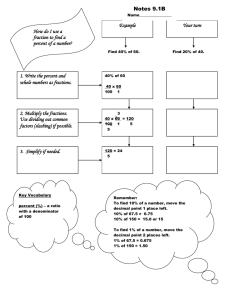
www.mymathscloud.com © MyMathsCloud GCSE/iGCSE Maths Formulae Sheet Area of Parallelogram Area of Rectangle Area of Trapezoid Circumference & Area: Circle Length of an arc ! " ! " Cuboid Volume Cylinder Surface Area Cylinder Volume Cone Surface Area Cone Volume Sphere Surface Area Sphere Volume Prism Volume Pyramid Volume Multiplication Division Negative Powers Fractions Find percentage of an amount Given % of an amount, find the full amount Increasing/decreasing by a % Density base x height !×# # $%& # $%& Pressure × 2() Quadratic Function: Solutions to QRC + SR + T = U Completing The Square QRC ± SR + T = U Max/Min Value SSS SAS AAS RHS "## &'( "## , c./ *° = , 1!2 *° = $%# $%# &'( . - / " ;0 = C √;E / - Percentages ; as a percentage of : ; × 100 : Look for the words as a percent of 1233454674 852926:; × 100 Look for the words percentage gain/loss/increase/decrease % × ;HIJKL 100 MN9=K ;HIJKL % 100 % amountA1 ± B Cumulative frequency Box Plot This is a running total of the frequencies % !±$%% Interest: = ;HIJKL × % × 1@UXY 5== % !&& × LNH= Note: Make sure t and % are same unit of time FV = PVA1 + B !&& B Fraction Of Amount Improper to Mixed Mixed to Improper + ;KZ − Fractions × Fractions ÷ Fractions Decimal to Fraction Decimal to Percent Fraction to Decimal Fraction to Percent Straight Line Equation Methods to find straight line equation @ ,(±√(&,E'F "' Finding a side: !! = #! + % ! − 2#% cos < Finding an angle: # ! + % ! − !! < = cos 45 = > 2#% 1 !#/@2A 2 & / Finding a side: = = Step 1: Find a factor of both numbers i.e. a number that fits in both the numerator AND denominator Step 2: Say how many times for each Step 3: Check whether you can do steps 1 and 2 again. ' of amount ( Step 1: Divide amount by b Step 2: Multiply answer found by ; Step 1: Divide the numerator by the denominator. Step 2: Write down the whole number a Step 3: Put the remainder in the numerator. The new denominator remains the same as that of the original improper fraction. Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the fraction’s denominator Step 2: Add that to the numerator Step 3: Then write the result on the top of the original denominator Need a common denominator (the smallest number that that both the numerator and denominator fit into) Don’t need common denominator. Can cancel diagonally or vertically, not horizontally. Don’t need common denominator. “Keep change flip” Write over 10,100,1000 etc depending on how many places after the decimal and simplify. Multiply by 100 Write as an equivalent fraction over 10,100,1000 etc and then easy to divide by this number OR Use short division if can’t write as an equivalent fraction Turn into a decimal and then just a decimal to percent question i.e. multiply decimal found by 100 Divide by 100 Write over 100 and simplify Geometry • Slope intercept . = H- + % • General ;- + :. + Z = 0 (get rid of fractions and move all on one side to get into this form) . = H- + % Step 1: Find gradient H • Given a graph – pick any 2 points on BHIJ the graph and use Area of Triangle Sine Rule )*+, )*+. )*+0 & / = = )*+, )*+. )*+0 Finding an angle: Circle Theorems Angle at the centre is double the angle at the circumference Angles subtended in the same segment by a chord are equal Angle in a semicircle is a right angle A tangent meets a radius at BC° Opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral add to DEC° Watch out: All points need to be on the circumference! Alternate segment theorem: The angle between a tangent and a side of a triangle is equal to the opposite angle For two intersecting chords, the products of their diagonals are equal !# = %F !(! + #) = %(% + F) B?- • Told parallel to another line⟹ same slope • Told perpendicular to another line ⟹”flip fraction and change the sign (slopes multiply to make −1) / ,/ • Given 2 points. Use formula & $ FV=future value, PV=present value L=times, )= interest rate Quadratics -= & / = = )*+, )*+. )*+0 123 , 123 . 123 0 Finding an angle: = = & / Finding a side: Fractions/Decimals/Percentages Simplifying Fractions Percent to Decimal Percent to Fraction =0>?-@ Non Right-Angled Trigonometry Sine Rule Cosine Rule !&& + if increase − if decrease FV =amount + T!U.V21 × Exact Values EF?GD?+/% /C&)) H*'>$ /&>?I"F% EF?GD?+/% Angle= × 360 >">&C $ + if increase − if decrease Look for the words originally, at the beginning, before… Compound Interest (interest added also earns interest) sin * ° = Frequency density = Pie chart × () " 1 =Area of cross section x height 1 1 = × :;<= ;)=; × ℎ 3 Indices - ' × - ( = - ')( (- ' )( = - '( (%- ' . ( )+ = % + - '+ . (+ -' - ' ÷ - ( = ( = - ',( 1 - ,- = ,! . / . .! A B = ! and A B = ! Reverse percentage Simple Interest (interest on initial amount) SOHCAHTOA Statistics Frequency Density 3D Shapes ,+ = 2-. + 2-0 + 2.0 where x, y , z are side lengths 1 = -.0 where x, y , z are side lengths ,+ = 2()ℎ + 2() " Note: Curved part: 2πrh 1 = () " ℎ ,+ = ()! + () " Note: Curved part: ()! where ! is slant length 1 1 = () " ℎ 3 ,+ = 4() " Note: Hemisphere 3() " 4 9 = () $ 3 " Note: Hemisphere= () $ / Percentage gain/loss (wants answer as a %) speed= % = 2(), + = () " Fractional Powers One amount as a % of the other amount (wants answer as a %) x base x height Pythagoras '*)>&+/? >*A? A&)) density= B"CDA? E"F/? pressure= &F?& Speed (sum of parallel sides) x height Area of a Sector Cuboid Surface area Right Angled Trigonometry !! + # ! = % ! Hint: Given hyp⟹subtract, finding hyp⟹add Compound Measures 2D Shapes Area of Triangle ,; ≠0 Extra helpful facts to remember: .&,.$ : " :" ; W- ± X + % − 2; 4; :" %− 4; Congruent Shapes Three sides of each triangle equal Two sides and included angle equal Two angles and corresponding side equal Contains right angle and hypotenuse and another side equal Proportion . is … proportional to G Directly: . = Y- , Inversely: . = . Straight Line Gradient Distance between 2 points (RK , \K ), (RC , \C ) Coordinates of midpoint of (RK , \K ), (RC , \C ) Circles Step 2: Find . intercept % • Given a graph – where the line crosses the . intercept • Plug point in(make sure this using correct point-line must pass through it). .", .! H= -", -! ](-", -! )" + (.", .! )" A -!) -" .!) ." , B 2 2 (- − ;)" + (. − :)" = ) " centre (;, :), radius ) Series (iGCSE only) IJK term: u3 = a + (n − 1)d sum of n terms n 2 S3 = [2a + (n − 1)d] = (! + P) 2 2 where ! =first term, d= common diff, P=last term Geometric sequence: u3 = ar 345 6(548!) 6(8!45) S3 = = ,r≠1 548 845 where ! =first term, r= common ratio Differentiation (iGCSE only) Rule * + ⟹ 2* +45 Remember: Constants go to 0 '% Turning/Stationary Points Solve = 0 ': (Max/Min) Proving whether Use knowledge of shape of graph Max/Min +* ! happy face min −* ! sad face max ; +* max on left, min on right ; −* min on left, max on right Arithmetic sequence: