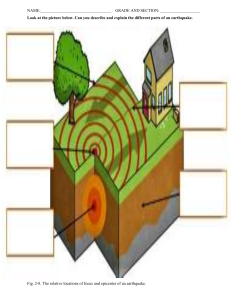
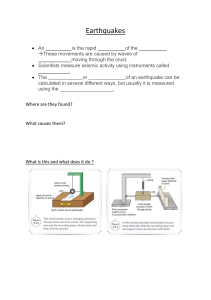
School: Teacher: . Teaching Dates and Time: GRADES 1 to 12 DAILY LESSON LOG MELC BASED MONDAY TUESDAY Grade Level: 8 Learning Area: SCIENCE Quarter: Q2 WEEK 1 WEDNESDAY THURSDAY Pamantayang Pangnilalaman (Content Standards) Pamantayan sa Pagganap (Perfomance Standards) the relationship between faults and earthquakes Pamantayan sa Pagkatuto (Learning Competencies) Using models or illustrations, explain how movements along faults generate earthquakesS8ES -IIa - 14 1. participate in decision making on where to build structures based on knowledge of the location of active faults in the community 2. make an emergency plan and prepare an emergency kit for use at home and in school Layunin Lesson Objective Explain how movements along faults generate earthquakes. Paksang Aralin (Subject Matter) Kagamitang Panturo (Learning Resources) Pamamaraan (Procedure) a. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting the New Lesson FRIDAY Describe the appearance of a fault Explain the effect of bending of rocks along faults and Relate fault movement and earthquake Describe what a fault is and how these faults related to earthquakes. Explain how a fault forms Explain how faults generate earthquakes; and EARTHQUAKES AND FAULTS (Introduction) What is a fault? Explain why not all movement along faults produces earthquakes. HOW DO FAULTS PRODUCE QUAKES Relate the pass Earthquakes happened in the country. Why do earthquake occur? What is the relationship between earthquakes and faults? How do Faults Produce quakes? ? Why not all movement along faults produce earthquake? Recall the appearance of a fault b. Establishing purpose for the lesson c. Presenting example/instances of the new lesson Describe the effect of Earthquake in lives of people. The epicenter of the quake, which struck at 4:26 p.m., was north of Manila in the . Nueva Ecija province. Reports indicate that the shaking went on for nearly a full minute. Collapsing buildings were the main cause of damage and death. Getting out of a multi-story building was a good safety precaution that afternoon, although many people were injured and a few even died in stampedes of others doing the same thing. At Christian College, a six-story building completely collapsed, trapping approximately 250 students and teachers inside. Heroic rescue efforts saved many, but some victims who did not die in the collapse were found dead later from dehydration because they were not pulled out in time. Demonstrate activity in LM pp. 120-122 . Show videos clips about fault. Demonstrate activity in LM pp. 122-124 on Stick ‘n’ shake Ask the class about Michael Jackson's famous moonwalk. Theteacher can demonstrate it or let a student do the moonwalk in front of the class. Ask the possible relationship of the movement of the shoes and the floor. Answer the questions in LM pp. 122. (Explain each answer as what have been seen in the activity -. d. Discussing new concepts e. Continuation of the discussion of new concepts f. 1. Where is the epicenter of the earthquake? 2. How many individuals are affecred? 3. Discuss how devastating a 7.7 intensity earthquake is. Show video clips from youtube showing and discuss the concepts about earthquake. Complete the paragraph by filling up the blanks with the correct words. Show videos abput How do Faults Produce quakes? A ___1_____ is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of___2___. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. This ____3______may occur rapidly, in the form of a ______4_____- or may occur slowly, in the form of creep. Faults may range in length from a few millimeters to thousands of kilometers. Most faults produce repeated ______5____over geologic time. (1.Fault; 2. rock;3. movement; 4. earthquake; 5. displacement) 1. What happened to the boxes as the rubber band is being pulled? 2. What happens to the house in relation to the position of the fault? Demonstarter activity in LM pp. 116-118. A Faulty set-up Developing Mastery 1. What happened to the pile of sand when you moved the sheet slowly into the opposte direction? 2. As you move the sheets, What is formed in the sandz? 1. What happens when the bending becomes too much? 2. What is the effect of bending of rocks along fault? Applying your learning on the lesson presented, explain why not all movement along faults produced earthquakes. The ground in the area of fault tends to remain not moving because of frictional force between the two opposing plates (boxes). As stronger forces (rubber band) shakes up the fault, the friction (tape) can no longer hold up the plates (box) thus resulting to a slip in the plates creating a jerk called earthquake . g. Finding practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living Role palying. Group the student into 5-7 groups to make a video clips about an earthqauke h. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. This movement may occur rapidly, in the form of an earthquake - or may occur slowly, in the form of creep. Faults may range in length from a few millimeters to thousands of kilometers.. tremor is also used for nonearthquake seismic rumbling. i. Evaluating learning What is an "earthquake"? What causes earthquakes? How do earthquakes cause damage? Does the earth open up during an earthquake? Where do earthquakes occur? What is the relationship between volcanoes and earthquakes? Will more shocks be felt after a strong earthquake? Can earthquakes be predicted? A fracture in the earth's crust is called a joint. It is called a _____ when there is displacement of rocks on either side of the fracture. a. fault b. earthquake c. focus d. epicenter The amount of energy that is released from an earthquake is its _____. a. intensity b. magnitude c. epicenter d. focus On earth's surface, directly above the location where an earthquake originates is called a(n): a. fault b. earthquake c. focus d. epicenter A magnitude 4 earthquake causes 10 times more ground motion than a magnitude 3 earthquake and ______ times more ground motion than a magnitude 2 earthquake. a. 2 b. 10 c. 20 d. 100 The _____ is the instrument that measures an earthquake's movement. a. seismograph b. Richter scale c. intensity scale d. Mercalli scale Make a Fault model Directions: Pair the given term according to your observation. Write your answer on the number below. Two box _____________ earthquake Tape _____________ shaking As you pull the rubber bond ____________ fault A crack on the ground ____________ frictional force A sudden jolt _________________ opposing plates Typically, the closer to an earthquake's epicenter, the more shaking is felt. a. True b. False How an earthquake is felt by others and the amount of damage an earthquake creates is determined by its: a. magnitude b. intensity c. duration of shaking d. time of day A zone where earthquakes occur but are generally less frequent and less severe is the: a. circum-Pacific belt b. Ring of Fire c. trans-Eurasian belt d. mid-ocean ridge belt An earthquake can only occur where plate boundaries exist. a. True b. False When one fault block moves up relative to a block on the opposite side, the exposed fault plane is called a(n): a. fault scarp b. fault c. fault trace d. uplifted block A ____ is the leading edge along a fault of the lower fault block. a. fault scarp b. fault c. fault trace d. uplifted block It is recommended that if you feel an earthquake and are near the coastline, you should make it to high ground without waiting for an official tsunami warning because: a. a tsunami is guaranteed to follow b. if you are near the epicenter, there is not enough time to receive an official warning c. tsunami warnings are never issued after an earthquake d. None of the above. It is never recommended people make it to high ground after an earthquake if they are near the coast j. Additional activities for application or remediation REMARKS REFLECTION a. Number of learners who earned 80% of the evaluation b. Number of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% c. Did the remedial lesson work? d. Number of learners who have caught up with the lesson e. Number of learners who continue to require remediation f. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? g. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers?