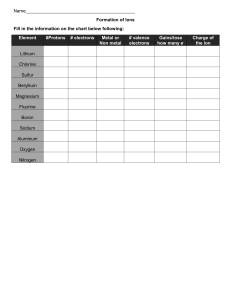
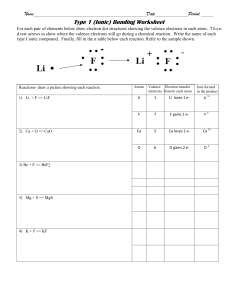
Ionic bonding activity Valence electrons are electrons in the outermost electron shell of an atom. The number of valence electrons largely defines the properties of the element, and relates to the group number. 1. Complete the following table: Element Number of Electronic outer shell Electron dot configuration (valence) model electrons Oxygen (2,6) 6 Lithium (2,1) 1 Fluorine Aluminium Sodium Chlorine Bromine (2, 8, 18*, 7) Magnesium Hydrogen * For elements beyond 20 electrons, our rule of 2,8,8 doesn’t apply Data table 1 2. A stable ‘octet’ is a valence (outer shell) arrangement of _________ electrons. a. 1 b. 6 c. 8 d. 12 3. Metals tend to ___________________________ electrons to form positive cations. a. gain/accept b. lose/donate 4. Non-metals tend to_________________________ electrons to form negative anions. 5. Complete the following table: Element Will it gain or How many Ion Metal or lose electrons electrons will it symbol non-metal? to become an gain or lose during with ion? ionisation? charge Oxygen non-metal gain e - 2 O Lithium metal lose e - 1 Li non-metal gain or lose 1 in either case H or H 2- + Fluorine Aluminium Sodium Chlorine Bromine Magnesium Hydrogen - + Data table 2 Ionic compound created Electron dot models Electron dot model including transfer of formula unit for the ionic electrons compound Hydrogen and Fluorine HF Lithium and Hydrogen Sodium and Chloride Magnesium and Oxygen Magnesium and Bromine Data table 3 Ionic compound created Electron dot models Electron dot model including transfer of formula unit for the ionic electrons compound Lithium and Oxygen Aluminium and Oxygen Aluminium and Fluorine Data table 4 ● Ionic compounds are formed when metal atoms react with non-metal atoms. ● Metal atoms lose their outer electrons to form positive ions (cations). ● Non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negative ions (anions). ● The positive and negative ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction between opposite charges. ● This force of attraction is known as an ionic bond, which holds the compound together.