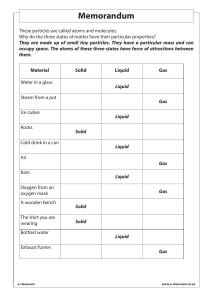
GRADE 7 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE MEMO WORKBOOK CONTENTS Sources of energy Introduction Where does energy come from? How is electricity actually produced? Renewable and non-renewable energy sources Non-renewable energy Renewable energy Hydropower Wind energy Biomass energy Geothermal energy Nuclear energy Solar energy The sun is the ultimate source of energy Advantages and disadvantage of renewable and non-renewable energy 2 2 2 3 4 4 4 4 5 6 6 6 7 8 8 Potential and kinetic energy Introduction Potential energy Elastic potential energy Gravitational potential energy Water reservoirs Chemical potential energy Energy is measured in joules Homework 13 Kinetic energy Potential and kinetic energy in systems Mechanical systems Thermal systems Electrical systems Biological systems Homework 14 The law of conservation of energy Energy cannot be created or destroyed Energy can be transferred 9 9 9 9 9 10 10 10 11 13 13 13 14 15 15 15 16 16 16 Heat transfer Introduction Heat as transfer of energy Homework 15 Conduction Homework 16 Experiment: Heat energy transfer in different materials Convection Let’s label the diagram: Radiation 17 17 17 18 20 21 22 23 23 24 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO MODULE 3: ENERGY AND CHANGE © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 1 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Sources of energy Introduction Why do we need energy? We need energy to light our homes, power our cars, cook our food and to be able to walk, think and write. Everything we do is connected to energy. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. We use energy to do WORK, for example when we lift something, or warm it up, or light something. As you can see, energy is an essential part of our daily lives. Where does energy come from? There are seven forms of energy. Forms of energy are types of energy. These are: • Electrical energy, e.g. from lightning or a light bulb • Light energy, e.g. from the sun • Heat energy, e.g. when we warm up food in the oven • Chemical energy, e.g. from batteries • Sound energy, e.g. the sound of a buzzing bee • Mechanical energy, e.g. when the fan turns • Nuclear energy from unstable atoms that split. Forms of energy can be converted from one form to another. There are many sources of energy. Sources of energy is where the energy comes from. Energy can come from millions of different places. We are only going to learn about the following sources of energy that produce electrical energy: • Fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) • Hydropower • Wind energy • Biomass energy • Geothermal energy • Nuclear energy • Solar energy In all these instances the aim is to make electricity. So we need to convert a form of energy into electrical energy. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 2 GRADE 7 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO TERM 3 How is electricity actually produced? Regardless of the source of energy, electricity is produced in the same way. Electricity is produced by turning turbines. The way a turbine looks will vary depending on the source of the energy. Here are some examples of turbines: Turbine in coal-fired power station Turbine for wind power Turbine for hydropower Turbine for nuclear power plant It all works on the same concept: Energy is required to turn the turbines to produce electricity. Most power plants today burn coal, which is used to heat water and produce steam. The steam is the energy that turns the turbine. In the case of wind energy, the wind provides the energy that turns a turbine. In the case of hydropower, flowing water provides the energy that turns a turbine. The spinning turbine causes large magnets to turn and release electrons, pushing them into electrical wires. This is known as electricity. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 3 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Renewable and non-renewable energy sources All energy sources can be categorised as either renewable or non-renewable. Non-renewable energy What is non-renewable energy? Energy that gets used up and cannot be replaced Fossil fuels are non-renewable. Fossil fuels include coal, oil and natural gas. Fossil fuels are formed from the remains of living things, including plants and animals. How are fossil fuels created? When plants and animals die, they are gradually buried by layers of rock. These buried remains are put under pressure and heat. Certain chemical reactions take place. Over time, they turn into fossil fuels, where chemical energy is stored. Plants and animals die and get buried all the time. So why do we consider fossil fuels a non-renewable energy source? Reserves are being depleted much faster than new ones are being made When we burn fossil fuels, chemical energy is transferred into heat energy and light energy. The light energy is not used, but the heat energy is used to boil water. The boiling water forms steam. The steam then turns the turbines in the form of mechanical energy. This generates electricity in the form of electrical energy. Most of the electricity that we use today comes from fossil fuels. Why is this not a viable source of energy for the future? It takes very long to form, making it non-renewable. The reserves will run out – scientists believe in 50 to 100 years. With time, it will get more and more expensive because it will become harder to tap into the deeper reserves of coal, oil and gas. Renewable energy What is renewable energy? Energy that does not run out and can be replaced Here are the most common types of renewable energy and how they work: Hydropower Moving water has mechanical energy. Therefore, mechanical energy in the moving water is converted into mechanical energy in the turning turbine, which is converted into electrical energy. In order to generate electricity from the mechanical energy in moving water, the water has to be moving with sufficient speed and volume to turn a turbine. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 4 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO 1. Wave machines use the up-and-down movement of waves to turn turbines. Wave hitting a wave machine that contains a turbine 2. Tidal barrages use the energy of the water as the tide turns to turn turbines. Turbines that turn as the tide turns 3. Hydroelectric power schemes store water high up in dams. When the water falls, turbines are turned. Hydroelectric power plant Wind energy Wind is caused by currents in the earth’s atmosphere. This moving air has huge amounts of mechanical energy. Therefore, mechanical energy in the wind is converted into mechanical energy in the turning turbine, which is converted into electrical energy. Wind turbine © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 5 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Biomass energy Biomass fuels come from living things. Crops and wood are biomass fuels. For example, what do we get when we burn wood? Heat and light We can therefore turn heat and light energy into electrical energy. This works in much the same way as when burning fossil fuels: The chemical energy is transferred into heat energy and light energy. The light energy is not used, but the heat energy is used to boil water. The boiling water forms steam. The steam then turns the turbines in the form of mechanical energy. This generates electricity in the form of electrical energy. This is the same process as when coal is burnt. So what is the difference, in other words, why is biomass energy renewable while fossil fuels are non-renewable? As long as we continue to plant crops and trees and to replace those we cut down, we will always have biomass fuel. Geothermal energy In some places, rocks underground are hot. Think of natural hot springs. These are warmed up by hot underground rocks. These hot rocks are called magma. Magma feeds volcanoes. Deep wells are drilled and cold water is pumped to the magma. The water runs through fractures in the rocks and heats up. It returns to the surface as hot water and steam. The steam is then used to turn turbines. Therefore, heat energy in the magma and steam is transferred to mechanical energy in the turning turbine, which is transferred into electrical energy. Hot rocks/magma Nuclear energy Certain atoms are radioactive, which means that they have an unstable nucleus. This means that the atom splits in two. When it splits, it releases a tremendous amount of energy. This energy is then used to heat water. The boiling water forms steam. The steam then turns the turbines to generate electricity. Therefore, nuclear energy is transferred into heat energy in steam, which is transferred into mechanical energy in the turning turbine, which is transferred into electrical energy. Nuclear power plant Solar energy There are two types of solar energy: solar cells and solar panels. Solar cells: Solar cells convert light energy from the sun directly into electrical energy. This is used for example in a solar calculator. It is also used in larger applications in industry and in homes to provide electricity. Solar cells © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 6 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Solar panels: Solar panels are different to solar cells because they convert light energy into heat energy. It is often found on roofs of buildings where the most sunlight is received. They then heat water in the geyser or the water of a swimming pool. This results in less electricity being used. How is solar energy different to the other types of energy that we have learnt about? No turbine is turned to generate electricity. Solar panels The sun is the ultimate source of energy We are not talking about solar energy here! We use many different forms of energy, and almost all of them originate from the sun. The sun does not only provide light and heat energy. Energy from the sun may change into many different forms. Let’s discuss a few. How do fossil fuels originate from the sun? Fossil fuels come from dead plants and animals. Without the sun, plants would not exist and in turn animals would not exist. How does wind power originate from the sun? Heat energy from the sun causes changing weather patterns that produce wind. How does hydropower originate from the sun? Water flows in rivers because heat energy from the sun causes evaporation and rain that keeps water moving through the water cycle. Advantages and disadvantage of renewable and non-renewable energy What are the main DISADVANTAGES of non-renewable energy? 1. Non-renewable energy will eventually run out. 2. Non-renewable energy emits many pollutants into the atmosphere and hence is associated with negative environmental impacts. What are the main ADVANTAGES of non-renewable energy? 1. Non-renewable energy is a reliable source of energy. 2. Large amounts of electricity can be generated from non-renewable energy. 3. Non-renewable energy is relatively cheap. What are the main ADVANTAGES of renewable energy? 1. Renewable energy will never run out. 2. Renewable energy is less detrimental to the environment than non-renewable energy. What are the main DISADVANTAGES of renewable energy? 1. It is difficult to generate the quantities of electricity that we need using renewable energy. 2. Renewable energy is relatively expensive to start up. 3. Renewable energy often relies on the weather, making is less reliable than non-renewable energy. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 7 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Potential and kinetic energy Introduction We need energy for everything that we do. What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Energy cannot be created from nothing, and energy cannot disappear or be destroyed. Energy can change from one form to another. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different types of energy that can be transferred (changed). Potential energy What is potential energy? Potential energy is energy that is STORED in an object. It means that the energy is not used right now, but it can be used to do work later. There are different types of potential energy: • Elastic potential energy • Gravitational potential energy • Chemical potential energy Elastic potential energy What is elastic potential energy? Energy that is stored in elastic material when we stretch it or compress it. The more we stretch a spring, the higher the elastic potential energy. If you compress a spring, it also has elastic potential energy because when you let go, the spring sections will separate. Therefore, the more we compress a spring, the higher the elastic potential energy. If you stretch a rubber band and then release it, it will fly across the classroom. This tells us that potential energy was stored in the elastic when it was stretched. If you stretch it even more, it will fly even further when let go, meaning that the potential energy that was stored in it was stored in it was higher.. Gravitational potential energy What is gravitational potential energy? Energy that is stored in an object because of its position above the earth. The earth attracts all objects towards its centre with the force of gravity. If a book lies on a table, it has gravitational potential energy because of its position above the ground. If the book falls off the table and hits a glass standing on the floor, the glass would fall over and maybe even break. This shows us that the book had stored energy when it was lying on the table. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 8 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Water reservoirs Water reservoirs are built to provide water to a certain area. They are built uphill from the houses in an area. In this way, the stored water has enough gravitational potential energy to flow downwards to the houses that they supply. Depending on how much higher the reservoir is from the houses, the water pressure will vary from high flow to just a trickle. Water reservoir in Tennessee, USA If the reservoir is much higher than the position of the houses, there will be high water pressure. If the reservoir is only a little higher than the position of the houses, there will be low water pressure. When a reservoir is built lower than the houses or when water is taken out of a borehole, the water has to be pumped up to the houses. This is because the water below the level of the houses does not have gravitational potential energy. Chemical potential energy What is chemical potential energy? Energy that is stored n particles of substances such as food and fuel. In order to release this energy, a chemical reaction needs to take place. An energy drink has chemical potential energy. When athletes drink it, their bodies digest it (chemical reactions occur) and they get more energy to run their race. You can find the amount of chemical potential energy in any food by looking at the food label. A battery also has chemical potential energy stored in it. When a battery is inserted into a torch, the torch can be switched on. This is because a chemical reaction has taken place inside the battery that has allowed the light bulb to light up. Another example is wood or coal. When wood or coal are burnt, they release their stored chemical potential energy in the form of heat and light energy. Energy is measured in joules All energy is measured in units called joules (J). The energy content in food is labelled on the food packaging. Food packaging shows the amount of energy stored in the food in kilojoules (kJ) per 100 g (1 kJ = 1 000 J). In the case of drinks, it shows kJ per 100 ml. Therefore, we can see how much chemical potential energy the food contains. Based on the diagram below, how many kJ of energy are there in 100 ml of fruit juice? 224 kJ. Nutritional information on a bottle of fruit juice © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 9 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Homework 13 1. Look at the following pictures and decide what kind of potential energy it is. Elastic potential energy Chemical potential energy Elastic potential energy Gravitational potential energy Chemical potential energy Elastic potential energy © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 10 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO 2. Look at the following food labels and identify the amount of energy that each food contains per 100 g. List the food and energy value in ascending order. White bread Milo cereal Low-fat yogurt Biscuits Low-fat yogurt 256 kJ White bread 985 kJ Milo cereal 1 620 kJ Biscuits 2 159 kJ © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 11 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Kinetic energy An object has potential energy when it is at rest. What is kinetic energy? Kinetic energy is energy that an object has because it is moving or being used. When a car moves forward, it gains kinetic energy. The air in blowing wind has kinetic energy. Water that falls in a waterfall has kinetic energy. If you let go of a stretched rubber band, it flies through the room. The elastic potential energy changed into kinetic energy. In the last section we learnt about seven forms of energy. What were they? Electrical energy, light energy, heat energy, chemical energy, sound energy, mechanical energy, nuclear energy What form of kinetic energy specifically does the flying elastic band have? Mechanical Potential and kinetic energy in systems What is an energy system? An energy system consists of different parts that work together to store, use or give out energy so that a specific task can be done. When different parts of the system interact, energy is transferred to another form. The energy transfer causes a change, and a specific task can be done. Again, we learnt about seven different forms of energy, but here were are going to focus on four energy SYSTEMS: • Mechanical systems • Thermal systems • Electrical systems • Biological systems Mechanical systems A mechanical system uses force to do a specific task. We use machines or tools to do work for us. We can lift a heavy box with a crowbar or hit a cricket ball with a bat. If the box or the cricket ball move, they have mechanical kinetic energy. Potential energy can be changed to kinetic energy in a mechanical system. Take, for example, a plastic ruler that is bent. The ruler has elastic energy when it is bent. As soon as you let go of the ruler, it moves back into place. It has kinetic energy. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 12 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Experiment: 1. 2. 3. 4. Place a bottle top on a desk. Bend a ruler a little bit. Release the ruler so that it hits the bottle top and then moves across the desk. Repeat, but this time bend the ruler a lot. What did you observe in the two instances? When we bent the ruler a lot, the bottle top moved much further than when we bent the ruler a little bit. Explain your observation. When we bent the ruler a little bit, there was only a small amount of elastic potential energy in the ruler and in turn there was only a small amount of mechanical kinetic energy in the bottle top. When we bent the ruler a lot, there was a large amount of elastic potential energy in the ruler and in turn there was a large amount of mechanical kinetic energy in the bottle top. Thermal systems Thermal energy is produced by heat. Heat energy is transferred between different parts of a thermal system. When a substance it heated, the particles move faster. The movement causes the temperature of the substance to rise. Hot water in a cup that is placed on a table eventually becomes cold. Where does the heat go and why? It goes to the surroundings because the surroundings are cooler than the water in the cup. Experiment: 1. Pour hot water into one cup and cold water into another cup. 2. Add two drops of food colouring to each. 3. Observe the movement of the food colouring in both cups. What did you observe in the two instances? The colour spread faster through the hot water than the cold water. Explain your observation. The mechanical kinetic energy of the particles increases with heat. Because the particles move faster in the hot water, the colour gets shifted around faster. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 13 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Electrical systems If a battery is connected to a closed circuit, electric current will flow. The battery stores chemical energy. Chemical reactions inside the battery supply charges that can move through electrical wires. Electric current is the movement of charges inside electrical wires. Because the charges move, they have kinetic mechanical energy. We cannot see the charges move, but we can observe the effect of an electric current. Biological systems All living organisms require energy for their vital processes, e.g. respiration and digestion.. Where does biological energy originate? The sun Where is biological energy stored? In plants and animals In what form of energy is biological energy stored? Chemical potential energy Energy that comes from the sun is converted into chemical energy by plants in the process of photosynthesis. Other animals eat the plants or they eat animals that have eaten the plants. A horse eats grass. What energy is stored in the grass that the horse ate? Chemical potential energy What type of energy is stored in an energy drink? Chemical potential energy. What happens to this energy when it reaches the body of the athlete? It gives energy to the athlete so he/she can run. This means that the chemical potential energy is converted into mechanical kinetic energy. Homework 14 Complete the table below. The first row is an example: Example of an energy system A man running Is it a mechanical, thermal, Identify the energy transferred electrical or biological system? in the system Chemical potential energy inside Biological the body of the man to mechanical kinetic energy in his legs A cat drinking milk A pair of scissors cutting a piece of paper An electric fan that’s turning A hot stone placed in cold water A windmill that’s turning © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 14 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO The law of conservation of energy What does the law of conservation of energy state? Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be transferred from one system to another or converted from one form to another. We learnt that energy is measured in joules. The total number of joules at the beginning and at the end is the same. This is demonstrated in the diagram below. What does the diagram show? 3 600 J of electricity is supplied to the bulb. Electrical energy is converted to light energy (360 J) and heat energy (3 240 J). 3 240 J + 360 J = 3 600 J. You can see from the diagram above that no energy was created or destroyed. The total number of joules at the beginning and at the end is the same. Energy cannot be created or destroyed Think of money as an analogy. When you use money, it doesn’t disappear. It is only transferred to another person, who can then use it. If you don’t have any money, you cannot create it from nothing. In the same way, energy does not disappear when we use it. It goes somewhere else where it is used in a different form. It also cannot be created from nothing. If you lift up an object, it gains gravitational potential energy. The higher you lift it, the the more gravitational potential energy it gains. When you release it and it drops, the mechanical kinetic energy will equal the gravitational potential energy that the object had before it was dropped. Energy can be transferred Consider an electric doorbell. When you press the button, electrical energy is transferred to the bell and the bell makes sound energy. When the electric windows of a car open and close, what type of energy is transferred into what type of energy? Electrical energy into mechanical energy © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 15 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Heat transfer Introduction Everything is made up of matter. Matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms. The particles are always moving, meaning that they have mechanical kinetic energy. This movement generates heat energy. Even when something is very cold, it generates a small amount of heat. Why? Because of the particles that are always moving Heat energy can be transferred from one place to another by: • Conduction in solids, liquids and gases. • Convection in liquids and gases. • Radiation through anything that will allow radiation to pass. Heat as transfer of energy What is energy transfer? When energy moves from one place to another place. What is another name for heat energy? Thermal energy Thermal energy is energy that is produced by heat. There is heat transfer when there is a temperature difference in two places. Does heat energy transfer occur from a hotter place to a cooler place or from a cooler place to a hotter place? Hotter place to a cooler place When will the heat energy transfer be complete? When both places have the same temperature So heat transfer is the movement of heat from a hotter place to a cooler place until the entire system is at the same temperature. When you touch something hot, such as hot water, you feel the heat burning you. This is because the hot water transfers heat energy to your hand. Your hand is cooler than the hot water, so heat energy is transferred from water to your hand.. If you put a frying pan on a stove, the pan will be hot in a few minutes. Why? Because the heat is transferred from the stove to the pan until they are at the same temperature. If you now put a block of butter into the hot pan, the butter will melt because the heat energy is now getting transferred from the hot pan to the cold butter. When it is a cold day, we feel cold because our body temperature is hotter than the outside temperature. Why doesn’t a lizard feel cold on a cold day? Because a lizard is cold blooded, so its body temperature is the same as the outside temperature. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 16 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Homework 15 How is HEAT energy transferred in the each of the following pictures? Explain in full. The first one is an example: Sharpening a pencil When you sharpen a pencil, the friction between the sharpener and the pencil produces heat. The heat is transferred to both the pencil and the sharpener. Using a hairdryer A hair dryer produces hot air that is transferred to your wet hair in order to dry it quickly. Using an iron An iron has a hot base that let off steam. This hot steam moistens and heats up the clothes, which allows them to straighten when the pressure of the iron is applied. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 17 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Drinking a cup of hot coffee For just a few seconds, a hot cup of coffee transfers heat to your hands, lips, mouth, oesophagus and stomach. (Our body maintains a stable body temperature so the effect does not last long.) Burning wood in a fireplace Burning wood produces heat, which then transfers the heat to the entire room. Conduction What is conduction? It is the transfer of heat within an object or between objects that are in direct physical contact with each other. In conduction, the heat energy travels from the source of heat through the object, or from the warmer object to the cooler object until they have the same temperature. In the diagram below, one part of the object is hot, and the other part is cold. The heat energy will transfer from: the hot side to the cold side until the entire object is at the same temperature. The diagram below is an example of conduction between two solid objects – the hot plate of the stove and the pan. The heat energy will transfer from from the hot plate to the pan until both objects are at the same temperature. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 18 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO You experience heat transfer by conduction whenever you touch something that is hotter or colder than your skin, e.g. when you wash your hands in hot water or in cold water. When you wash your hands in hot water, the heat energy from the water gets transferred to your hands. When you wash your hands in cold water, the heat energy from your hands gets transferred to the water. The form of heat energy is always from hot to cold.. The diagram below is an example of conduction. The heat travelled from the hot plate of the stove, to the pot and the pot’s handle.. Then when you touch handle, some of the heat is transferred to your hand.. We usually refer to conduction as heat transfer between solids. However, conduction may also take place between a solid and a liquid, a solid and a gas, a liquid and a gas, two gases or two liquids. For example, when you make a hot cup of coffee, heat energy is transferred from the hot water to the mug and the spoon.. This is a good example of conduction between a solid and a liquid. On a cold day, we don’t want the heat energy to be transferred from our body to the surroundings. We therefore wear clothes that are thick and made of materials that slow down the transfer of energy.. When you remove food from the oven, you use oven gloves in order to prevent the heat of the oven dish from transferring to your hands. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 19 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO Homework 16 In the following pictures, use an arrow to show the direction of the heat transfer through conduction. Walking on hot sand Using an iron Holding a hot mug of tea 1. Name three examples of heat energy transfer through conduction in the home that have not been discussed in this handout. When you have a bath, the heat transfers from the water to your body. When you use the oven, heat is transferred from the oven to the oven dish to the food that is being cooked. When you work on the computer, heat is transferred from the computer to the surroundings. 2. Name three examples of heat energy transfer through conduction in industry that have not been discussed in this handout. Gold is melted to make gold bars. To make steel, different metals are melted and mixed together. In coal-fired power plants, cooling towers are used to condense steam back into water. Experiment: Heat energy transfer in different materials Materials: ceramic cup, glass cup, polystyrene cup, plastic cup, metal cup Methods: 1. Fill each cup halfway with boiling water. 2. Wait 2 minutes. 3. Touch each cup. What did you observe? The metal cup feels the hottest. The polystyrene cup feels the least hot. As you can see from the experiment above, some materials transfer heat energy faster and more effectively than others. We say that such materials are good conductors of heat. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 20 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO For example, metals are good conductors of heat. However, some metals are better conductors of heat than other metals. Aluminium is an excellent heat conductor, which is why we use it to make pots and pans. Some substances, such as plastic, are poor conductors of heat. We call such materials heat insulators. Insulators are used in situations where we don’t want the heat energy to be conducted. For example, the pot’s handle should not conduct heat, or else we will burn our hands. Heat insulators are also important to prevent heat energy from being wasted by being lost to the surroundings. For example, people have their geyser covered in a geyser blanket, which is a heat insulator and slows down the heat loss from the geyser. This in turn helps to save electricity. Convection We already learnt that all matter is made of tiny particles, and that those particles are always moving. Look at the diagram below. The particles that make up a solid are really close together with hardly any spaces between them. The particles that make up a liquid are further apart. The particles that make up a gas are much further apart. Where do particles move around most freely – in a solid, a liquid or a gas? They move around most freely in a gas, and less freely in a liquid. There is the least movement in a solid. We refer to gases and liquids as fluids. What happens to the particles of the fluid as the fluid is warmed up? The particles start to move around faster, they expand (meaning that they take up more space) and they rise. Consider the diagram on the next page. The particles of water at the bottom of the pot, closer to the heat source, heat up first. Those particles now rise and take over the space of the colder particles, which are forced to sink. This is how heat energy moves around in a liquid or gas. Let’s label the diagram: The hotter liquid rises The colder liquid sinks What is convection? It is the transfer of heat through liquids or gases © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 21 GRADE 7 TERM 3 NATURAL SCIENCES ENERGY AND CHANGE - MEMO This upward movement of the hot fluid and downward movement of the cold fluid forms a convection current. A heater is switched on in a small enclosed room. Explain how the room gets heated. Hot air is generated by the heater. This hot air from the heater rises and forces the cold air down. Convection currents forms, circulating the air, until it is at the same temperature. Now you open the window, allowing cold air in. Look at the diagram below: As you can see, the hot air from the heater rises. The cold air coming from the outside immediately rises. The hot air escapes from the upper portion of the window. When the window is open, no convection currents form in the room, so the room cannot heat up. The cold air accumulates at the bottom of the room, while the hot air accumulates at the top of the room and escapes through the window. This is a waste of electricity. Radiation What is radiation? The transfer of the sun’s energy to the earth via electromagnetic waves. This is what electromagnetic waves look like. They travel from the sun to earth at the speed of light in about 8 minutes. Electromagnetic radiation is able to move through a vacuum. What is a vacuum? Empty space where there is no matter, not even gas This is different to conduction and convection, which transfer heat energy through matter. An object will absorb the electromagnetic waves and become hot. This means that electromagnetic radiation gets transferred into heat energy. A dark object absorbs the electromagnetic radiation better than a light object. That is why darker objects get hotter than lighter objects. Matt objects also absorb radiation better than shiny objects. The diagram on the next page shows that a matt black object will get hotter than a shiny white object. © e-classroom www.e-classroom.co.za 22