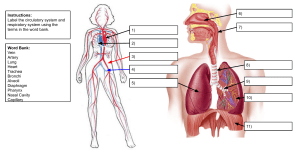
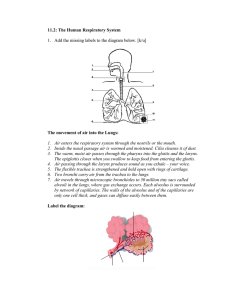
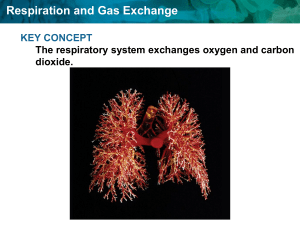
The Human Gas Exchange System Objectives: 1.Recall the parts and functions of the respiratory system 2. Describe the gas exchange process in the respiratory system Our respiratory system is responsible for bringing air into the body, from which we can get oxygen. oxygen Gas exchange Gas exchange – YouTube It also moves air back out of the body—the exhaled air contains more of our waste gas, carbon dioxide. carbon dioxide But how do we get oxygen from the air to our body cells and get carbon dioxide out? air Let’s follow the journey of a breath of air, starting with the moment you inhale. nasal cavity oral cavity pharynx larynx Air enters the body through the nose and mouth, where it is filtered and warmed. trachea primary bronchi Air then passes through the trachea and the two primary bronchi. These structures are held open by rings of cartilage. bronchiole alveoli Each bronchus then branches many times into bronchioles, terminating at tiny air-filled sacs called alveoli. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged at the alveoli. The process involved in the exchange of these gases is called diffusion. air moving in and out of the alveolus How does diffusion occur? Carbon dioxide—a waste gas—moves from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled. capillary red blood cell carbon dioxide air moving in and out of the alveolus Oxygen then moves from inside the alveoli across the walls and into the blood. This oxygen is used for respiration by the body’s cells. capillary red blood cell oxygen They are covered in a network of tiny capillaries, ensuring enough blood supply. Their surfaces are moist, allowing the gases to dissolve. How are the alveoli adapted for gas exchange? Their walls are only one cell thick, providing a short diffusion distance. Their lobed-shape gives them a huge surface area. If given a chance, how would you improve the design of alveoli? To Recap The human respiratory system moves fresh air into the body while removing waste gases. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged at the alveoli. The alveoli are well-adapted to carry out their job by having a thin, moist and large surface area.