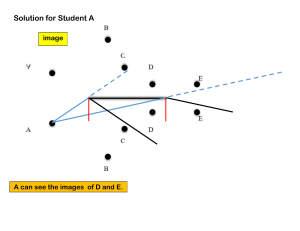
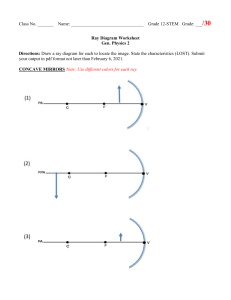
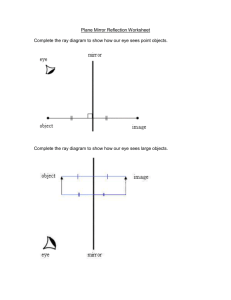
K-12 LEARNING PLAN Subject/Grade level: Science 10 Period Covered: First Quarter Unit Topic: Earth Science Chapter Topic: Plate Tectonics Content Standard: The learners demonstrate an understanding of the relationship among the locations of volcanoes, earthquake epicenter, and mountain ranges. Performance Standard: The learners should be able to demonstrate ways to ensure disaster preparedness during earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions and suggest ways by which he/she can contribute to government efforts in reducing damage due to earthquakes, tsunamis and volcanic eruptions. Learning Competencies: 1. Identify and relate the distribution of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and major belts to Plate Tectonics Theories. 2. Explain the continental drift theory. 3. Describe the different types of plate boundaries. 4. Suggest ways by which he/she can contribute to governments efforts in reducing damage due to earthquake, tsunamis, and volcanic eruption. 5. Explain the different processes that occur along the plate boundaries 6. Explain the possible causes of plate movement 7. Demonstrate ways to ensure disaster preparedness during earthquakes, tsunamis and volcanic eruptions. Learning Targets: 1. I can discuss and relate the distribution of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenter, and major belts to Plate Tectonics Theory. 2. I can explain the Continental Drift Theory. 3. I can illustrate the types of plate boundaries 4. I can explain the different processes that occur along plate boundaries and possible cause of plate movement. 5. I can guide my students in demonstrating ways to ensure disaster preparedness during earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions. Lesson/Topics: Introduction to Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Theory Modification of the Continental Drift Theory Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Explain the early ideas about continental movement and the evidences. Define the continental drift theory Identify the evidences in continental drift theory. Explain why the theory was rejected Explain what Arthur Holmes discovered. 6. Identify and explain what SONAR Echo Sounding are. 7. Enumerate the ocean Topography Explore/Introduction: The students will watch a video clip from the movie Ice Age. After watching, the students will be asked the following questions: a. What have you observed in the video? b. Can you describe what happened when the Earth’s core moved? The teacher will explain that the movie is fictional but there is a theory about the movement of the plates. The teacher will introduce the lesson, Introduction to plate tectonics and Continental Drift Theory. Firm up/Interaction: After the motivating activity, the teacher will discuss the early ideas on continental movement which is proposed by the following scientist with evidences: a. Abraham Ortelius b. Eduard Suess c. Roberto Mantovani d. Alexander du Toit The teacher will explain the theory of Alfred Wegener the Continental Drift Theory. The teacher will also discuss the evidences of Wegener and emphasize that it was rejected because it lacks the driving mechanism on how the continents moved. The students will have a quiz. Deepen/Interaction The Teacher will discuss that as time passed by many scientists studied the movement of plate which led to the modification of the Continental Drift Theory. The teacher will emphasize that Arthur Holmes was the one who explained that the continents are moving because of the current happening inside the Earth. There are also other discoveries such as SONAR and echo sounding which enables scientist to map the ocean floor and study more about the movement of the continents. The Teacher will discuss the topography of the ocean floor. The students will have an activity where they need to label the ocean floor and research research three recent continental movement. Transfer/Integration: The students will have an activity where they will create a model of the convection current using a plastic container, mugs, hot water, cold water, and the food coloring to show how the convection current works. Lesson/Topics Magnetic Anomaly Detection New Understanding of the Ocean floor Crustal Plates Objectives: 1. Describe the magnetic map of the Earth. 2. Explain Earth’s magnetic field reversal. 3. Content Standard: The learners demonstrate an understanding of the different regions of electromagnetic spectrum, the images formed by the different types of mirrors and lenses, and the relationship between electricity and magnetism in electric motors and generators. Performance Standard: The learners should be able to create a periscope or kaleidoscope using plane mirrors and cardboards. Learning Competencies: 1. Identify what mirrors and lenses are. 2. Predict the qualitative characteristics (orientation, type, and magnification) of images formed by plane and curved mirrors and lenses. 3. Solve problems on mirrors and thin lenses. 4. Identify ways in which the properties of mirrors and lenses determine their use in optical instruments (e.g., cameras and binoculars). 5. The learners should be able to create a periscope or kaleidoscope using plane mirrors and cardboards. Learning Targets: 1. I can discuss what mirrors and lenses are. 2. I can explain how to predict the qualitative characteristics (orientation, type, and magnification) of images formed by plane and curved mirrors and lenses. 3. I can show how to solve problems on mirrors and thin lenses. 4. I can discuss ways n which the properties of mirrors and lenses determine their use in optical instruments (e.g., cameras and binoculars). 5. I can guide my students in creating periscope and kaleidoscope using plane mirrors and cardboards. WEEK 3 Lesson/Topics: Mirrors and Lenses Objectives: 1. Identify mirrors and lenses. 2. Identify the terms and notation in geometric optics. 3. Describe the characteristics of images formed by mirrors and lenses. Explore/Intoduction: The students will watch a video which shows the burining of paper using a magnifying glass. The teacher will ask the following questions: a. What have you observed? b. Ho does the paper burn? The teacher will explain that the paper burn because the sunlight that go through the magnifying glass is concentrated in the center of the glass because to the lens used. The teacher will introduce the lesson, Mirrors and Lenses. Firm up/Interaction: The teacher will discuss what mirror and lenses are emphasizing the differences of the two by using images. Then eacher will also discuss the terms and notation in geometric optics which are the following: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Principal Axis Object Center of Curvature Focal Point Focal Length Image Radius of Curvature Deepen/Interaction: The teacher will then discuss the characteristics of image formed by mirrors and lenses which are the following: a. b. c. Orientation Type Real image Virtual image Magnification The teacher will also discuss the concept of Ray Diagramming or Ray Tracing in the Geometric Optics which is the systematic process of tracing or diagramming rays in forming an image from the object to the lens. The use of ruler and protractor is very important to determine accurately the image formed. The students will have a shotrt quiz. Transfer/Integration: The students will have an activity where the students will create a table comparing the types of mirrors and lenses. WEEK 3 Lesson/Topics: Ray Tracing of Plane Mirrors Analytical Method for Plane Mirrors Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Identify what plane mirror is. Illustrate ray tracing for plane mirrors. Create a ray diagram for plane mirrors. Explain the image formed using analytical method in plane mirrors. Differentiate the ray diagram and analytical method. Predict the image formed by plane mirrors using the law of reflection and the law of refraction. Explore/Introduction: The teacher will show an image of ray diagram and will ask the students to identify the notations used in geometric optics. The teacher will then introduce the lesson, Ray tracing and Analytical method for plane mirrors. Firm up/Interaction: After the motivating activity, the teacher will discuss what plane mirros is and how to create a ray diagram for plane mirrors and how to predict the characteristics of the image formed. Deepen/Interaction: The teacher will then discuss how to use the analytical method in geometric optics where the students will have to solve or compute to predict the characteristics of plane mirrors using the law of reflection and the law of refraction. Transfer/Integration: The students will have an activity where they need to create a ray diagram and use the analytical method to mpredict the characteristics of the image formed in a plane mirror using the law of reflection and the law of refraction. WEEK 4 Lesson/Topics: Ray Tracing of Spherical Mirrors Analytical Method for Spherical Mirrors Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify what spherical mirror is. Differentiate the two kinds of spherical mirror. Illustrate how to create a ray diagram for spherical mirror. Create a ray diagram for spherical mirrors. Identify the formulas needed in analytical method for spherical methods. 6. Explain how to predict the characteristics of a spherical mirror using analytical method. 7. Solve problems about spherical mirrors. Explore/Introduction: The teacher will show an image of ray diagram and will ask the students to identify the notations used in geometric optics. The teacher will then introduce the lesson, Ray tracing and Analytical method for spherical mirrors. Firm up/Interaction: After the motivating activity, the teacher will discuss what spherical mirror is and its two type, the concave mirror and the convex mirror. The teacher will also differentiate the two by using an illustration. The teacher will then discuss how to create a ray diagram for spherical mirrors and how to predict the characteristics of the image formed. The students will have a quiz. Deepen/Interaction: The teacher will then discuss how to use the analytical method in geometric optics where the students will have to solve or compute to predict the characteristics of spherical mirrors. Transfer/Integration: The students will have an activity where they need to create a ray diagram and use the analytical method to predict the characteristics of the image formed in a spherical mirrors. WEEK 5 Lesson/Topics: Ray Tracing of Thin Lens Analytical Method for Thin Lens Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Identify what thin lens is. Illustrate ray tracing for thin lenses. Create a ray diagram for an image formed by thin lenses. Identify the formulas needed in analytical method for Thin lenses. Explain how to predict the characteristics of a thin lenses using analytical method. Solve problems about thin lenses. Explore/Introduction: The teacher will show an image of ray diagram and will ask the students to identify the notations used in geometric optics. The teacher will then introduce the lesson, Ray tracing and Analytical method for thin lenses. Firm up/Interaction: After the motivating activity, the teacher will discuss what a thin lens is and its type which are the following: a. b. c. d. e. f. Biconvex Plano-convex Convex-meniscus Biconcave Plano-concave Concave-meniscus The teacher will also differentiate the types by using illustrations. The teacher will then discuss how to create a ray diagram for thin lenses and how to predict the characteristics of the image formed. Deepen/Interaction: The teacher will then discuss how to use the analytical method in geometric optics where the students will have to solve or compute to predict the characteristics of thin lenses. Transfer/Integration: The students will have an activity where they need to create a ray diagram and use the analytical method to predict the characteristics of the image formed in a thin lenses. WEEK 6 Lesson/Topics: Optical instruments Obectives: 1. Identify what optical instruments are. 2. Enumerate some optical instruments. 3. Explain how the properties and characteristics of mirrors and lenses are used in optical instruments. Explore/Introduction: The teacher will show pictures of optical instruments and ask the students the following questions: a. What have you observed? b. What do these instruments have in common? The teacher will explain that the instruments the is shown are common optical instruments which is the lesson for the week. Firm up/Interaction: After the motivating activity, the teacher will discuss optical instrument which is a device that processes light waves (or photons), either to enhance an image for viewing or to analyze and determine their characteristic properties. The students will have a recitation. Deepen/Interaction: The teacher will then cite some optical instrum etns that are commonly used and describe it with its functions. Here are the optical instruments: a. b. c. d. Magnifying glass Compound microscope Telescope Camera The students will have a short quiz. Transfer/Integration: The students will have an activity where they will draw an optical instrument, describe it and cite its functions. Chapter Topic: Electricity and Magnetism Content Standard: The learners demonstrate an understanding of the different regions of electromagnetic spectrum, the images formed by the different types of mirrors and lenses, and the relationship between electricity and magnetism in electric motors and generators. Performance Standard: The learners should be able to create a periscope or kaleidoscope using plane mirrors and cardboards. Learning Competencies: 1. Differentiate electricity and magnetism. 2. Relate electricity and magnetism. 3. Explain the operation of a simple electric motor and generator. Learning Targets: 1. I can differentiate electricity and magnetism. 2. I can relate electricity and magnetism. 3. I can explain the opertation of a simple electric motor and generator. WEEK 7 Lesson/Topics: Electricity and Magnetism Objectives: 1. Identify what electricity and magnetism are. 2. Explain how electric motors and generators work. 3. Relate electricity and magnetism in electric motors and generators. Explore/Introduction: The students will watch a video which is a compilation of experimetns using magnets. The students will be asked the following questions: a. What have you observed in the video that you have watched? b. What is the main material used in the experiments? The teacher will explain that the video they have watched are all experimetns including magnet, how it would react to different materials or how materials will react to magnet. The teacher will introduce the lesson, electricity and magnetism. Firm up/Interaction: The teacher will ask the students “What is electricity and Magnetism?”. The teacher will discuss electricity and magnetism and will emphasize its differences. The teacher will also discuss that these two are interconnected in terms of producing a magnetic field and electricity. The students will have a recitation. Deepen/Interaction: The teacher will discuss how electric motors and generator works. The teacher will emphasize that motors and generators are electromagnetic devices. They have current-carrying loops that rotate in magnetic fields. This rapidly changing magnetic field produces electromotive forces, called emfs or voltages. Electric motors and generators are the opposite of each other. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, while electric generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The students will have a recitation. WEEK 8 Transfer/Integration: The student will write a 200-word essay to relate electricity and magnetism in electric motors and generators. WEEK 9 Lesson/Topics: Long Quiz Objectives: 1. Answer 100% of the questions in the test. 2. Follow properly the instructions. 3. Show honesty, integrity, and hard work. Explore/Introduction The teacher will motivate the students to do their best and be honest. Firm up/Interaction: The teacher will discuss the instructions and parts of the long quiz. Deepen/Interaction: The teacher will give the students the opportunity to ask before answering. Transfer/Integration: The teacher will start the long quiz. Prepared by: Aaron P. Timario Science 10 Teacher