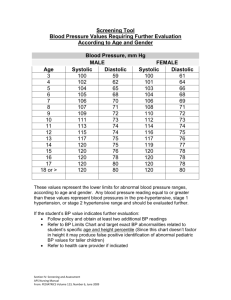
Practical Procedure for Carrying Out a Blood Pressure Test Blood pressure (BP) measurement is a fundamental clinical procedure used to assess the pressure exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels. Accurate BP measurement is crucial for diagnosing and managing various medical conditions, such as hypertension. The procedure can be performed using a manual sphygmomanometer and stethoscope or an automated blood pressure monitor. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide for both methods. Materials Needed Carrying Out a Blood Pressure Test Manual Method: Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Alcohol swabs earpieces) (for cleaning Automated Method: Digital blood pressure monitor stethoscope Pre-Test Preparation Patient Preparation: Ensure the patient is relaxed and seated comfortably with their back supported. The patient's feet should be flat on the floor, and legs should not be crossed. The arm used for the measurement should be bare, supported at heart level, and slightly flexed. Ask the patient to avoid caffeine exercise, and smoking for at least 30 minutes prior to the test. Allow the patient to rest quietly for 5 minutes before taking the measurement Equipment Preparation Check the sphygmomanometer for accuracy and ensure the stethoscope is clean and functioning If using an automated monitor, ensure it is properly calibrated and has fresh batteries. Equipment Preparation Procedure: Manual Method Cuff Placement: Wrap the blood pressure cuff snugly around the upper arm, positioning it so that the lower edge of the cuff is about 2.5 cm (1 inch) above the antecubital fossa (bend of the elbow). Ensure the cuff’s bladder is centered over the brachial artery. Positioning the Stethoscope: Place the stethoscope’s earpieces in your ears, ensuring they are pointed forward Position the stethoscope’s diaphragm over the brachial artery, just below the cuff’s edge. Equipment Preparation Inflation and Measurement: Close the valve on the bulb and inflate the cuff by squeezing the bulb until the pressure is about 20-30 mmHg above the expected systolic pressure (usually around 180-200 mmHg). Gradually release the valve to deflate the cuff at a rate of 2-3 mmHg per second. Listen for the first appearance of repetitive sounds (Korotkoff sounds). The pressure at which you hear the first sound is the systolic pressure. Continue to deflate the cuff and note the pressure at which the Korotkoff sounds disappear. This is the diastolic pressure. Recording the Results: Record the systolic and diastolic pressures, typically presented as “systolic/diastolic” (e.g., 120/80 mmHg). Automated Method Cuff Placement: Wrap the blood pressure cuff snugly around the upper arm, ensuring correct positioning as indicated by the monitor's instructions (usually similar to the manual method). Initiating the Measurement: Turn on the digital monitor and follow the on-screen instructions. Press the start button to begin the measurement. The cuff will automatically inflate and gradually deflate. Reading the Results: The monitor will display the systolic and diastolic pressures on the screen once the measurement is complete. Record the results as displayed (e.g., 120/80 mmHg). Automated Method Post-Test Procedures Patient Care: Remove the cuff from the patient’s arm. Ensure the patient feels comfortable and has no questions or concerns about the measurement. Interpretation of Results Normal Blood Pressure: Systolic < 120 mmHg and Diastolic < 80 mmHg Elevated Blood Pressure: Systolic 120-129 mmHg and Diastolic < 80 mmHg Hypertension Stage 1: Systolic 130-139 mmHg or Diastolic 80-89 mmHg Hypertension Stage 2: Systolic ≥ 140 mmHg or Diastolic ≥ 90 mmHg Hypertensive Crisis: Systolic > 180 mmHg and/or Diastolic > 120 mmHg (requires immediate medical attention) SOME OF HYPERTENSIVE DRUGS ARE amlodipine, diltiazem, verapamil, doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin, clonidine, methyldopa, hydralazine, minoxidil Interpretation of Results Normal Blood Pressure: Systolic < 120 mmHg and Diastolic < 80 mmHg Elevated Blood Pressure: Systolic 120-129 mmHg and Diastolic < 80 mmHg Hypertension Stage 1: Systolic 130-139 mmHg or Diastolic 80-89 mmHg Hypertension Stage 2: Systolic ≥ 140 mmHg or Diastolic ≥ 90 mmHg Hypertensive Crisis: Systolic > 180 mmHg and/or Diastolic > 120 mmHg (requires immediate medical attention) SOME OF HYPERTENSIVE DRUGS ARE amlodipine, diltiazem, verapamil, doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin, clonidine, methyldopa, hydralazine, minoxidil Safety and Accuracy Tips Always use the correct cuff size for the patient’s arm to ensure accurate measurements. Avoid talking to the patient during the measurement to prevent inaccuracies. Take multiple readings (at least two, spaced 12 minutes apart) and average the results for greater accuracy