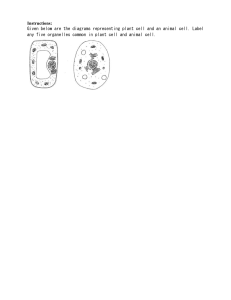
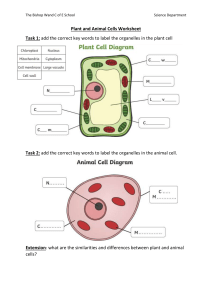
Plant and Animal Cells Discovery of the Cell Early microscope was invented in the mid-1600s. Robert Hooke first saw cells in 1663. He called the tiny units he saw under the microscope “cells” because they resembled the cells of honeycombs in a bee hive. What is a CELL? Not all cells are the same but all cells share certain traits and structures. Cell theory states that: ● Cells are the basic unit of life. ● All living things are made of cells. ● All cells come from preexisting cells. Cells Parts and Their Functions Our bodies are made up of between 10 trillion and 100 trillion cells. The smaller parts that make up cells are called organelles. By themselves organelles are not considered alive but together with all the other organelles they form a cell; a living unit. Different organelles have different structures and functions. The Purpose of Organelles Organelles maintain the life processes of the cell, including: ● Intake of nutrients ● Movement ● Growth ● Response to stimuli ● Exchange of gases ● Waste removal ● Reproduction The Organelles - Cell Membrane ● Forms the protective barrier around the cell. It is made of a double layer of lipids (fats). Cell membranes are designed to allow different substances to move through them. The Organelles - Cell Membrane ● Diffusion is one way of moving substances across the membrane. It does not require energy. The substance simply moves from the side of the membrane with the higher concentration of the substance to the side with the lower concentration of the substance. The Organelles - Cytoplasm ● This is a jelly-like substance that fills the cell. All other organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm. It contains the nutrients required by the cell. The Organelles - Nucleus ● This is the “brain”/control centre of the cell. It controls all activities within the cell. ● The nucleus is surrounded by its own membrane called the nuclear envelope. ● Most nucleii contain a dense centre called the nucleolus. ● Contains the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), which is the blueprint for the cell. DNA is coded information for making proteins and molecules. The Organelles – Vacuoles and Vesicles ● Membrane-bound organelles that store and transport nutrients, wastes, and other substances in the cell. ● Plant cells have one VERY large central vacuole that stores water and provides rigidity to the plant. The Organelles - Mitochondria ● The “Powerplant” of the cell. ● Chemical energy in sugar is converted to useable energy in the mitochondria by a chemical reaction called cellular respiration. The Organelles - Lysosomes ● Small organelles filled with enzymes. ● They break down invading bacteria and damaged parts of the cell. ● They are the “cleaners” of the cell This is a joke. The Organelles – Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) The “highway” of the cell. It is made of a series of tubes that carry materials through the cell. Extra Info 2 kinds: ● Rough ER (rER) → covered in ribosomes and used for making proteins. Ribosomes are where proteins are assembled. ● Smooth ER (sER) → has no ribosomes. Used in the production of fats and oils. The Organelles - Cytoskeleton ● An internal network of fibres made of proteins filaments. ● It helps maintain the cell’s shape. Plant vs Animal organelles Plant cells have some organelles that animal cells do not. They are the cell wall and chloroplasts. Animal cells have centrioles (used in cell division) which plant cells do not. Plant-specific Organelles – Cell Wall ● Plants, bacteria, fungi and some algae have cell walls. ● It is a rigid frame that wrap around the cell membrane and helps to provide strength, protection and support. Remember these things don’t have bones like animals do. Plant-specific Organelles Chloroplasts ● Found only in plant cells and some algae. ● Contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. ● Chlorophyll converts energy from the sun into usable chemical energy in the form of sugar. SUMMARY - Differences between plant and animal cells ● Plants have cells walls and chloroplasts ● Plants have chlorophyll, used for photosynthesis. ● Plants have a large central vacuole used for support. ● Plant cells store energy as starch or oils while animal cells store energy as glycogen, carbohydrates or lipids in the form of fats. ● Some animal cells have specialized compounds like hemoglobin. ● Animal cells have centrioles, which are used in cell division. What we’re working on Pg 16 #1-5 Pg 25 #1-5