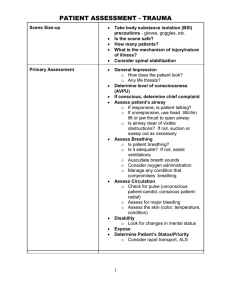
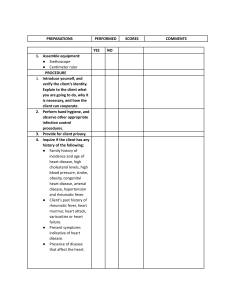
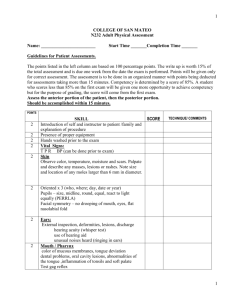
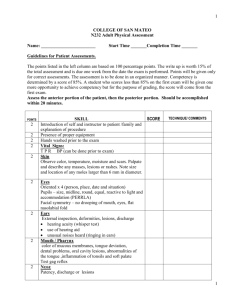
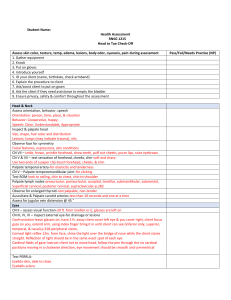
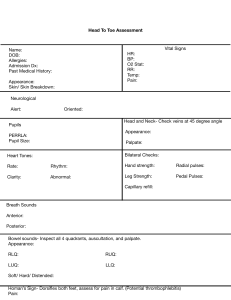
1. General Overview First, you obtain a general overview of the patient’s health state. These are the details to keep an eye on in this phase of the assessment. - - Collect their vital signs. (It’s encouraged to ask permission before touching a patient. Also, explaining what you are doing/what assessment you are performing will help the patient feel more relaxed.) Check heart rate Measure blood pressure Take body temperature Pulse oxymetry Respiratory rate Check pain levels Check hight and weight and calculate their BMI 2. Hair/ Skin/ Nails - Once you have a general overview, you can start from the top of the body and make your way down. The assessment is called head to toe for a reason. Some things to look out for are: - - Hair distribution(even/uneven) Hair infestations (lice, alopecia areata) Bumps, nits, lesions on the scalp Tenderness on scalp Tenderness, lumps on the skin Lesions, bruising, or rashes on skin Temperature, moisture, and skin texture (is the patient pale, clammy, dry, cold, hot, flushed?) Edema Consistency, color, and capillary refill of nails Pressure areas 3. Head - Shape is rounded, symmetrical - Upon palpation, no nodules, masses or depressions are identified - Face appears smooth and symmetrical with no nodules or masses present. 4. Eyes - Check external structures - Assess eye symmetry - Check conjunctive and sclera - Check for PERRLA - Perform visual acuity test - Check eyes for drainage - Check vision with Snellen Chart - Check six cardinal positions of the gaze head to toe assessment script 5. Nose - Palpate nose and check symmetry - Check septum and inside nostrils - Patency of nares (patient can breath through each nostril) - Check sense of smell - Palpate sinuses 6. Mouth and Throat - Check lips for color and moistness - Inspect teeth and gums - Examine tongue - Inspect the inside of mouth - Look at tonsils and uvula - Assess hypoglossal nerve by asking patient to move tongue from left to right - Check the patient’s ability to taste, to swallow, and their gag reflex 7. Ears - Inspect for drainage or abnormalities - Test hearing with whisper test - Look inside ear: inspect the tympanic membrane and asses ear discharge - Tuning fork tests (Weber’s Test, Rinne Test) 8. Neck - Check neck muscles to be equal in size - Palpate lymph nodes - Check head movements and whether they happen with discomfort - Observe neck range of motion. - Check trachea placement - Check shoulder shrug with resistance 9. Chest: Cardiovascular Assessment - - Listen to the heartbeat. Areas where to auscultate heart sounds: aortic, pulmonic, Erb’s point, Tricuspid, Mitral Palpate the carotid and auscultate apical pulse 10. Chest: Respiratory Assessment - Auscultate lung sounds front and back - Observe chest expansion - Ask abour efforts to breathe/coughing - Palpate thorax head to toe assessment documentation example 11. Abdomen - Inspect abdomen - Listen to bowel sounds in all four quadrants - Palpate all four quadrants of the abdomen to check for pain or tenderness - Ask about bowel or bladder problems 12. Extremities - Assess range of motion and strength in arms, legs, and ankles - Assess sharp and dull sensation on arms and legs - Inspect arms and legs for pain, deformity, edema, pressure areas, bruises - Palpate radial pulses, pedal pulses - Check capillary refill on fingernails/toenails - Assess gait - Assess handgrip strength and equality 13. Back area Inspect back and spine Inspect coccyx/buttocks