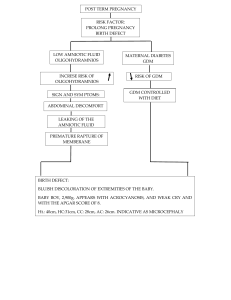
VARISHA KHAN MSC IST YEAR JABALPUR INSTITUTE OF HEALTH SCIENCES AMNIOTIC FLUID Amniotic fluid is the liquid that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy. Located in the amniotic sac, amniotic fluid protects the growing baby and provides nutrients to the developing fetus that help it mature, grow, and maintain a consistent body temperature . At the earliest stage of development, amniotic fluid consists mainly of water. At approximately 20 weeks, the baby’s urine becomes the primary substance. The volume of amniotic fluid increases as the pregnancy progresses and reaches its peak at about 34 weeks OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS Oligohydromnios is extremely rare condition where the liquor amnii is deficient in amount to the extent of less than 200ml at term. Oligohydramnios occurs when the volume of fluid in the amniotic sac is too low. ETIOLOGICAL FACTORS Oligohydramnios is typically caused by the following: Placental issues Fetal chromosomal anomalies Intrauterine infections Drugs- PG inhibitors, ACE inhibitors Obstruction of urinary tract of fetus IUGR Maternal problems SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Measurements of uterine size smaller than what is normal for gestational age Low maternal weight gain Sudden drop in fetal heart rate Little to no fetal movement, or decreasing fetal movement Low amniotic fluid on an ultrasound DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION History ◦ Inquire about symptoms of leaking fluid and feeling damp all the time (often described as new urinary incontinence). Examination ◦ Measure the symphysis fundal height. ◦ Perform a speculum examination (can a ‘pool’ of liquor be seen in the vagina?). Ultrasound ◦ Assess for liquor volume, structural abnormalities, renal agenesis and obstructive uropathy. COMPLICATIONS FETAL 1. ABORTION 2. DEFORMITY 3. FETAL PULMONARY HYPOPLASIA 4. CORD COMPRESSION 5. HIGH FETAL MORTALITY MATERNAL 1. PROLONG LABOUR 2. INCREASED OPERATIVE INFERENCES MANAGEMENT MANAGEMENT Oral intake of fluids Installation of a saline solution into the amniotic sac (amnioinfusion) during labor. Investigational therapies MANAGING OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS DURING THE FIRST TRIMESTER Reduced amniotic fluid during the first trimester is a rare finding, and information regarding the causes of this diagnosis are equally rare. Serial ultrasounds are helpful for following the natural history of the pregnancy MANAGING OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS DURING THE SECOND TRIMESTER Management and prognosis of oligohydramnios during the second trimester depend on the cause and severity of lowered amniotic fluid volume Medical professionals usually recommend serial ultrasounds to determine if the condition is stable MANAGING OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS DURING THE THIRD TRIMESTER Cases of oligohydramnios during the third trimester are often caused by maternal conditions, such as preeclampsia or maternal vascular diseases. These conditions are often related to preterm premature rupture of membranes. SUMMARIZATION Definition of oligohydramnioas. Etiology of oligohydramnioas. Risk factors of oligohydramnioas. Signs & symptoms of oligohydramnioas. Investigation for oligohydramnioas. Complications Management of oligohydramnioas.