider leak detection and alarm equipment for storage area. Work/Hygiene: Have emergency eyewash/shower facilities as appropriate in the vicinity of any potential splash areas. Practice good hygiene practices including washing hands prior to eating, drinking, using the toilet, etc. Do not eat, drink, or smoke in areas of use and/or storage. Promptly remove contaminated clothing and launder prior to reuse. Use care when laundering to prevent formation of flammable/harmful vapours. 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS / PERSONAL PROTECTION General Considerations: Ventilation: Respiratory Protection: Skin Protection: Eye/Face Protection: Exposure to this material can be controlled in many ways. The measures appropriate for a particular worksite depend on how this material is used and on the extent of exposure. General ventilation. Use explosion-proof mechanical ventilation. Local exhaust ventilation if necessary to keep vapours below allowable limits. Full face breathing apparatus during transfer to rail or tank car and sampling. Use self-contained or supplied air breathing apparatus for levels exceeding TLV. Follow NIOSH criteria for working (and entry) into confined space (tank entry). Wear appropriate personal protective clothing to prevent the skin from becoming frozen from contact with the liquid or from contact with vessels containing the liquid. Wear appropriate eye protection to prevent eye contact with the liquid that could result in burns or tissue damage from frostbite. 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Physical State: Odour: Appearance: Vapour density (Air =1): Boiling Point (oC): Freezing Point: Evaporation Rate: Solubility in Water: Molecular Weight Specific Gravity (Water=1): Specific Gravity (Air=1): Odour Threshold: Vapour Pressure: pH: Coefficient Water/Oil Distribution: Density (g/ml): Gas/liquid Typically odourless. At high concentrations, n-butane has a characteristic natural gas or petroleum-like odour. Colourless 2 0.5 oC Not Applicable Not applicable for gas. Liquefied n-butane will evaporate rapidly at room temperature. Practically insoluble (49 mg/L) at 25 oC 58.122 g/mol 0.6 0.6 50,000 ppm 214.0 kPa at 21.1 oC) Not applicable Log P(oct) = 2.89 Not applicable 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY Hazardous Decomposition Products: Stability: Incompatible With: None This material is stable. NOTE: Chemical reactions that could result in a hazardous situation (e.g. generation of flammable or toxic chemicals, fire or detonation) are listed here. Many of these reactions can be done safely if specific control measures (e.g. cooling of the reaction) are in place. Although not intended to be complete, an overview of important reactions involving common chemicals is provided to assist in the development of safe work practices. The risk of a hazardous incident occurring due to accidental mixing of n-butane with other substances is low because n-butane only reacts with a very small number of chemical classes that are commonly used in the workplace. If an accidental mixing does occur, these few reactions may be severe. STRONG OXIDIZING AGENTS (e.g. peroxides, perchlorates) - Increases the risk of fire and explosion. Reaction may be delayed.(36) Conditions to Avoid: Corrosivity to Metals: Corrosivity to Non-Metals: HALOGEN COMPOUNDS (e.g. chlorine, and bromine) Risk of fire and explosion. Fluorine gas reacts explosively.(37) ) Mixtures with around 20% or more of chlorine are explosive. However, if any mixture of nbutane and chlorine gas is exposed to direct sunlight there is almost always an explosion.(38) The presence of some metallic salts or oxides (e.g. ferric chloride, copper oxide) or metals (e.g. mercury, zinc) increases the reactivity with the halogen compounds.(36,38,39) Reaction with iodine is not vigorous. Static charge, heat, sparks, open flames and other ignition sources Pure isobutane gas or liquefied gas is not corrosive to aluminum or carbon steel. Pure n-butane gas is corrosive to polypropylene, highdensity polyethylene (HDPE), polystyrene, and polyurethane; and is slightly corrosive to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). n-Butane gas is not corrosive to fluorinated plastics, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), most polyamides, ultra high molecular weight polyethylene, and polyacetals. 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION LD50: LC50: Acute Effects: Not applicable LC50 (rat) – 680,000 mg/m3/ 2hr At low concentrations n-butane is essentially non-toxic. At high concentrations, it can cause depression of the central nervous system (CNS) with symptoms such as headache, nausea, dizziness, drowsiness and confusion. It is expected to cause unconsciousness (narcosis) due to CNS depression at approximately 17,000 ppm (1.7%). (Note that n-butane is extremely flammable). No symptoms except drowsiness were experienced by 3-6 volunteers during a 10-minute exposure to 10,000 ppm (1%). n-Butane gas concentrations can become so high that oxygen is displaced, especially in confined spaces. Life-threatening asphyxiation (suffocation) may result. n-Butane displaces oxygen to 18% in air when present at 14% (14,0000 ppm). n-Butane and some other closely related aliphatic hydrocarbons (propane and isobutane) are weak cardiac sensitizers in humans following inhalation exposures to high concentrations. Cardiac sensitizers may cause the sudden onset of an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) and, in some cases, sudden death. The asphyxiant effects of n-butane may enhance cardiac sensitization. Chronic Effects: Carcinogenicity: Reproductive Effects: Teratogenicity: Mutagenicity: Irritant: Sensitizer: Synergistic Effects: Exposure to rapidly expanding gas or vaporizing liquid may cause frostbite (cold burns) and permanent eye damage. None Not considered carcinogenic by IARC, NTP, ACGIH, or ASHA Not available Not available Not available Not available Not available Not available 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION Not available Ecotoxicity: Not available Persistence/Degradeability: Bioaccumulation/Accumulation: Not available Note: Due to high volatility, it is expected to rapidly disperse in the atmosphere and undergo photochemical degradation and as such, is not expected to cause ground or water pollution if released into the environment. 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS Disposal: Allow to dissipate to the atmosphere (if permitted by applicable regulatory authorities). Dispose in a safe location, possibly by flaring. If material cannot be flared, take care to ensure gas has dissipated to concentrations below its flammable limits. 14. TRANSPORTATION INFORMATION UN/PIN Number: TDG: Class: Shipping Name: 1011/1075 2.1 Butane Special Shipping Information: Handle as extremely flammable gas. Avoid static accumulation during transportation. Workers should take special precautions to minimize risk of inhalation. 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION UN/PIN Number: DSL (Canada): WHMIS Class: TDG: 1011/1075 Yes (CAS Number: 106-97-8) Class A- Compressed Gas Class B1 – Flammable Gas 2.1 Class: Butane Shipping Name: NFPA Hazard Ratings: 1 – Slightly Hazardous Health: Flammability: 4 - Very flammable gas 0 - Normally stable Reactivity: “This product has been classified in accordance with the hazard criteria of the CPR and the MSDS contains all of the information required by the CPR” 16. OTHER INFORMATION MSDS Preparation: Date Issued: Information Sources: Glossary: Prepared by: EHS Services, Spectra Energy Transmission Phone 250-262-3422 Number: Fax Number: 250-262-3638 January 25th, 2010 Canadian Centre for Occupation Health and Safety Cheminfo, industry publications, and material analysis. NIOSH – National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health WHMIS – Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System TDG – Transportation of Dangerous Goods NFPA – National Fire Protection Association IDLH – Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health SCBA - Self Contained Breathing Apparatus SABA - Supplied Air Breathing Apparatus TLV – Threshold Limit Value (herein refers to 8-hour unless otherwise stated) STEL – Short Term Exposure Limit (herein refers to 15 minute unless otherwise stated) Disclaimer: The information presented in this Material Safety Data Sheet is based on tests, research and reports from the above mentioned sources, which are believed to be accurate and reliable. The data and information are presented without warranty, guarantee or liability on the part of the preparer in good faith.