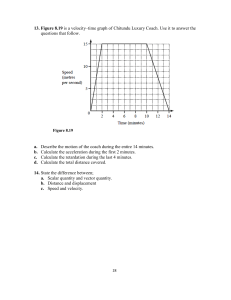
-2 -3 LIST OF PHYSICAL CONSTANTS Item 1 refers to the following and their base units. Universal gravitational constant G Specific heat capacity of water Specific latent heat of fusion of ice Specific latent heat of vaporization of water atm P 1.00 x 10 kg m (C) (D) L 3.34 x 10° J kg L, 2.26 x 10° J kg! N 6.02 x 10 per mole R 8.31 J K mo! 5.67 x 0 2. 6 Acceleration Which group of physicalquantities contains Avan of mass 2500 kg travelling due south collides with a car of mass 1500 kg travelling due north at 80 km hr. If the two vehicles fuse on impact, what is the final velocity and direction of the vehicles? Time (B Mass (C) Speed Displacement Force Distance Energy Power AccelerationForce 7. 82.5 kmn hr (D) 82.5 km hr exceed due south due north A metal case is dropped out of a the case just before it hits the (A) (B) (C) (D) 273.16 K hovering ground? 0.0 ms-! 8.2 m s! 28.0 ms! 39.6 m s! 49 kg ± 1 kg 49 kg ± 2 kg (C) 50 kg ± 1 kg (D) SI kg + 2 kg 8. In an inelastic collision Which of the dimensions of constant, G? (A) m s2 (B) (C) (D) kg' m' s² ing units gives the universal gravitational between two bodies, which quantity remains constant? (A) GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE 7.5 km hr' due north hitting the ground. What is the velocity of suitcase? 4. 7.5 km hr' due south (B) (C) helicopter and plummets 80 m before Mary is on her way to New York and wants the 50 kg limit. She stands on the scale and finds her mass is 55 kg + 1 kg. She then lifts her suitcase and the mass changes to 104 kg 1kg. What is the mass of her 1000 kg 8.89 s (A) (A) Velocity (A) (B) (D) at 60 km hr to ensure that her suitcase does NOT 6.626 x104 Js T, Speed Distance (D) Momentum 340 m s! (C) 0.37 s 0.61s 2.98 s Force W m²K4 3.00 x 10 ms Planck's constant represent? only vectors? 3. Speed of sound in air 1tonne (A) (B) 4200 Jkg' K Speed of light in free space (vacuum) Triple point temperature JK-1 C, Stefan-Boltzmann's constant What quantity does 1 A tennis ball is given a velocity of 8m s' when it is hithorizontal at a height 1.8 m above the ground. The ball is in the air for (A) (B) R: kg m's 1.00 x 10Nm 1.38 x 10- Avogadro's constant Molar gas constant P: kg m 6.67 x 10-" Nm² kg ² 9.81 ms Boltzmann's constant Density of water 5. Q: kg ms Acceleration due to gravity 1Atmosphere quantities (B) (C) (D) Momentum of cach body Kinetic energy of each body Total momentum of the system Total kinetic energy of the system kg m²s! kg- ml _-! GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE -4. 9. An object of mass 400 g is attached to a string. The mass is set in circular motion such that it moves in the with a radius of 0.77 m. horizontal plane -5 Item 12 refers to the following graph which 14 A truck is moving at a speed of 40 m s but the engine is only producing 20 kWof shows the velocity of a small ball bearing useful power. What is the driving force travelling through ameasuring cylinder of produced by the engine? glycerine. What is the anticipated of the object if it takes 16 acceleration s to complete 20 revolutions? (A) (B) (C) (D) 10. 19.5 m s (A) (B) (C) 500 N 800 N S00 kN (D) 800 KN 15. 74.0 m s Two cars that have the same kinetic travel with a velocity of V, and V,. energy If the mass of the first car is twice the mass of the second car, which of the Its acceleration is zero. It moves with the same 12. The points labelled X and Y respectively velocity as (A) (B) Its angular velocity is equal to that (D) the earth. (C) of the earth. (D) geographical location changes A rocket in gravity-free space is 5.0 x 10° kg of fuel Iper second. The burning exhaust gases are expelled at 8.0 x 10 ms relative (B) (C) (D) Amplitude first car? force and acceleration terminal velocity and acceleration acceleration and terminal velocity uniform velocity and displacement (2000 kg Lo to the rocket, whose mass is 2.0 x 10 kg at that time. What is the rocket's acceleration? (A) (B) expressions represents the velocity of the represent (B) 2V, 2 (C) (C) Item 13 refers to the following diagram which shows a bus of mass 2000 kg travelling down a hill of vertical height 50 m. as the earth rotates. 11. Amplitude following (A) (C) (A) Time 56.7 m s² satellite? (B) Which of the following graphs represents abody undergoing critical damping? 47.5 m s Which of the following statements describes the motion of a geostationary (A) 17. Amplitude (D) 2 Time 16. The displacement of a particle undergoing simple harmonic motion is given by (D) Ampiltude x=8 sin 0.4 nt. 10 ms2 20 m s² 50 m The frequency of oscillation of the particle is 400 m s Time 2500 mn s X 13. Assuming there is no energy loss, what is the speed of the bus at point X? (A) 11.0 m s-! (B) (C) 15.7 m s! 22.2 ms! (D) 31.3 ms! GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE (A) (B) (C) (D) 0.2 Hz 0.4 Hz 5.0 Hz 8.0 Hz GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE -7 -6 20. 18. Two sources of water waves, X and Y, generate waves which are of identical frequency but out of phase by 180°. The waves from Xare of amplitude S m and the waves from Yare of amplitude 3 m. Which ofthe following graphs BEST represents the between total energy, E,. potential energy, E,, kinetic energy. E, , and displacement ofarelationship particle moving in a straight line with simple harmonic motion? (A) Energy Which of the following statements is NOT true about a progressive wave? (A) It consists of one wave moving in (B) It appears to travel from one point (C) Energy is not transferred along the (D) It consists of crests and troughs. a single direction. Which of the following graphs correctly describes the oscillation ofa particle which (C) Energy 21. to another. is equidistant from Xand Y? wave. Displacement(m) -E, 22. (A) (B) (D) Energy Time E, Displacement Displacement Abeam of monochromatic light is incident normally on a diffraction grating having 500 lines per millimetre. If the second order of diffraction is found at 30° to the normal, what is the wavelength of light used? Energy Displacement(m) (A (B (C) (D) E E, (B 480 nm 500 nm S60 nm 600 nm E, Displacement Displacement(m) Displacement 2 (C) 19. Time Stationary waves are produced by superimposing progressive waves of frequency 500 Hz. Successive nodes are separated by a distance of 2 m. What is the speed of the progressive waves? (B) 125 m s 250 m s (C) 1000 ms (D) 2000 ms (A) Displacement(m) (D) ( GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE Time GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE -8 -9 23 The following displacement-position graph represents a stationary wave at two different instants. Item 27 refers to the following diagram which shows a snapshot of a rope as a Displacement 30 25 cm from the eye. The focal length of the lens needed to correct this defect is (A) Position 27. The distance PQ represents half the (A) Which of the following sets of arrOws correctly shows the directions of the motion of points X, Y and Z on the rope? period (B) velocity (C) amplitude wavelength (D) X Y 31. Z true about polarization? (A) Transverse waves can be polarized. (B) Longitudinal waves can be polar (C) Polaroids only allow vibrations in ized. one direction to pass through them. (D Polarization is used to differentiate between transverse and longitu dinal waves. 26. Which of the following statements is NOT (D) (A) Noise is an unintended or unwanted 28. Noise is determined by the pitch of (C) Loudness is determined by the intensity of sound. 1.6 mm 2.9 mm 5.3 mm 30 cm 150 cm A resistance thermometer has a resistance (A) (B) 34.35 °C 65.60 C (C) (D) 152.32 °C 291.12 °C (D Loudness is a subjective sensation (A) (B) (C) and is dependent on the listener. (D) changing temperature? (A) 0.60 0.80 (B) (C) (D) 1.25 1.50 A student's range of hearing is from 40 Hz to 15 kHZ. What is the SHORTEST Which of the following instruments is MOST Ssuitable for measuring a rapidly sound. 33. (AY 0.022 m 0.045 m 8.25 m (C (D) Resistance thermometer Alcohol-in-glass thermometer Mercury-in-glass thermometer true about matter? wavelength of sound that she can hear if the (B Thermocouple Which of the following statements is/are Whilst speed of sound in air is 330 ms1? 0.2 mm? (B) (C) (D) 32. refractive index of the medium is (B) of the yellow fringes formed on a screen 1.8 m from a double slit with a spacing of 0.2 mm As light travelling in air enters a medium, its speed changes to 2.4 x 10 ms. The sound. The wavelength of a yellow light source is 5.89 x 10 m. What is the separation (A) (C) (D) true about sound? 29. 25 5 cm 25 cm in a boiling liquid. What is the at which the liquid is boiling? temperature (A) (C) Which of the following statements is NOT (B) of 35.00 Q at the ice point, 42.54 Q at the steam point and 37.57 2 when immersed (B) 24. The near point ofa defective eye is 30 cm from the eye. The normal near point is transverse wave passes along it from left to right. substance is melting. its temperature remains constant. The triple point ofa substance has a constant value. The boiling point of a liquid does not depend on the pressure ofthe 22.0 m surroundings. (A) I only (B) (C) I and Il only Iland Il only (D) 1, II and III GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE - 1|- - 10 - 34. Item 39 refers to the following diagram showing the P-V graph for a gas undergoing a cycle from A-+B+C+D’A. The equation which defines the relationship between the heat capacity and specific heat capacity of an object is (A) (x 10) Specific heat capacity =heat capacity mass (B) PIPa Heat capacity = Specific heat capacity mass (C) Mass = heat capacity x specific heat capacity (D) Specific heat capacity = nass² x heat capacity B 1.6 0.8 0.4 35. Water falls from a height of 500 m. What A small black sphere has an absolute an enclosure whose walls are at a higher to internal energy in the water? absolute temperature, T,. The net rate of (A) 36. 37 is the rise in temperature of the water at the bottom, ifall the energy gained is converted (B) 0.19 K 0.24 K (C) 0.49 K (D) 1.17 K temperature, T,. It is hung in the centre of gain of thermal energy by the sphere is proportional to (A) (T (B) (C) (D) (TJ- (T) Metals are generally better thermal 1.4 1.6 2.0 V/m (x 10) 39 (T,y How much work is done on the gas during the process (A) 0.16 J (B) 1.6J 6.4 J 8.0 J (C) (D) (T,-T)" C’D? conductors than non-metals because 38 (A) they contain free electrons (B) they contain more electrons (C) their molecules are closer together their molecules are less firmly (D bonded A contractor builds an office window of 40. In the kinetic theory of an ideal gas, height 150 cm and width 200 cm with a (A) glass pane of thickness 0.5 cm. The tem (B) perature difference across the glassis 15K (C) and the thermal conductivity of the glass is 0.65 W m-' K-. What is the heat energy (D) per second conducted through the window? (A) (B) (C) (D) 1.63 kW 5.85 kW 163 W 585 W GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE 41. which of the following assumptions is NOT corect? The molecules have negligible The duration of a collision is attraction for each other. negligible compared with the timne between the collisions. The volume of the molecules is The molecules have negligible negligible compared with the volume in which they move. momentum change on collision with the container walls. Helium gas is kept in a container at a 0.92 kg m', what is the root mean squarepressure of 1.7 x 10 Pa. If the density of helium is speed of the helium atoms? (A) (B) (C) (D) 248 m s! 330 m s! 430 m s-! 745 m s-! GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE - 13 - 12 Item 42 refers to the following graph which shows the force extension in millimetres, E, of a material. Item 44 refers to the following force-extension graph for a newtons, F, required for the region where elastic deformation oOccurs. F(N) Force/N E(mm) 42. stretched wire. OX represents the 120 According to the graph, which of the following statements is/are true? 90 The graph represents the extension of a metal. The graph represents the extension of rubber. 60 Plastic deformation is predominant. 30 43. (A) (B) (C) Ilonly (D) II and III only I only Iand III only 40 In the equation for the first law of thermodynamics, AU =Q+ W. Which of the following pairs of phrases is true of Q and W? 44. (A) (D) Heat lost by the system Work done on the system (B) Heat lost by the system Work done by the system (C) Heat supplied to the system Work done by the system (D) Heat supplied to the system Work done on the system GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE 80 Extension/um What is the strain energy stored in the wire for an extension of 40 um? (B) (C) (A) 60 1.2 uJ 2.4 J 1.2 mJ 2.4 mJ GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE - 14 - Item 45 refers to the following forceextension graph of two different wires. FIN 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 2 45. 4 6 Elmm What is the difference in energy stored between the two wires when extended 6 mm? (A) (B) 0.06 J 0.12 J (C 0.18 J (D 0.30 J END OF TEST IF YOU FINISH BEFORE TIME IS CALLED, CHECK YOUR WORK ON THIS TEST.