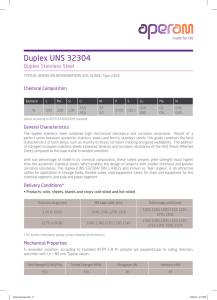
Weight C % Cr Ni Mo Mn Si P S N Cu W ER 0.03 82.5- 2.5 1 0.03 0.02 0.20- 1.5 1.0 24-27 2594 max 10.5 4.5 max max max max 0.30 max max Alloy ER 2594 is a superduplex welding wire. The Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number (PREN) is at least 40, thereby allowing the weld metal to be called a superduplex stainless steel. This welding wire provides matching chemistry and mechanical property characteristics to wrought superduplex alloys such as 2507 and Zeron 100 as well as superduplex casting alloys (ASTM A890). This welding wire is overalloyed 2-3 percent in Nickel to provide optimum ferrite/austenite ratio in the finished weld. This structure results in high tensile and yield strength along with superior resistance to SCC and pitting corrosion. Set the parameters to obtain a heat input of 10,000 -30,000 Joules/inch. Preheat is not required. The interpass temperature should be maintained at 300ºF max. If post weld annealing is required this weld metal will require a higher annealing temperature than that required by the duplex base metal. Alloy ER 2594 is a Stainless Steel TIG, MIG and SUB-ARC wire used for welding. For all stock availability contact Sales. Specifications AWS 5.9 ASME SFA 5.9 AWS ER2594 UNS 32750 Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number Pitting resistance equivalent number (PREN) is a predictive measurement of a stainless steel's resistance to localized pitting corrosion based on its chemical composition. In general: the higher PREN-value, the more resistant is the stainless steel to localized pitting corrosion by chloride. PREN is frequently specified when stainless steels will be exposed to seawater or other high chloride solutions. In some instances stainless steels with PREN-values > 32 may provide useful resistance to pitting corrosion in seawater, but is dependent on optimal conditions. However, crevice corrosion is also a significant possibility and a PREN > 40 is typically specified for seawater service. These alloys need to be manufactured and heat treated correctly to be seawater corrosion resistant to the expected level. PREN alone is not an indicator of corrosion resistance. The value should be calculated for each heat to ensure compliance with minimum requirements, this is due to chemistry variation within the specified composition limits. There are several PREN formulas. They commonly range from: PREN = %Cr + 3.3 × %Mo + 16 × %N to: PREN = %Cr + 3.3 × %Mo + 30 × %N.[4] There are a few stainless steels which add tungsten (W), for those the following formula is used: PREN = %Cr + 3.3 × (%Mo + 0.5 × %W ) + 16 × %N All % values of elements must be expressed by mass, or weight (wt. %), and not by volume. Tolerance on element measurements could be ignored as the PREN value is indicative only.