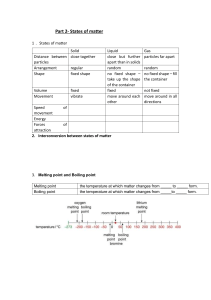
Matter Is anything which occupies space and has mass Is made of particles → (atom- molecule – ions ) Atom : are singular particles. Molecule : made of two or more atoms bonded together. Ions : is a positively or negatively charged particle. There are three states of matter Solid Liquid Gas There are three states of matter Points of compression Solid Liquid Gas Arrangement of particles Regular Closely packed Irregular Touching Irregular Far apart Movement Vibrate in fixed position Slide over each other Move freely and randomly Separation Touching Touching Far apart Shape Fixed shape Take the shape of the container Random-fill any container Volume Fixed Fixed Not fixed Attraction force between particles Very strong Moderate Weak Intermolecular space Very small Moderate Wide Density High Medium Low Ability to compressed Not compressible Not compressible Compressible How do substances change from one state to another? Kinetic particle theory 1- Matter is composed of particles which are in continuous motion 2- The motion of these particles depend on • Temperature → as the temperature increase, the particles movement increase. • Pressure → as pressure increase, the particles movement decrease. • The particle weight → lighter particles move faster 3- The physical properties of matter Melting process • Particles gain energy • Move faster • Over come attraction force • Particles occupy more space • Solid state change to liquid state Melting point : is temperature in which solid change to liquid sate Evaporation process • Particles gain energy • Move faster • Over come attraction force • Particles occupy more space • Liquid state change to gas state Boiling point is the temperature at which liquid change to gas Boiling Evaporation At fixed temperature ( boiling point ) At a range of temperature ( low boiling point ) Fast rate of reaction Occurs throughout the liquid Slow reaction Occurs on surface Bubbles appear No bubbles The rate of evaporation increase by increasing 1) The temperature ( by increasing temp, the evaporation increase) 2) The surface area ( by increasing the surface area, the evaporation increase) 3) The nature of liquid (volatile or Non- volatile) Condensation • Particles lose kinetic energy • Move slower • Inter molecular space decreases • Intermolecular force increase • Gas change to liquid • Condensation point (Is the temperature at which all the gas changes to liquid). The temperature stays the same until all gas changes to liquid. Freezing • Particles lose kinetic energy • Move slower • Inter molecular space decreases • Intermolecular force increase • Liquid change solid • Freezing point (Is the temperature at which all the liquid changes to solid). The temperature stays the same until all liquid changes to solid. Heating curve Heating curves show how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up. have horizontal flat parts where the state changes 1. MELTING POINT 2. FREEZING POINT Cooling curve The temperature goes down the longer the cooling continues. have horizontal flat parts where the state changes 1. Freezing point 2. Condensation point Sublimation process: The change from solid state to gas state directly without passing through liquid state.