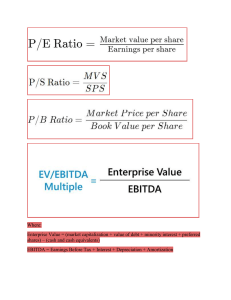
Liquidity, Solvency, Profitability Gross Profit = Net Sales - COGS Net Sales = Gross Sales - Sales Returns - Allowances - Discounts Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue - COGS)/Revenue * 100 Operating Profit = Gross Profit - Operating Expenses Accounts Receivables and Sales Transaction Practice 1- Jenkins and John Company have prepared the following aging schedule for the company at December 31, 2014. Number of Days Outstanding Total 0–30 31–60 61–90 91–120 Accounts receivable $375,000 $220,000 $90,000 $40,000 $10,000 % uncollectible 1% 4% 8% 16% Estimated bad debts 15100 2200 3600 3200 1600 Over 120 $15,000 30% 4500 1. Complete the table to include the estimated bad debts 2a. Assuming the company has a $2,500 debit balance in the allowance account at the beginning of the period, write the journal entry to record bad debt expense in the journal below. 2b. Assume that in the current year, Jerkins and John identify an account to be written off for $5000. Prepare the write-off journal entry. Date Accounts DEBIT CREDIT 2a Bad Debts Expense 17600 Allowance for ADA 17600 15100+2500 2b ADA 5000 A/R 5000 2c Show the NRV of Accounts Receivable after the above journal entries: Net Realizable Value = Total A/R - ADA Before Write-off NRV= 375000-15100 = 359900 Accounts Receivable= 375000-5000=370000 Less: ADA = 15100-5000=10100 Net Realizable Value = 370000-10100=359900 More Capital Asset Practice On May 5, 2014, Knottinghill Company purchased a property for $400,000 cash. The property included the following long-lived assets and closing costs: Appraised Value Land $105,000 Building 200,000 Equipment* 100,000 Paved area 20,000 Outdoor Lighting 10,000 Closing Costs on the Land Purchase 15,000 $450,000 *Annual Insurance for the equipment is expected to be $2,400. Instructions a. Give the journal entry to allocate the purchase price between the above assets. Round all amounts to the nearest dollar, if necessary. appraised value/ total appraised value * purchase price Land = 105000+15000 = 120,000 [120,000/450,000 * 400,000] = 106,667 Building = 200,000 [200,000/450,000* 400,000] = 177,778 Equipment = 100,000 [88,889] Land Improvements = 30,000 [26,667] Total Appraised Value = 450,000 Journal Entry: Land 106,667 Building 177,778 Equipment 88,889 Land Improvements 26,666 Cash 400,000 b. Prepare a compound journal entry to record depreciation of the long-lived assets on December 31, 2014, assuming the following additional details: Useful Life in Years Residual Value Rate Building 30 $20,000 Equipment 5 10,000 Land Improvements 5 -0100%/5*2 = 40% Prorate depreciation based on the number of months the asset has been in use. Use DECLINING BALANCE for the Land Improvements and STRAIGHT-LINE for the Building. The equipment has an estimated total of 1,500,000 machine hours and used 90,000 in the current year. Land Improvements = DDB Rate = 100%/5yr*2=40%*26,666=10,666*8/12=7111 Equipment = [88889-10000]/1500000*90000=4733 Building = [177778-20000]/30*8/12=3506 Amortization Expense Accumulated Amortization - Building Accumulated Amortization - Equipment Accumulated Amortization - Land Improvements 15,350 3,506 4,733 7,111 The entry to record shares issued for cash (IPO): Dr.___Cash_______________ Cr. ____Common Shares_ or _Preferred Shares__________ The entry to record shares issued for non cash goods/services: RULE: Under IFRS, use the fair value of the goods/services RECEIVED by the corporation issuing the shares (if possible). Otherwise, use the current market value of the shares given up. Dr. ___eg. Legal fees_or equipment___ Cr. ___Common Shares__or Preferred Shares