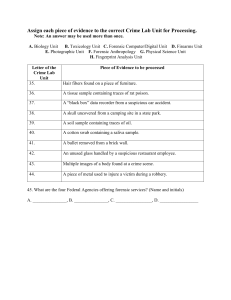
1. Introduction to Forensic Science: o Lesson 1: Basics of Forensic Science Explore the history and significance of forensic science. Understand its interdisciplinary nature (biology, chemistry, physics, etc.). o Lesson 2: Crime Scene Investigation (CSI) Discuss the importance of securing a crime scene. Learn evidence collection techniques (hair, fibers, soil, etc.). o Lesson 3: Forensic Pathology Study autopsies and cause-of-death determination. Explore famous forensic pathologists and cases. o Lesson 4: Forensic Anthropology Identify skeletal remains. Analyze bones for age, sex, and trauma. o Lesson 5: Forensic Odontology Study dental records and bite marks. Role of dentists in criminal investigations. o Lesson 6: Forensic Entomology Use insect evidence to estimate time of death. Case studies involving insects. o Lesson 7: Forensic Toxicology Analyze body fluids for drugs, alcohol, and poisons. Discuss famous toxicology cases. o Lesson 8: Forensic Serology Blood typing, DNA profiling, and paternity testing. Real-world applications. o Lesson 9: Forensic Ballistics Study firearms, bullets, and gunshot wounds. Trace evidence from firearms. o Lesson 10: Forensic Document Examination Authenticate signatures, handwriting, and documents. Detect forgery. 2. Crime Scene Protocols: o Lesson 11: Mock Crime Scene Simulation Set up a realistic crime scene. Students practice evidence collection. o Lesson 12: Fingerprint Analysis Learn fingerprint patterns and classification. Use powder, tape, and chemical methods. o Lesson 13: DNA Profiling Understand PCR, gel electrophoresis, and CODIS. Solve a DNA mystery. o Lesson 14: Trace Evidence Analysis Microscopic examination of fibers, hair, and soil. Analyze transfer evidence. o Lesson 15: Forensic Photography Techniques for documenting evidence. Importance of accurate photographs. 3. Forensic Psychology: o Lesson 16: Criminal Profiling Explore psychological profiling techniques. Case studies (e.g., the FBI’s Behavioral Analysis Unit). o Lesson 17: Eyewitness Testimony Discuss memory biases and reliability. Role of psychology in courtrooms. o Lesson 18: Interrogation Techniques Understand legal and ethical methods. Role-playing scenarios. o o Lesson 19: Victimology Study victim behavior and vulnerability. Empathy and support for victims. Lesson 20: Ethical Dilemmas in Forensic Psychology Discuss confidentiality, dual roles, and conflicts. Debates in the field.