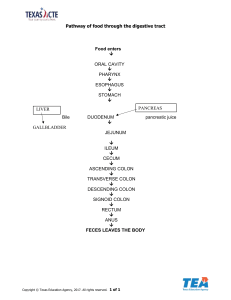
Embryology of Abd Wall and Cavity Lecture The Ventral Mesentery is derived from the Septum Transversum and gives rise to the ligaments of the liver GI tract formed from endoderm intraperitoneal–completely covered with visceral peritoneum liver, stomach, proximal ⅓ duodenum, tail of pancreas, jejunum, ileum, transverse colon retroperitoneal–partially covered with parietal peritoneum SAD PUCKER→suprarenal gland, aorta/IVC, distal duodenum, pancreas head and body, ureters, colon (ascending and descending), kidneys, esophagus, rectum Foregut–celiac artery, CN10 Midgut–superior mesenteric artery, CN10 Hindgut–inferior mesenteric artery, sacral spinal cord segments S2-4 RUQ R lobe of the liver Gallbladder Pylorus of the stomach Duodenum Pancreas head R kidney R adrenal gland Hepatic flexure Distal portion of the R half of transverse colon Superior portion of the ascending colon LUQ L lobe of the liver L half of transverse colon Splenic flexure Spleen Stomach L kidney L adrenal gland Pancreas body and tail Superior descending colon RLQ Ileum Cecum Appendix inferior portion of the ascending colon R ovary R uterine tube R ureter R spermatic cord Uterus–is enlarged Bladder–if full LLQ Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum L ovary L uterine tube L ureter L spermatic cord Uterus–is enlarged Bladder–if full Carbs(the enemy)→simple sugars Fats→triglycerides proteins→AA Digestive Tract and Abdominal Viscera Lecture Digestive tract MAJOR process→elimination Enteric nervous system largely fxns independently from the CNS BUT CNS sends parasymp control via CN 10 and sacral segments S2-4 MOUTH: ● Teeth ○ Incisors–cut ○ Canines–pierce, tear, and rip ○ Premolars, molars–grind and crush ● Salivary Glands–produce saliva (serous fluid→mostly water and proteins→resembles serum) ● ○ Submandibular gland→serous and mucus (CN7) ○ Sublingual gland→serous and mucus (CN7) ○ Parotid gland→serous (CN9) Salivary Amylase and Lingual Lipase separate from pancreatic enzymes ESOPHAGUS: ● The oropharynx and esophagus convey food, fluids, and oral secretions to the stomach via? Deglutition ● Stroke of vertebrobasilar artery→dysphagia ● Upper ⅓ lined with skeletal muscle→voluntary control ● Lower ⅔ lined with smooth muscle→ENS control→involuntary control ● EsophagoGastric Jxn ○ Z-line→jagged line demarcating the abrupt transition from esophageal to gastric mucosa DIAPHRAGM: ● Hiatuses (I 8 10 EGGs AT 12)--holes in diaphragm thru which certain structures go thru and their vertebral levels ○ T8→IVC ○ T10→Esophagus and Vagus ○ T12→Aorta, Azygos and Thoracic Duct STOMACH: ● Which of the following areas of the GI tract includes an additional muscular layer? ○ stomach → longitudinal, circular, oblique ● Parietal cells–oxynitic cells ○ Secrete HCl and intrinsic factor (extrinsic factor absorption) ● Chief cells–pepsinogen→pepsin with acid ● Enteroendocrine cells ○ G cells→ON SWITCH ■ ○ Gastrin→stimulate parietal cells D cells→OFF SWITCH ■ Somatostatin→inhibit parietal cells INTESTINES: ● Meissner’s Plexus (Submucosal–Sensory) ● Auerbach’s Plexus (Myenteric–Motor) ● Plica Circularis→increase surface area/volume ratio ● Peyer’s patches aka GALT aggregation of lymphoid tissue found throughout GI tract ● ● ● ● ● EXCEPT STOMACH ○ Most prominent in the ileum and large intestine Muscular layer of the intestine ○ Inner circular layer ○ Myenteric plexus–Auerbach ○ Outer longitudinal layer Duodenum ○ Brunner’s glands AKA Duodenal glands ○ Panneth cells–secrete antimicrobial peptides Jejunum ○ Plica circularis most prominent in the jejunum ○ Ileum ○ Peyer's patches Large intestine ○ Peyer’s patches ○ Goblet cells PANCREAS: ● Exocrine and endocrine fxns ● Head ○ RUQ ○ Retroperitoneal ○ Uncinate process ● Neck ○ R/LUQ ○ Retroperitoneal ● Body ○ LUQ ○ Retroperitoneal ● Tail ○ LUQ ○ Intraperitoneal–fully covered by visceral peritoneum SPLEEN: ● LUQ ● Left hypochondriac below costal cartilage LIVER: ● Second largest organ ● Skin the largest organ ● Porta hepatis contains the portal triad ○ Bile duct ○ Hepatic portal vein ○ Hepatic artery ● 4 anatomical/structural lobes ○ R and L ○ Caudate and Quadrate ● 2 fxnal lobes ● ● ● ○ R lobe→supplied by R hepatic artery ○ L lobe–including caudate and quadrate→supplied by L hepatic artery True ligaments are remnants of fetal vessels: ○ Ligamentum teres aka round ligament used to be umbilical vein ○ Ligamentum venosum used to be ductus venosus False ligaments: ○ Falciform→attaches liver to anterior abdominal wall ○ ○ R and L triangular Ant and Post Coronary Superior aspect of the liver→bare area–not covered by peritoneal lining ● Liver sinusoids ○ Kuppfer cells–macrophages ■ Remove expired RBCs ■ Fight infection PORTAL SYSTEM: ● Portal vein is formed by the Splenic and Superior Mesenteric Veins & gastric veins JEJUNUM: ● Microvilli→brush border ● Plica circularis ILEUM: ● Peyer’s patches ASCENDING COLON/PROXIMAL ⅔ of TRANSVERSE COLON: ● Peyer’s patches ● Haustra ● Taenia coli ○ Mesocolic ○ Omental ○ Free DISTAL ⅓ of TRANSVERSE COLON/DESCENDING COLON/SIGMOID COLON/RECTUM/ANAL CANAL: ● Internal anal sphincter→involuntary ● External anal sphincter→voluntary Referred pain from and to ● Foregut structures→Epigastric ● Midgut structures→Umbilical ● Hindgut structures→Hypogastrium Innervation of Abdomen Lecture Although considered efferent, sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers CAN and DO carry afferent/sensory signals ANS ● Sympathetic–Splanchnic nerves ○ Pre ganglionic cells located in Lateral horns T5-L2 ○ Post ganglionic cells located in ■ Paravertebral ganglia ● Sympathetic chain ganglia ■ Prevertebral ganglia ○ ● ● Superior cervical ganglia→esophagus ● Celiac ganglia→foregut ● Superior mesenteric ganglia→midgut ● Inferior mesenteric ganglia→hindgut Neurotransmitters ■ NE ■ Neuropeptide Y ■ enkephalins ○ Fxn ■ Decrease blood flow ■ Inhibit glandular secretion and GI motility Parasympathetic ○ Pre-gg cells in dorsal motor nucleus of CN 10 and nucleus Ambiguus ■ Exit thru jugular foramen ○ Post-gg cells located near target organs/tissues ○ ○ Neurotransmitters ■ Ach ■ Substance P ■ Gastrin-releasing peptide ■ Vasoactive intestinal peptide Fxn ■ Increase GI blood flow, glandular secretion, and motility Enteric NS ● Nerve cell bodies in small ganglia within Meissner’s (Submucosal–Sensory) and Auerbach’s (Myenteric–Motor) Plexuses ● Meissner’s (Submucosal–Sensory) ○ Monitor wall tension, wall integrity, pH/osmolality/nutrient levels of intestinal contents ● Auerbach’s (Myenteric–Motor) ○ Vasoconstriction/dilation of blood vessels ○ Control of circular and longitudinal smooth muscle, secretory glands, endocrine cells, and absorptive epithelium ○ Peristalsis ● ■ Bolus→chyme in the stomach ■ Retrograde-peristalsis→vomitting ○ GI motility ○ Sphincter control Enteric glial cells that support ENS neurons are analogous to which cells of the CNS? ○ Astrocytes **Memorize tables x 3*** GI Neurotransmitters and Neuromodulators Parasympathetic/Enteric–GI TRACT ON SWITCH Ach Contracts wall muscle Relaxes sphincters Increases salivary, intestinal, and pancreatic secretions Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Relaxes sphincters Increases salivary, intestinal, and pancreatic secretions Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Increases gastrin secretion Stimulates mucosal hypertrophy Substance P Contracts wall muscle Increases salivary secretions Sympathetic/Enteric–GI TRACT OFF SWITCH NE Relaxes wall muscle Constricts sphincters Decreases secretions Neuropeptide Y Relaxes wall muscle Decreases secretions Enkephalins Constricts sphincters Decreases secretions GI Hormones Hormone Secretory Cell Fxn GI TRACT ON SWITCH CCK I cells in duodenum and jejunum Inc enzyme secretion, contract GB, inc gastric emptying Gastrin G cells in antrum Increase acid secretion (from the parietal cells) Motilin M cells in upper GI tract Increase GI motility Secretin S cells in SI Release bicarb and pepsin GI TRACT OFF SWITCH Glucose-dep Insulinotropic Peptide K cells in duodenum and jejunum Release insulin, inhibit acid secretion Somatostatin D cells in stomach, duodenum, and pancreas Inhibits gastric acid secretion GI Paracrines–GI TRACT ON SWITCH Paracrine Secretory Cell Fxn Histamine enterochromaffin-like cells and mast cells increase gastric acid secretion PGs cells lining GI tract increase mucus secretion, bicarb secretion, and blood flow Digestion and Absorption Lecture Stomach ● Body: ○ Parietal cells ○ ■ HCl→activates pepsinogen to pepsin ■ Intrinsic Factor→needed to absorb Extrinsic Factor is B12 Chief cells ■ ● Pepsinogen→pepsin via acid Antrum: ○ D cells ■ ○ Somatostatin→inhibits GI tract and secretions via inhib. of parietal cell G cells ■ Gastrin→stimulates GI tract and secretion via stim. of parietal cells Exocrine fxns of the pancreas Intercalated ducts→interlobular ducts→accessory and main pancreatic ducts ● Acinar cells→synthesize and secrete digestive enzymes that break down different macromolecules and nucleic acids: ○ ○ ○ ○ Carbs ■ Amylase Lipids ■ Lipase ■ Phospholipase ■ Phospholipase A2 Proteins ■ All of the following enzymes digest proteins except? ■ Chymotrypsinogen→chymotrypsin ■ Trypsinogen→trypsin ■ Procarboxypeptidase A & B ■ Proelastase Nucleic Acids ■ deoxyribonuclease→DNA ■ ribonuclease→RNA ● Ductal cells→secrete bicarb with the help of carbonic anhydrase ● Intercalated ducts→lined with ductal cells; empty into interlobular ducts ● Interlobular ducts→empty into pancreatic and accessory pancreatic ducts ● Pancreatic duct→joined by the common bile duct at the Ampulla of Vater that empties into the major duodenal papilla (accessory pancreatic duct empties into the minor duodenal papilla) Liver ● ● Bile acid recycling via the enterohepatic circulation ○ Unconj bile acids reabsorbed passively in the terminal ileum and large intestine Metabolism ○ Carbs→gluconeogenesis (generation of glucose) and glycogenolysis (breakdown glycogen into glucose) ○ Lipids→converts AA and carbs into lipids; mobilizes FAs thru lipolysis for release into circulation to be used for energy ○ Proteins→breakdown of protein into AA and synthesis of plasma proteins such as albumin ■ Albumin–transport and maintain colloid osmotic pressure ● ● Storage of fat soluble vitamins and minerals ○ ADEK; iron, copper, magnesium Detox ○ ● ● Ammonia→urea via urea cycle ○ Alcohol metabolized via alcohol dehydrogenase Drug biotransformation ○ Phase 1–oxidation ■ Used to activate ACE-I ○ Phase 2–conjugation and elimination Immune fxns ○ Kuppfer cells are specialized macrophages that engulf and remove intestinal bacteria and RBC fragments from spleen Small Intestine ● Secretions ○ Enteroendocrine cells secrete: ■ CCK→contracts GB, increase GI secretions, promote gastric emptying ■ Secretin→releases bicarb and pepsin ■ Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Peptide→inhibits acid secretion, releases insulin ● Digestion and absorption ○ Carbs: ■ 4kcal/g ■ broken down by amylase (salivary and pancreatic) ■ ○ ○ Absorption into the portal system→active transport EXCEPT fructose, which is via facilitated diffusion Proteins: ■ 4kcal/g ■ Absorption across epithelial lining of SI via CoTransport; into the portal system via facilitated diffusion Lipids ■ 9kcal/g ■ TriAcylGlycerols (TAGs)→Free FAs→Small, Medium, and Long Chain FA ● ■ Small and medium chains are water soluble and can therefore cross epithelium via diffusion ● LCFAs are less soluble and form micelles ○ Once in the portal system they are assembled into chylomicrons and exocytosed into the lymphatic system Emulsification–process whereby fats/lipids are mechanically broken down into smaller droplets ■ ■ ■ Pancreatic lipase is the primary enzyme for digesting TAGs Cholesterol esterase digest cholesterol Phospholipase A2 targets glycerophospholipids such as phosphatidylcholine Large Intestine ● GastroColic Reflex→IleoCecal valve opening in response to Gastrin and CCK when food is present in the stomach/duodenum ● Water/electrolyte reabsorption ○ Proximal colon via Na/H exchanger ○ Distal colon via Na channels regulated by aldosterone Endocrine Glands Lecture Amines→(derived from tyrosine) catecholamines and thyroid hormones Peptide/proteins Steroids Catecholamines (Amine) Thyroid hormones (Amine) Synthesis Synthesized and stored in secretory vesicles Synthesized in the ER Synthesized and stored in secretory vesicles Synthesized in the ER Transport Water soluble, unbound in bloodstream Largely not water soluble, bound to carrier proteins Water soluble, unbound in bloodstream Largely not water soluble, bound to carrier proteins Mech of Action Bind to surface Testosterone (lipid Bind to surface receptors→ soluble)→passes receptors→hormone- hormone- directly thru the cell receptor complex receptor membrane to bind activates second Passes directly thru the cell membrane to bind intracellular receptors that either activate or inhibit transcription complex intracellular receptors messenger activates second that either activate or system→protein messenger modification and inhibit transcription system→protein modification and synthesis initiated Other steroids bind to surface receptors and activate second messenger systems synthesis initiated **peptide/proteins & catecholamines; steroids & thyroid hormones have the same syn/transport/MOA Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis Pituitary gland(hypophysis) Posterior→Neurohypophysis ADH (vasopressin)→binds to vascular smooth muscle receptors causing vasoconstriction; released in response to hypovolemia Oxytocin→secretion/ejection of breast milk **prolactin signals to breastmilk production (ant. pit.) Anterior→Adenohypophysis Hypothalamus→embryologically derived from diencephalon Plugs into the pituitary gland via 2 different sets of axons: Neuroendocrine axons→posterior pituitary Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal portal system→anterior pituitary 4 releasing, 2 inhibiting GH releasing and inhibiting hormones GHIH aka Somatostatin Prolactin inhibiting hormone aka Dopamine Adrenal glands Cortex→from mesoderm “GFR” Zona Glomerulosa→mineralcorticoids (aldosterone) Zona Fasciculata→glucocorticoids (cortisol) Zona Reticularis→androgens (testosterone, progesterone, estrogen, DHEA) Medulla→from neuroectoderm catecholamines (epi, NE) Thyroid Hormones T3–Triiodothyronine→active form T4–Thyroxine→produced in greater quantity compared to T3 Increase CO and vent Increase BMR Increase body temp CNS maturation and maintenance Synthesis of new proteins→work with GH to facilitate growth and maturation of the neuro-MSK system Thyroid hormone pathway Thyroglobulin (TG)–very rich in Tyrosine Residues Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) catalyzes 4 rxns: Converts ioDIDE to ioDINE Attaches ioDINE to Tyrosine Residue→MIT and DIT (Mono-Iodo, Di-Iodo Tyrosine) Couples 2 DITs→T4 Couples 1 DIT and a MIT→T3 T3 and T4 are transported to target proteins via Thyroxine-Binding Globulin Target tissues have an enzyme that converts T4 to T3 Parathyroid PTH is secreted by Chief Cells in response to low concentrations of Ca2+ Regulation of Ca2+, phosphate (PO43-) Bone ● Episodic/pulsed release of PTH ○ Increase in new bone synthesis (can be used as tx for osteoporosis) ● Prolonged release of PTH ○ Old bone resorption→releasing Ca2+, phosphate (PO43-) Kidneys (Nephron) ● Increases Ca2+ reabsorption at the DCT ● Decreases PO43- reabsorbtion at the PCT ● Activates vitamin D Ca2+ imp for: blood coag cascade, muscle contraction, nerve conduction, enzyme activation/deactivation Phosphate imp for: cellular metabolism (ATP), enzyme activation/deactivation Vitamin D Bone ● Increase new bone synthesis ● Increase old bone resorption Kidneys (Nephron) ● Increases Ca2+ reabsorption at the DCT ● Decreases PO43- reabsorption at the PCT Small intestine ● Increases Ca2+ and PO43- absorption Vit D deficiency→rickets in children Ca2+ deficiency HYPERreflexia Chvostek’s sign→facial nerve twitching when the facial nerve is tapped Trousseau’s sign→involuntary hand and feet spasms when subjected to prolonged hyperinflation of a BP cuff Endocrine fxns of the pancreas Islets of Langerhans (cluster of 4 different cell types): Alpha→secrete glucagon→increase blood glucose and FA concentration Glucagon (hormone of starvation) promotes: Gluconeogenesis–lipids/proteins→glucose Glyconeogenesis–lactic acid→glycogen Glycogenolysis–glycogen→glucose Beta→secrete insulin→decrease blood glucose, AA, FA, and K+ Insulin (hormone of excess) also released in response to incretins Delta→secrete somatostatin F cells