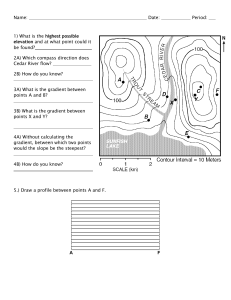
Estimating the Gradient of a Curve Answers 1. Find the gradient of each line segment. a. 3 b. y 3 c. y 2 2 2 1 1 1 x -3 -2 -1 3 0 1 2 3 x -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 x -3 -2 -1 0 -1 -1 -1 -2 -2 -2 -3 -3 -3 gradient = 2 gradient = -4 gradient = 5 d. 3 e. y 3 2 -1 0 2 3 4 y 1 x -2 1 2 1 -3 y 1 2 3 x -3 -2 -1 0 -1 -1 -2 -2 -3 -3 gradient = 1 gradient = - 2 2 1 2 3 3 2. Find the gradient between each pair of coordinates. a. (3, 5) and (2, 1) gradient = 5–1 =4 3–2 b. (3, -2) and (0, 0) gradient = -2 – 0 = - 2 3–0 3 c. (-1, 2) and (7, 5) gradient = 2 – 5 = 3 -1 – 7 8 d. (7, 5) and (3, -2) (-2) 7 = 7–3 4 gradient = 5 – e. (3, 0) and (-2, 4) gradient = 0 – 4 = - 4 3 – (-2) 5 1 of 5 Estimating the Gradient of a Curve Answers 3. Match each of the graphs below with the correct interpretation of its gradient. If there is not a matching pair, write one. a distance-time graph the interest rate a velocity-time graph the speed a speed-time graph the rate of change of the water a graph of the amount of money owed the acceleration a graph of the amount of water in a tub the acceleration 4. For each of the graphs below, estimate the gradient at the given value of x. The gradients given are estimates. Answers should be considered correct if they are within 0.2 of the given answer. a. at x = 2 5 b. at x = 1 y 3 4 y 2 3 1 2 -1 1 0 1 2 3 4 x 5 x 3 2 gradient = 1.6 at x = 3 10 1 -1 gradient = -0.2 c. 0 d. y at x = 4 3 y 8 2 6 4 1 2 0 2 gradient = 1 4 6 x 8 0 1 2 gradient = 0.25 3 4 5 x 6 2 of 5 Estimating the Gradient of a Curve Answers 5. The graph below is a distance-time graph for a sprint runner. Find the speed of the runner after 5 seconds. 20 distance (m) 15 10 5 0 5 10 time (s) 15 The gradient at 5 is 1.5, therefore the speed of the runner is approximately 1.5m/s. 6. The graph below is a velocity-time graph for a new racing car. 60 a. The manufacturer claims the car can go from 0m/s to 45m/s in 3 seconds. Comment on the manufacturer’s claim. 50 The speed at 3 seconds is less than 45m/s so, in this case, the car has not done 0m/s to 45m/s in 3 seconds. velocity (m/s) 40 30 b. Calculate the acceleration of the car at 4 seconds. 20 The gradient at 4 seconds is approximately 4, therefore the 2 acceleration is approximately 4m/s 10 0 2 4 time (s) 6 8 10 3 of 5 Estimating the Gradient of a Curve Answers 7. The speed-time graph below shows a car braking. a. Interpret the y-intercept of the graph. 15 The y-intercept represents the initial speed of the car, 15m/s. b. Estimate the deceleration of the graph after 5 seconds. speed (m/s) 10 The gradient at 5 seconds is approximately -1, therefore the 2 deceleration is 1m/s 5 0 2 4 6 time (s) 8 10 12 8. The graphs below represent two rowing squads in a race. Graph 1 is a distance-time graph for squad 1. Graph 2 is a speed-time graph for squad 2. Graph 1 700 a. Describe Graph 2, referencing the speed and acceleration of the rowing squad during the race. distance (m) 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 10 20 30 40 50 time (s) 60 70 80 Graph 2 14 b. After 10 seconds, which squad is travelling faster? Justify your answer. speed (m/s) 12 10 8 Squad 1: the gradient at 10 seconds is roughly 10, so their speed is 10m/s 6 4 2 0 The squad accelerate quickly in the first 10 seconds, then continue to accelerate at a slower rate until 50 seconds. They then travel at a constant speed of 12m/s until 65 seconds where they accelerate again for the last 5 seconds of the race. Squad 2: their speed is 8.5m/s 10 20 30 40 50 time (s) 60 70 80 Squad 1 is travelling faster. 4 of 5 Estimating the Gradient of a Curve Answers Challenge Below is the graph of y = x2. Complete the table with the gradient of the graph for each value of x. What do you notice? 10 y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 x -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 x 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 Gradient 1 2 3 4 5 6 Each gradient is approximately double the value for x. 5 of 5