Pressure Gradient and Winds Investigation
advertisement

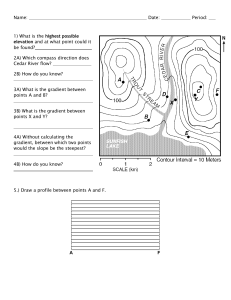
Name __________________________________________ Date __________________ Block ___________ Pressure Gradient and Winds Investigation Directions: Pressure gradient force, also known as wind, is an important variable in the atmosphere that helps to define weather on Earth. By analyzing the differences in pressure between two points on the Earth’s surface, it is often possible to predict local wind direction and speed. Using the surface weather map, calculate the pressure gradient in millibars per mile between the points shown in Table. Show your calculations and record your answers in the spaces provided on the table. Using the letters H ( high pressure) and L (low pressure), fill in the boxes with the correct letter for the two pressure systems on the map. Draw arrows to show the direction of air movement for each of the pressure systems. Points of Map Change in Pressure (mb) Distance (miles) Calculations Pressure Gradient A-B 1024mb-1009mb=15mb 700mi 15mb÷700mi .021 mb/mi A-C A-D A-E H-F H-G H-I