Amniocentesis, Fetal Profile, Newborn Care Guide
advertisement

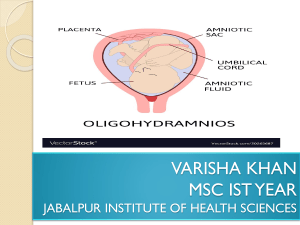
Amniocentesis | LAPATHA, SJ C. Diagnostic Tests AMNIOCENTESIS Aspiration of amniotic fluid at 14 – 16 weeks AOG - 15ml of fluid is withdrawn guided by UTZ (Ultrasounds) Review: - Amniotic Fluids such as Fetal structures, umbilical cord, amniotic pillar. - Amniotic Fluid is formed by amniotic villi that is being ingested by the child then it comes to produce urine that’s why it’s in cycle that the child might drink his own urine. - Polyhydramnios is when you have too much amniotic fluid that is more than 2000mL . Amniotic fluid is the fluid that surrounds your baby while they're in your body before birth. - Renal agenesis is the name given to a condition that is present at birth that is an absence of one or both kidneys. - Also, cause by Olygohydramnios is when you have too little amniotic fluid or less than 300 mL. - Complications: a. Miscarriage – an any form of Abortion or the mother by herself. Abortion is refers to the availability of pregnancy before the age viability, (GTPAL) so less than 26 weeks you are inevitable abortion b. Infection – when there is a complication of amniocentesis because there is an invasion of the skin activity into the amniotic sac c. Preterm Labor - caused by dehydration, urinary tract infection (UTI), chorioamnionitis (fetus and amniotic fluid are infected by bacteria). REMINDERS: - Advise woman to avoid DBE (deep breathing exercise) Because of the possible accidental puncture into the child that is too much moving. - Place woman supine with towel at the - right buttocks Review: Supine hypotensive syndrome – or inferior vena cava compression syndrome. Caused when the gravid uterus compresses the IVC in a supine position, leading to decreased venous return centrally. (if OB condition during MCN, always answer left side lying, except in quarterlocks that is Trendelenburg position ) FINDINGS: I. AFP – Alpha-fetoprotein - Developing’s fetus’s liver and yolk sac. - If there are opening of the child’s body, so the AFP will go out into the amniotic fluid. Then,if high, possible multiple pregnancy, Neural tube defects (a condition where the mother is deficient of folic acid) or MULTIFETAL; if low, DOWN SYNDROME. - Needed 400 mg of folic acid in pregnancy. - If less than 400mg FA, Neural Tube Defects. Kinds of NTDs: 1. absence of brain or Anencephaly, 2. smaller brain/head or Microcephaly, 3. Spina bifida 4 types: occulta non-fusion of the spinal vertebra Meningocele – least severe, vertebra do not close, opening the back, that allows the meninges, CSF to sac out through opening. Myelomeningocele – severe, vertebra don’t close completely, spinal cord is protective by meninges 4. Encephalocele an opening of the skull, so the brain will go out into the cranial defects. II. Chromosomal Analysis - Determine any chromosomal abbreviations - Defects: - If C7, 65 roses or Cystic Fibrosis - If C10, Hirschsprung’s Disease - If C21, Trisomy 21, Down Syndrome - If C22, Tetralogy of Fallon III. COLOR - Normal water color to slight yellow - Strong yellow – RH incompatibility (Mother is (-), fetus(+) – erythroblastosis fetalis) - Green – meconium staining - Black meconium – fetus is died IV. Lecithin Sphingomyelin Ratio 2:1 (the child is mature lungs), - if DM or diabetes, ratio is 3:1 V. Bilirubin Determination Amniocentesis | LAPATHA, SJ 2. BIOPYSICAL PROFILE Purpose: Determine is child is survivable while in the womb. Each component is 2 points , if perfect is 10 points COMPONENT DEFINITION Fetal movements 3 body or limb movements Fetal tone One episode of active extension and flexion of the limbs: opening and closing of hand Fetal breathing movement Episode of >= 30 seconds in 30 minutes. Hiccups are considered breathing anxiety Amniotic fluid volume Single 2 cm x 2cm pocket is considered adequate Non-stress test 2 accelerations > 15 beats per minute of at least 15 seconds duration. Review: anthropometric measurement of the baby Head Circumference = more than hydrocephalus, less than is microcephaly. Anencephaly – No cerebral defects Neural Tube defects – deficiency of folic acid. VI. I. V. PROFILE OF AN AVERAGE NEWBORN A. Head Circumference = 34 – 35 cm, Middle of the forehead B. Chest Circumference = 32 – 33 cm Nipple line and surrounds it D .Abdominal Circumference = 30 – 31 cm Above abdomen C. Length = 43 – 53 cm Oxyput to feet Weight = 2.5 – 3.5 kg is VITAL SIGNS TEMPERATURE 37.2 degrees celcius or 99 degrees Farenheit - Through Rectum Temp NURSE ROLE - In the first day of life – take temperature q4 hours. - Thereafter, the temperature is taken OD (once a day) unless, the temperature is elevated. II. PULSE - 120 – 140 bpm - Slightly irregular immature regulatory system at the medulla oblongata. III. RESPIRATION - 30 – 60 CPM (Cycle per minute) - PERIODIC RESPIRATIONS are normal (periods of apnea for less than 15 seconds – with NO CYANOSIS) - >15s id Pathologic apnea, <15 is Physiologic apnea. Amniocentesis | LAPATHA, SJ IV. BLOOD PRESSURE - Somewhat inaccurate – not routinely assessed Important! A depressed respiratory effort might be anticipated in a new born whose mother received large amounts of analgesia or a general anesthetic during labor or birth. VII. MATERNAL – INFANT BONDING 1. Uninterrupted Skin to Skin Contact for 90 minutes 2. Breastfeeding Checklist Anatomy Male – Female Mens 1 Mens 2 Growing Fetus 1 2 3 Appearance of Newborn 1 2 Immediate Newborn Care 1 Immediate Newborn Care 2 Done: Profile of a Newborn Extrauterine Tansition Growth and Development Hypertonc &Hypotonic Intrapartum Complication HMOLE Preterm Labor & Incompetent Cervix Danger signs of labor Stages of Labor !V. GTPAL V. Diagnosis of Pregnancy Fetal Circu & Milestone Fetal Movement & FHT PIH RH INCOM EDC & AOG Leopolds Hydrocephalus Cardiac 1 2 2 Gastro 1 2 Postpartum Bladder Postpartum Breast Postpartum Homan Muscolo Sickle Anemia Tetralogy of Fallot