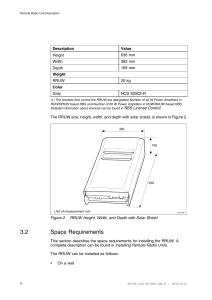
RBS Description RBS 6101 and RBS-TMR 6101 DESCRIPTION 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD Copyright © Ericsson AB 2010–2013. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced in any form without the written permission of the copyright owner. Disclaimer The contents of this document are subject to revision without notice due to continued progress in methodology, design and manufacturing. Ericsson shall have no liability for any error or damage of any kind resulting from the use of this document. Trademark List All trademarks mentioned herein are the property of their respective owners. These are shown in the document Trademark Information. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Contents Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Product Overview 3 2.1 Main Features 3 2.2 Optional Equipment 4 3 Technical Data 9 3.1 Dimensions 9 3.2 Space Requirements 10 3.3 Environmental Characteristics 12 3.4 Power Supply Characteristics 15 3.5 System Characteristics 17 4 Hardware Architecture 19 4.1 RBS Overview 19 4.2 RBS-TMR Overview 22 4.3 Space for Optional Equipment 24 5 Multistandard Configurations 27 5.1 Single Mode 27 5.2 Mixed Mode 27 6 Connection Interfaces 29 6.1 RBS 30 6.2 RBS-TMR 36 6.3 Position A, ESD Wrist Strap Interface 39 6.4 Position B, Grounding Interface 40 6.5 Position C, SAU Interface 41 6.6 Position D, External Alarm Interface 42 6.7 Position E, Radio Interface 43 6.8 Position E, Transmission Interface 45 6.9 Position E, LMT Interface (Optional) 45 6.10 Position F, GPS Interface or Power Cable Outlets 49 6.11 Position G, Power Connection Interface 52 6.12 Position H, Antenna Interface or Transmission Cable Inlet 54 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 RBS Description 6.13 Position I, Service Outlet Interface (Optional) 55 7 Transmission Standards 57 7.1 Electrical Ethernet (Optional) 57 7.2 Optical Ethernet (Optional) 59 7.3 E1, T1, and J1 (WCDMA only) 60 7.4 E1 and T1 (GSM only) 62 7.5 STM-1 63 8 Alarms 65 8.1 Internal Alarms 65 8.2 External Alarms 65 9 Acoustic Noise Emission 67 10 Standards, Regulations, and Dependability 69 10.1 Regulatory Approval 69 10.2 Dependability 71 10.3 Spare Parts 71 10.4 Vandal Resistance 71 10.5 Transportation and Storage 71 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Introduction 1 Introduction This document is a general description of the RBS 6101 and the Transmission Rack version, RBS-TMR 6101. All sections and subsections of this document are applicable to the RBS. However, not all sections or subsections in this document are applicable to the RBS-TMR. If a section or a subsection is not applicable to the RBS-TMR, it is indicated by a sentence at the beginning of the section or the subsection or at any other appropriate place in the document. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 1 RBS Description 2 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Product Overview 2 Product Overview The RBS 6101, a member of the RBS 6000 family, is an outdoor RBS. The RBS consists of an outdoor cabinet that can be configured with either internal or external Radio Units (RUs), or a combination of both internal and external RUs. The external unit can be a Remote Radio Unit (RRU) or an Antenna Integrated Radio (AIR) unit. The RBS has the capacity to power feed external radio units from the cabinet. An optical cable connect each external radio to the cabinet as shown in Figure 1. For more information about RUs and RRUs, refer to Radio Unit Description and Remote Radio Unit Description, respectively. For more information about AIR, refer to Antenna Integrated Radio Unit Description. AIR Unit / RRU AIR Unit Antenna AIR Unit / RRU Optical cables RRU RF cables RBS with Internal RUs Ge3011A Figure 1 2.1 RBS with Internal and External Radios Main Features This section describes the main features of the RBS and RBS-TMR. Note: Not all features are supported by all RBS configurations. Current RBS configurations can be found in RBS Configurations. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 3 RBS Description 2.1.1 RBS The main features of the RBS are the following: • Supports GSM, WCDMA, LTE, and CDMA standards. • Supports single mode and mixed mode multistandard configurations. For more Information about single mode and mixed mode multistandard configurations, see Section 5 on page 27. • Includes transmission equipment and internal battery backup. • Can be equipped with various RUs, RRUs and AIR units. • Can be equipped with Digital Units (DUs). • Can be configured with the Transport Connectivity Unit (TCU). • Can be configured with the AuXiliary Multiplexing Unit (XMU), the Channel Element Expansion Module (CEEM), and the Digital Baseband Advanced (DBA). • Has the following power supply alternatives: 0 100–250 V AC (supply voltage below 200 V AC must be connected phase-to-phase. Single-phase connection requires 200–250 V AC.) 0 -48 V DC (two-wire) • Supports up to 11U transmission spaces. • Supports Global Positioning System (GPS) as a synchronization source. • Supports external alarms. 2.1.2 RBS-TMR The main features of the RBS-TMR are the following: • Supports up to 13 U transmission spaces. • Has the following power supply alternative: 0 100–250 V AC (supply voltage below 200 V AC must be phase-to-phase connected. Single-phase connection requires 200–250 V AC.) 2.2 Optional Equipment The equipment presented in this section is optional and can be ordered separately. It is not necessary for basic RBS functions. The overview and position of optional equipment, which can be installed inside the RBS, is described in Section 4 on page 19. 2.2.1 ASC, TMA, RETU, and RIU This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. The following mast-mounted units are placed close to the antenna: • Tower Mounted Amplifier (TMA) • Antenna System Controller (ASC) 4 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Product Overview • • Remote Electrical Tilt Unit (RETU) RET Interface Unit (RIU) The TMA and the ASC are uplink amplifiers and improve the RX sensitivity. The RETU enables remote tilt of the antenna system. An ASC or an RIU is required to enable the RBS to communicate with the RETU. The RBS supports AISG 2.0/3GPP. 2.2.2 Battery Backup For RBS-TMR, there are no internal battery backups. Battery backup can either be external or internal. The external batteries are connected to an optional DC filter, the Power Connection Filter (PCF) inside the RBS. The maximum distance between the RBS and the external batteries is 10 m. The internal battery backup provides backup power from 5 to 15 minutes. Enersys BU 0102 (12Ah) is used for internal battery backup. 2.2.3 GPS This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. The RBS can be connected to a GPS unit, which is used for timing synchronization of the RBS. 2.2.4 Laptop Shelf The laptop shelf is an optional mechanical unit installed inside the cabinet. The shelf can be raised, with one hand, to either horizontal or a slightly angled position. 2.2.5 SAU This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. The Support Alarm Unit (SAU) is an alarm and connection unit installed in the RBS. It is connected to the Overvoltage Protectors (OVPs) also serve as external connections. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 5 RBS Description 2.2.6 Site Installation Alternatives The RBS can be installed directly to site ground, Generic Base Frame (GBF) 6101 or Battery Backup Unit (BBU) 6101. If the RBS is installed replacing an RBS 2116 or RBS 3116, an adapter frame could be used for mounting the RBS to site ground. More information on drill pattern can be found in Section 3.2.2 on page 11. 2.2.7 Site LAN The RBS supports Ethernet-based site Local Area Networks (LAN). 2.2.8 Transmission Equipment The RBS supports the following transmission solutions within the Transmission (TM) space: • MINI-LINK TN 2p • MINI-LINK TN 6p • MINI-LINK TN 20p • MINI-LINK TN 1p/MMU2Cs • MINI-LINK CN • Optical Multi Service (OMS) 846 • OMS 860 2.2.9 TCU This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. The TCU is the common transmission module in a multistandard RBS 6000. It is used to realize a common transmission node for GSM, WCDMA, LTE, and CDMA. The TCU supports backhauling of multistandard RBSs (including GSM/WCDMA/LTE/CDMA) over both Ethernet and E1/T1/J1 transmission services with advanced QoS and shaping functionality, minimizing the requirements on the transport network. The TCU is an 8U high and 31 mm wide unit. It requires -48 V DC, which is standard RBS voltage, minimizing the need for extra power supply. More information about the TCU can be found in TCU Description. Note: 6 The TCU is installed after all the required DUs have been installed. The TCU is installed in slot 17 in the Aux 8U unit compartment, if that slot is available. For more information about installing the TCU, see Installing RBS. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Product Overview 2.2.10 XMU The XMU provides general processing, multiplexing, radio interfacing, and synchronization by using GPS signals. The XMU supports CDMA and LTE RANs to be deployed with shared radios and the antenna plant. For more information about the XMU, refer to XMU Description. 2.2.11 DBA The DBA provides switching, traffic management, timing, baseband processing, and radio interfacing for CDMA. For more information about the DBA, refer to DBA Description. 2.2.12 CEEM The CEEM provides capacity expansion, digital card housing, air cooling, High Speed Serial Link (HSSL), and alarm interfacing. For more information about the CEEM, refer to CEEM Description. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 7 RBS Description 8 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Technical Data 3 Technical Data This section describes the physical characteristics, environmental data, and the power supply of the RBS. 3.1 Dimensions Table 1 lists the dimensions, weight, and color of the RBS. Table 1 Dimensions, Weight, and Color Dimensions Height (without adapter frame) 1450 mm Height (including adapter frame) Maximum 1520 mm Width 700 mm Depth (Including door) 700 mm Figure 2 shows the dimensions. Weight RBS maximum/standard equipped, without backup batteries 180 kg Color Gray 700 700 1450 Unit of measurement: mm Figure 2 1520 Ge0866A Dimensions 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 9 RBS Description 3.2 Space Requirements This section describes the RBS space requirements. 3.2.1 Installation requirements Minimum distances to provide adequate working space and to ensure sufficient airflow can be found in Figure 3 and Figure 4. 200** 100* 50** 100* 50** 700 Ge0876B Figure 3 10 Climate and Maintenance Requirements 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Technical Data 500*** 400** 150* 100** Ge0875B Figure 4 Earthquake and Climate Requirements * For earthquake proof installation. ** For climate requirements *** For maintenance requirements 3.2.2 Drill Pattern Figure 5 shows the drill pattern for the RBS. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 11 1 680 78 500 RBS Description 600 Front 90 50 700 Unit of measurement: mm Figure 5 3.3 Ge0895B Drill Pattern Environmental Characteristics This section describes the environmental characteristics of the RBS. 3.3.1 Operating Environment This section describes operating environment parameters for RBS operation. There are three operating environments for the RBS: normal, exceptional, and non-destructive. 12 • Normal: Under normal conditions, all units function as specified. • Exceptional: Under an exceptional environmental stress outside of normal operating limits, all units continue to function, but with reduced performance or capacity. When conditions return to normal, the systems resume 'Normal operation' status. • Non-destructive: Under a non-destructive environmental stress beyond exceptional limits, no equipment function is guaranteed, and performance may degrade in an unspecified manner. However, the equipment will still fulfill legal requirements and not become hazardous to people. When 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Technical Data conditions return to normal, no on-site intervention is needed to restore full RBS performance. Table 2 and Table 3 give the values for the RBS operating environment for an RBS with and without a heater, respectively. Table 2 Operating Environments with Heater Temperature (C) Relative Humidity (%) Normal -33 to +50 15–100 Exceptional -40 to +50 15–100 Non-Destructive -40 to +60 15–100 Operating environme nt Table 3 Operating Environments without Heater Temperature (C) Relative Humidity (%) Normal 0 to +50 15–100 Exceptional 0 to +50 15–100 Non-Destructive 0 to +60 15–100 Operating environme nt 3.3.2 Heat Dissipation The values in this list represents the worst-case heat dissipation of a fully equipped RBS, taking optional equipment and future expansion into account. Maximum heat dissipation 3.3.3 4800 W Acoustic Noise Summary Table 4 shows the sound pressure levels in accordance with EN ISO 11201, at a bystander position 1 m from the cabinet and 1.5 m above the floor. The calculations are valid for free field installation. If the RBS is located in a room, the sound pressure level will be higher than indicated in Table 4. The calculations are in accordance with EN ISO 11203. Table 4 shows the values for typical sub-configurations. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 13 RBS Description Table 4 RF Output and Sound Pressure Level at Bystander Position of 1 meter at 20C and 45C Temp in C Number of Radio Units RF output (dBm) Front dB(A) Left dB(A) Right dB(A) Back dB(A) 20 6 RUS 01 B4 LTE 48 44 39 40 43 6 RUS 02 B0 GSM 50 6 RUS 02 B3 GSM, WCDMA, LTE 49 49 45 48 46 6 RUS 02 B8 GSM, WCDMA, LTE 50 6 RUS 02 B0 GSM 50 6 RUS 02 B3 GSM, WCDMA, LTE 49 51 51 51 53 6 RUS 02 B8 GSM, WCDMA, LTE 50 45 Detailed information about acoustic noise emission is presented in Section 9 on page 67. 3.3.4 Vibration This section describes the RBS tolerance to vibrations. The RBS operates reliably during seismic activity as specified by test method IEC 60 068-2-57 Ff. Maximum level of Required Response Spectrum (RRS) 50 m/s2 within 2-5 Hz for DR=2% Frequency range 1–35 Hz Time history signal VERTEQ II The RBS operates reliably during random vibration as specified by test method IEC 60 068-2-64 Fh method 1. Random vibration, normal operation 0.05 m2/s3 Random vibration, safe operation 0.1 m2/s3 Random vibration, non destruction operation 0.2 m2/s3 The RBS operates reliably during shock as specified by test method IEC 60 068-2-27 Ea. 14 Peak acceleration 50m/s2 Duration 18 ms 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Technical Data 3.3.5 Materials The materials in the RBS are managed through the Ericsson lists of banned and restricted substances, based on legal and market requirements. 3.4 Power Supply Characteristics This section describes the power supply, power consumption, and fuse and circuit breaker recommendations for the RBS. 3.4.1 AC Power Supply Characteristics The AC power source must provide protection for overcurrent, short circuit, and ground fault. The sum of impedances of the AC source, distribution wiring, and overcurrent protection devices between the AC source and the RBS input terminal must be low enough to allow the overcurrent protection devices to clear an internal fault in the RBS within the time requirements stated in national wiring regulations. Note: Different requirements may apply in TN, TT and IT power systems. The AC-powered RBS is available for split-, single- or three-phase AC power system. Table 5 lists voltage values and ranges for AC power supply. Table 5 AC Power Supply Values and Ranges Conditions Nominal voltage (1) Operating voltage (1) 200 to 250 V AC 180 to 275 V AC Non-destructive voltage 0 to 300 V AC Operating frequency 45 to 65 Hz Recommended fuse for fully equipped cabinet PCU AC 01: Single/split-phase 63 A Three-phase 3×63 A Maximum cross-section al cable area PCU AC 01: 16 mm2 PCU AC 06: Single/split-phase 100 A Three-phase 3×63 A PCU AC 06: 35 mm2 (1) Phase-to-phase or phase-to-neutral. Fuse and Circuit Breakers for an AC-Powered RBS The RBS external AC fusing must meet the following characteristics: • Fuse, type gL-gG-gD, in accordance with IEC/EN 60 269-1 or UL 248-8. • Circuit breaker in accordance with IEC 60 947-2 or UL 489. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 15 RBS Description All power supply sources, both AC and DC, must have a circuit breaker with adequate breaking capacity in the supply circuit. Table 6 lists the minimum fuse and circuit breaker recommendations for the RBS. The figures are based on peak power consumption and give no information about power consumption during normal operation. Table 6 Minimum Fuse and Circuit Breaker Recommendations for AC-Powered RBS Voltage Range (1) 3 x PSU without Heater 3 x PSU with Heater 4 x PSU without Heater 4 x PSU with Heater 180–275 V AC, single-phase 40 50 50 60/63 90–132 V AC, split-phase 40 50 50 60/63 108–275 V AC, three-phase 15/16 30/35 30/35 30/35 (1) Single-phase value 3.4.2 DC Power Supply Characteristics This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. The DC-powered RBS is available with a two-wire -48 V DC supply. Table 7 lists voltage values and ranges for DC power supply. Table 7 Two-Wire -48 V DC Power Supply Conditions Values and Ranges Nominal voltage -48 V DC Operating voltage -40 to -58.5 V DC Non-destructive voltage 0 to -60 V DC Fuse and Circuit Breakers for a DC-Powered RBS The RBS external DC fusing must meet the following characteristics: • Fuse, type gL-gG-gD, in accordance with IEC/EN 60 269-1 or UL 248-8. • Circuit breaker in accordance with IEC 60 947-2 or UL 489. The fuse and circuit breaker recommendations given in Table 8 are based on peak power consumption and give no information about power consumption during normal operation. 16 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Technical Data Table 8 Fuse and Circuit Breaker Recommendations for DC-Powered RBS DC Power Recommended Fuse for Fully (1) Equipped Cabinet (A) Maximum Cross-Sectional Cable Area DC-powered PCF 01 01: 160 PCF 01 01: 95 mm2 -48 V, two-wire PCF 01 03: 250 PCF 01 03: 2×95 mm2 (1) Maximum fuse class in accordance with RBS design restrictions. 3.4.3 Power Consumption The following factors affect power consumption: • RBS configuration, both HW and SW • Operating conditions, traffic-related and environment-related • Specific component variations Refer to Power Consumption Guideline for RBS 6000 for detailed information regarding RBS 6101 power consumption in different configurations and operating conditions. 3.5 System Characteristics This section describes the system characteristics of the RBS. 3.5.1 RF Electromagnetic Exposure General information about Radio Frequency (RF) Electromagnetic Fields (EMF) can be found in Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields. Information about radio-access-specific compliance boundaries for electromagnetic exposure can be found in Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Exposure. 3.5.2 Software Information about software dependencies can be found in Compatibilities for Hardware and Software. 3.5.3 Radio Configurations This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. Information about available radio configurations can be found in RBS Configurations. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 17 RBS Description 18 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Hardware Architecture 4 Hardware Architecture This section contains information on both mandatory and optional hardware units based on a fully equipped RBS and an RBS-TMR. Note: 4.1 The currently available configurations are described in RBS Configurations. RBS Overview This section contains an overview of the standard hardware units required, regardless of configuration or frequency. Figure 6 shows the hardware unit locations, and Table 9 describes the hardware units in the RBS. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 19 RBS Description A B D G C F E J I D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 B2 B1 A3 A2 A1 48V XMU 02 01 H R S 10M K T HSSL L U M Q N O P Ge2234H Figure 6 Table 9 Position Hardware Units Hardware Units Name of Units No. of Units External fans 3 Heat exchanger 1 B Internal fans 2 C Heater 0–1 D SCU Description A More information can be found in Climate Unit Description. (1) 1 The SCU controls the fans and supports the external EC-bus, including power to the SAU. More information on the SCU can be found in SCU Description. E SHU (2) 1 The SHU connects peripheral units such as PSUs, PDUs, and the SCU to the DU. The SHU is required if the RBS is equipped with PSUs. More information on the SHU can be found in SHU Description. 20 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Hardware Architecture Table 9 Position Hardware Units Name of Units No. of Units Description Power subrack containing the units listed below. For more detailed information on the location of the units in the power subrack, see Non-RF Connections. PDU (3) 1–4 The PDU distributes fused -48 V DC power to the units in the RBS. More information on the PDU can be found in PDU Description. PCU (4) DC 0–1 The PCU is a DC interface for the RBS. More information on the PCU can be found in PCU Description. F BFU (5) 0–1 The BFU supervises, connects, and disconnects the battery backup. More information on the BFU can be found in BFU Description. PSU (6) 0–4 The PSU converts incoming voltage to -48 V DC. More information on the PSU can be found in PSU Description. PFU (7) 0–1 The PFU stabilizes the -48 V DC in the RBS. More information on the PFU can be found in PFU Description. G SAU (8) 0–1 The SAU is an alarm connection panel that connects external alarms and transmission through the OVP. More information on the SAU can be found in SAU Description. The DU provides switching, traffic management, timing, baseband processing, and radio interface. 0–3 DU More information on the DU can be found in Digital Unit Description. The RBS can support up to five DUs. For CDMA, the RBS can support up to 3 DUs. H TCU 0–1 The TCU is the common transmission module in a multistandard RBS. More information on the TCU can be found in TCU Description. XMU 0–1 The XMU provides general processing, multiplexing, radio interfacing, and synchronization of GPS signals. More information on the XMU can be found in XMU Description. I DU 1–5 For information on DU, see Page 21. DU adapter 0–1 The DU adapter is used for RBSs with external radios only. RU 0–6 The RU receives digital data and converts it to analog signals. It also receives radio signals and converts them to digital signals. (9) More information on the RU can be found in Radio Unit Description. XMU 0–2 For information on XMU, see Page 21. J Laptop shelf 0–1 A laptop shelf (optional) can be installed on the cabinet door. More information on installing the laptop shelf can be found in Replacing Internal Supplementary Parts. K Smoke detector 0–1 A smoke detector failure alarm is connected to the smoke detector. L Space for optional equipment M Internal light 0–1 The lighting for internal maintenance is activated by the opening of the door. N PCF (11) 0–1 The PCF connects -48 V DC power from the site DC power or the external battery backup to the RBS. (10) For information on space for optional equipment, see Section 4.3 on page 24. More information on the PCF can be found in PCF Description. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 21 RBS Description Table 9 Hardware Units Position Name of Units No. of Units O Bottom plate 1 OVP 0–12 Description The bottom plate holds cable inlets for routing Radio Frequency (RF) cables, transmission, OVPs and SPDs into the cabinet. (12) The OVPs protect the RBS from damages caused by overvoltage, and also serves as external connections. The OVPs can be installed on the DIN rail on the bottom plate and on the right wall of the cabinet. P SPD (13) The SPDs protect the RBS from damages caused by overvoltage and also serve as external connections for power feeding of external radio units. 0–10 The SPDs can be installed on the DIN rail on the bottom plate and the right wall of the cabinet. The PCU is an AC interface for the RBS. Q PCU AC 0–1 The PCU AC is equipped with a service AC power outlet. More information on the PCU can be found in PCU Description. DU 0-2 For information on DU, see Page 21. XMU 0-2 For information on XMU, see Page 21. DBA 0–2 The DBA provides switching, traffic management, timing, baseband processing, and radio interfacing for CDMA. R S More information on the DBA can be found in DBA Description. T CEEM 0-1 RU 0–6 The CEEM provides capacity expansion, digital card housing, air cooling, HSSL, and alarm interfacing. The unit can be equipped with XCEM and AEM. The RU receives digital data and converts it to analog signals. It also receives radio signals and converts them to digital signals. More information on the RU can be found in Radio Unit Description. U DU 1 For information on DU, see Page 21. XMU 1 For information on XMU, see Page 21. (1) Support Control Unit (SCU) (2) Support Hub Unit (SHU) (3) Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (4) Power Connection Unit (PCU) (5) Battery Fuse Unit (BFU) (6) Power Supply Unit (PSU) (7) Power Filter Unit (PFU) (8) Support Alarm Unit (SAU) (9) There is no position I in RBS configurations with 11U spaces for optional equipment in position L. (10) This is possible in doors equipped with six T30 screws on the internal side of the door. The laptop shelf cannot be used in BYB 405 07/08 with R-states earlier than R2B. (11) Power Connection Filter (PCF) (12) Alarm OVPs are twice the size of ordinary OVPs. (13) Surge Protection Device (SPD) 4.2 RBS-TMR Overview Figure 7 shows the hardware unit locations, and Table 10 describes the hardware units in the RBS-TMR. 22 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Hardware Architecture A D B C E G F H I J L M K N Ge3017A Figure 7 Table 10 Hardware Units RBS-TMR Hardware Units RBS-TMR Position Name of Units No. of Units A External fans 3 B Internal fans 2 C Heater 0–1 D SCU 1 Description More information can be found in Climate Unit Description. The SCU controls the fans and supports the external EC-bus, including power to the SAU. More information on the SCU can be found in SCU Description. E SHU 1 The SHU connects peripheral units such as PSUs, PDUs, and the SCU to the DU. The SHU is required if the RBS is equipped with PSUs. More information on the SHU can be found in SHU Description. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 23 RBS Description Table 10 Position Hardware Units RBS-TMR Name of Units No. of Units Description Power subrack contains the following units (for information about unit locations in the power subrack, see Non-RF Connections): 1–3 PDU The PDU distributes fused -48 V DC power to the units in the RBS. More information on the PDU can be found in PDU Description. F BFU 0–1 The BFU supervises, connects, and disconnects the battery backup. The BFU can be installed inside (internal BFU) or outside (external BFU) the cabinet. More information on the BFU can be found in BFU Description. The PSU converts incoming voltage to -48 V DC system voltage. 0–4 PSU More information on the PSU can be found in PSU Description. G 1 DU The DU provides switching, traffic management, timing, baseband processing, and radio interface. More information on the DU can be found in Digital Unit Description. (1) 0–1 A laptop shelf (optional) can be installed on the cabinet door. More information on installing the laptop shelf can be found in Replacing Internal Supplementary Parts. H Laptop shelf I Transmission Equipment J Smoke detector 0–1 A smoke detector failure alarm is connected to the smoke detector. K PCU AC 0–1 The PCU AC is the AC interface for RBS-TMR and also the internal RBS AC distribution unit. This space is used for transmission equipment. More information on the PCU can be found in PCU Description. L Internal light 0–1 The lighting for internal maintenance is activated by the opening of the door. M SPD 1 The SPD is for power feed of external equipment. N PCF 0–1 The PCF is an interface for external battery backup. More information on the PCF can be found in PCF Description. (1) This is possible with doors that are equipped with six T30 screws on the inside of the door. The laptop shelf cannot be used in BYB 405 07/08 with R-states earlier than R2B. 4.3 Space for Optional Equipment The RBS has a space that is intended for optional equipment. The space is 19 inches(1) (483 mm) and 2–11 U high (2 U if the RBS has internal batteries). The maximum measurement on the equipment is 483 mm + 0.5–11 U + 300 mm (width + height + depth). There are 40 mm space for cables at the front and the rear. For RBS configurations with 2 U up to 4 U spaces for optional equipment, 400 W is reserved in the power consumption budget and 240 W for heat dissipation. For RBS configurations with 11 U spaces for optional equipment, 1000 W is reserved in the power consumption budget and 600 W for heat dissipation. Note: 24 Ensure that any additional equipment being installed in the space is inserted from the bottom to top. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Hardware Architecture (1)According to IEC 60297-3. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 25 RBS Description 26 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Multistandard Configurations 5 Multistandard Configurations This section is not applicable to RBS-TMR. A multistandard RBS supports installation of nodes of different radio access systems in the same cabinet. The nodes must always be configured as primary or secondary nodes. In a multistandard RBS, the support system is shared between the nodes in the cabinet. Each radio access system node is managed separately using its own radio standard tools, but only the primary node controls and supervises the support system. Each node calculates its own cooling requirement; however, the primary node determines the fan speed according to the highest cooling requirement. Multistandard configurations can be either single mode or mixed mode configurations. The following sections describe single mode and mixed mode configurations in more detail. 5.1 Single Mode Single mode allows an RBS to be configured with different radio access systems within the same cabinet. More information on single mode can be found in Expanding to Multi-Standard Single Mode, RBS Configurations and Support System. Single mode allows the following combination of radio access systems: 5.2 • GSM and WCDMA • GSM and LTE • WCDMA and LTE • LTE and CDMA Mixed Mode Mixed mode allows nodes of different radio standards within a cabinet to share radio and antenna resources. Mixed mode requires a license. More information on mixed mode and supported configurations and frequencies can be found in Mixed Mode in Multistandard RBS, Expanding to Mixed Mode in Multistandard RBS and RBS Configurations. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 27 RBS Description Mixed mode allows the following combination of radio access systems: 28 • GSM and WCDMA • GSM and LTE • WCDMA and LTE • LTE and CDMA 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces 6 Connection Interfaces This section contains information about the connection interfaces of the RBS and the RBS-TMR, including the cable inlets. Section 6.1 on page 30 describes the connection interfaces of the RBS. Section 6.2 on page 36 describes the connection interfaces of the RBS-TMR. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 29 RBS Description 6.1 RBS Figure 8 shows the connection interfaces of the RBS, and Table 11 describes them. C A E F H I G D J B Ge0926B 30 Figure 8 Connection Interfaces for RBS Table 11 Connection Interfaces for RBS Position Description (1) A ESD wrist strap interface B Grounding interface C SAU interface D External alarm interface E Site LAN, LMT , or radio interface F GPS interface G Power connection interface H Antenna interface (2) 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces Position Description I Service outlet interface J Gas-ventilation tube interface (1) Electrostatic Discharge (2) Local Maintenance Terminal 6.1.1 Cable Inlets There are five variants of bottom plates with cable inlets.Table 12 shows which variants can be used in specific RBS configurations. Table 12 Bottom Plate Variants RBS Configurations No. of RUs No. of RRUs/A IR Units Variant RBS with Internal Radios 1–6 0 Variant 1 Variant 2 RBS with Internal and External Radios 1–6 1–3 Variant 2 1–3 1–6 Variant 3 RBS with External Radios 0 1–9 Variant 4 RBS with External Radios and MINI-LINK TN 20P 0 1–6 Variant 5 Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, and Figure 13 show the different bottom plates. Table 13, Table 14, Table 15, Table 16, and Table 17 describe the cable inlets of the bottom plates. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 31 RBS Description A B C D C E E F Ge0855C Figure 9 Cable Inlets, Variant 1 Table 13 Cable Inlets, Variant 1 Position Description A DC connection, including temperature sensor connection B AC cable inlet C RF cable inlet (antenna) D TM cable inlet E TM cable inlet Co-site cable inlet F 32 OVP cable inlet, GPS receiver cable inlet 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces A B C C D E F E Ge3029A Figure 10 Cable Inlets, Variant 2 Table 14 Cable Inlets, Variant 2 Position Description A DC connection, including temperature sensor connection B AC cable inlet C RF cable inlet (antenna) D TM cable inlet E TM cable inlet Co-site cable inlet F OVP cable inlet (small) SPD inlet cable (large) 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 33 RBS Description A B C D G E F E Ge2813A Figure 11 Cable Inlet, Variant 3 Table 15 Cable Inlets, Variant 3 Position Description A DC connection, including temperature sensor connection B AC cable inlet C RF cable inlet (antenna) D Optical cable inlet E TM cable inlet Co-site cable inlet F OVP cable inlet (small) SPD cable inlet (large) G 34 OVP cable inlet 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces A B C D E F Ge3030A Figure 12 Cable Inlet, Variant 4 Table 16 Cable Inlets, Variant 4 Position Description A DC connection, including temperature sensor connection B AC cable inlet C Optical cable inlet D TM cable inlet E TM cable inlet Co-site cable inlet SPD cable inlet F OVP cable inlet 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 35 RBS Description A B C D E F G Ge3319A Figure 13 Cable Inlet, Variant 5 Table 17 Cable Inlet, Variant 5 Position Description A DC connection, including temperature sensor connection B AC cable inlet C Optical cable inlet D TM cable inlet E SPD cable inlet (DC cable outlet -48 V DC) F TM cable inlet G OVP cable inlet SPD cable inlet (DC cable outlet -48 V DC) 6.2 RBS-TMR Figure 14 shows the connection interfaces of the RBS-TMR, and Table 18 describes them. Figure 15 shows the cable inlets of the RBS-TMR, and Table 19 describes them. 36 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces A E H I G F B Ge0926C Figure 14 Connection Interfaces for RBS-TMR Table 18 Connection Interfaces for RBS-TMR Position Description A ESD wrist strap interface B Grounding interface E Site LAN or LMT interface F Power cable outlets G Power connection interface H TM cable inlets I Service outlet interface 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 37 RBS Description F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 Ge3053A 38 Figure 15 Cable Inlets for RBS-TMR Table 19 Cable Inlets for RBS-TMR Position Description F1 DC connection, including temperature sensor connection F2 AC cable inlet F3 Power cable outlets F4 TM cable inlets F5 TM cable inlets 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces 6.3 Position A, ESD Wrist Strap Interface OM DC M N T DI P OI NG N O ES The ESD wrist strap interface provides two connection points, each consisting of a BS 3/8-inch input for the ESD wrist strap as shown in Figure 16. The wrist strap protects boards and units from being damaged by ESD from the person working with the board or unit. GROUN Ge0884B Figure 16 ESD Interface 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 39 RBS Description 6.4 Position B, Grounding Interface All equipments must be connected to the same Main Earthing Terminal (MET) at the site using a 35 mm2 copper cable, or equivalent as shown in Figure 17. Ge1074A Figure 17 40 Grounding Interface 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces 6.5 Position C, SAU Interface This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. Fan Group 2 Fault Fan Group 1 SAU EC-bus A Fan Group 3 EC-bus C Fault EC-bus B Fan Group 4 Outdoor functions The SAU is connected to the SCU board. Power is supplied to the SAU by the Enclosure Control Bus (ECB) through the 10 pole RJ-45 connector, as shown in Figure 18. Ge0318A Figure 18 SAU Power Interface 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 41 RBS Description 6.6 Position D, External Alarm Interface This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. The RBS can have up to 16 external alarm interfaces that are connected with screw terminals located on the OVPs, as shown in Figure 19 and from there connected to the SAU. Ge0893C Figure 19 42 External Alarm Interface 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces 6.7 Position E, Radio Interface The connection between the RBS and an external radio is made by an optical cable. Optical cables are available in standard lengths, from a few meters up to several hundred meters. For longer distances between the RBS and an external radio, and for greater connection flexibility in general, an existing optical fiber transmission network can be used to increase the total length of the optical cable. Optical cables are connected to the optical fiber transmission network through a connection box. Figure 20 shows the supported scenarios for connection of optical cables between an RBS and an external radio. 1) RRU or AIR Unit LC/ODC 2) RRU or AIR Unit LC/ODC Optical Cables LC Optical Cables Extension Cables or Leased Line LC Optical Cables LC/ODC LC LC DU in RBS DU in RBS Ge2811A Figure 20 Optical Cables Connection Scenarios Figure 21 shows the optical cable interface on the DU. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 43 RBS Description Ge2812A Figure 21 Optical Cable Interfaces on DUs Specific information about optical cables can be found in Installing Optical Cables for Main-Remote Solutions. 44 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces 6.8 Position E, Transmission Interface Several transmission alternatives are available. The alternatives with their corresponding cable types are described in Section 7 on page 57. 6.9 Position E, LMT Interface (Optional) The client is connected to the cabinet for configuration and service purposes. In WCDMA the site LAN is used to communicate with the RBS Element Manager (EM). In LTE and CDMA the Local Maintenance Terminal (LMT) is used to communicate with the RBS EM. In GSM the site LAN is used to communicate with the Operation and Maintenance Terminal (OMT). The client is connected to the LMT port on the DU. The LMT, LMT A, and LMT B ports are RJ-45 connectors. For initial configuration LMT A is used as shown in Figure 24. If the DU only has one LMT port, an LMT splitter cable is used to access LMT A, as shown in Figure 22. For site LAN access LMT B is used as shown in Figure 24. If the DU only has one LMT port, that LMT port is configured as an LMT B port by default, see Figure 23. The LMT B can also be accessed via the LMT splitter cable as shown in Figure 22. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 45 LMT RBS Description LMT B LMT A Ge3464A Figure 22 46 Connecting to the Client, DU with LMT Port. Accessing LMT A and LMT B using an LMT Splitter Cable. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 LMT Connection Interfaces Ge3465A Figure 23 Connecting to the Client, DU with LMT Port. LMT B by Default. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 47 LMT B LMT A RBS Description Ge3466A Figure 24 Connecting to the Client, DU with LMT A and LMT B Ports. In CDMA, Vortex (VRX) is used to commission the HW units. A client can be connected to the DBA through VRX for configuration and service purposes. Figure 25 shows the DBA VRX interface. 48 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces DBA 224 IPBH DYCHN VRX 7 RS-232 1 ALM HSSL 8 9 ANT 10 10M 8X EVEN 6 RM1 RM6 PWR VRX Ge2727B Figure 25 DBA VRX Interface Detailed information is found in Hardware Maintenance Instructions. 6.10 Position F, GPS Interface or Power Cable Outlets Position F in RBS is the GPS interface (optional). Position F in RBS-TMR is the power cable outlets. 6.10.1 Position F in RBS, GPS Interface (Optional) The RBS may be connected to a GPS receiver system, which is used for timing synchronization of the RBS. The incoming cable to the GPS receiver unit is routed via the GPS cable inlet as shown in Section 6.1.1 on page 31. The cable from the GPS receiver unit is routed to the GPS interface on the DU or XMU shown in Figure 26 and Figure 27. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 49 GPS RBS Description Ge0699C Figure 26 GPS Interface on the DU Figure 27 shows the GPS interface on the XMU. A1 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 B2 B1 A3 A2 A1 48V XMU 02 01 SK0000969B Figure 27 50 GPS Interface on the XMU 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces 6.10.2 Position F in RBS-TMR, Power Cable Outlets Figure 28 shows the power cable outlets in the RBS-TMR. Ge2580A Figure 28 Power Outlets in RBS-TMR 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 51 RBS Description 6.11 Position G, Power Connection Interface Several power connection interfaces are currently available and described in this section. 6.11.1 100–250 V AC AC power is routed through the AC inlet to the PCU AC as shown in Section 6.1.1 on page 31. Parallel AC and DC power feeds are not supported. Incoming AC power, including protective grounding, is connected by screw terminals in the PCU AC. The terminals accept cables with an area between 2.5 mm2 and 16 mm2 if a PCU AC 01 is used, and up to 35 mm2 if a PCU AC 03 is used. Figure 29 shows the connection interface. Ge0879A Figure 29 52 PCU AC Connection 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces 6.11.2 -48 V DC This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. Incoming DC power (two-wire) or external batteries are connected by terminals to the PCF. The terminals accept cables with an area between 16 mm2 and 95 mm2. More detailed information on cross-sectional cable areas and fuse sizes can be found in Section 3.4.2 on page 16. Figure 30 shows the connection interfaces. PCU PCU PCF 01 01 or PCF 01 03 Ge2819A Figure 30 -48 V DC PCF Connection 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 53 RBS Description 6.12 Position H, Antenna Interface or Transmission Cable Inlet Position H in RBS is the antenna interface. Position H in RBS-TMR is the transmission cable inlet. 6.12.1 Position H in RBS, Antenna Interface The RF cables are routed through the cable guide and connected directly to the RU. The antenna connection interface on the RU consists of two 7/16 connectors as shown in Figure 31. Information about connections for various configurations can be found in Antenna and RF Connections. RF A RF B Ge0708B Figure 31 54 Antenna Interfaces on RU in RBS 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Connection Interfaces 6.12.2 Position H in RBS-TMR, Transmission Cable Inlet Figure 32 shows the transmission inlets in the RBS-TMR. Ge2581A Figure 32 6.13 Transmission Inlets in RBS-TMR Position I, Service Outlet Interface (Optional) The service outlet is provided with a 10 A two-pole circuit breaker and Residual Current Breaker (RCB). The service outlet is optional. There are five types of service outlet, each according to the following regional standards: AU, EU, CH, UK, and US. Figure 33 shows the different types of service outlets. Note: The service outlet is only available for AC-powered RBS with PCU AC. CH AU EU UK US Ge0540C Figure 33 Service Outlet Types 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 55 RBS Description 56 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Transmission Standards 7 Transmission Standards This section describes the transmission standards supported by the RBS. The following transmission alternatives are available: • MINI-LINK or OMS transmission installation in the RBS cabinet. More information is found in Transmission Installation and Configurations. • Electrical Ethernet transmission • Optical Ethernet transmission • E1/T1/J1 electrical transmission (WCDMA only) • E1/T1 electrical transmission (GSM only) • STM-1 (Synchronous Transport Module level-1): WCDMA only Table 20 lists the transmission standards. Table 20 Transmission Standards Transmission Standard Transmissi on Capacity (Mbps) Ethernet (electrical) 100/1000 Cable Impedance ( ) Cable Type Physical Layer 100 Twisted pair, balanced lines IEEE 802.3-100/1000Base-T Supported SFP connectors: • 1000Base-SX • 1000Base-LX Ethernet (optical) 1000 Max attenuation 0.5 dB/cabling Optical • 1000Base-LX10 • 1000Base-LX40 • 1000Base-ZX • 1000Base-BX10 • 1000Base-BX20 E1 2.0 120 T1 1.5 100 1.5 100 Japan JT-I431a (ITU-T I.431) 1.5 110 Japan JT-G703 (ITU-T G.703) 155.5 Max attenuation 12 dB/cabling ETSI ETS 300 166 & ITU-T G.703 Twisted pair, balanced lines ANSI T1.403 J1 SFP connectors: STM-1 Optical • S-1.1 • L-1.1 7.1 Electrical Ethernet (Optional) The electrical Ethernet transmission interface from the DU must be routed through the TM cable inlet as shown in Section 6.1.1 on page 31. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 57 RBS Description For CDMA, the electrical Ethernet connection interface on the DBA is equipped with a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) female connector and occupies the position IPBH. On the AEM the electrical Ethernet interface is on port ENET1 and ENET2, and on the XCEM the interface is on port DMI. Figure 34 and Figure 35 show the electrical Ethernet connection interfaces. A shielded cable is required for the connection, and the shield must be grounded at the cabinet entry. TN A Note: Ge0700D Figure 34 DU Electrical Ethernet Interface DBA 224 IPBH DYCHN VRX 7 RS-232 10 10M 8X EVEN 6 RM6 1 2 3 4 PWR DMI ENET1 RS-232 RM1 ENET2 HSSL ESD 9 ANT T1/E1 1 ALM 8 PWR ALM HSSL SK0001058C Figure 35 58 Electrical Ethernet Connections for CDMA 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Transmission Standards 7.2 Optical Ethernet (Optional) The optical Ethernet transmission interface from the DU must be routed through the TM cable inlet as shown in Section 6.1.1 on page 31. The optical Ethernet connection interface on the DU is equipped with optical connectors and occupies positions TN B and TN C if available. The optical Ethernet connection interface on the DBA is equipped with an optical connector and occupies the position IPBH. When using the DU or DBA with optical transmission, one compatible SFP module is needed. Only use SFP modules approved and supplied by Ericsson. These modules fulfill the following: • Compliance with Class 1 laser product safety requirements defined in standard IEC 60825-1. • Certification according to general safety requirements defined in standard IEC 60950-1. • Functionality and performance verified to comply with RBS specifications. Recommended SFP modules are obtained from the product packages of the RBS and the Main Remote Installation products. See Spare Parts Catalog and Main-Remote Installation Products Overview for more information. TN C TN B Figure 36 and Figure 37 show the optical Ethernet connection interfaces. Ge0701E Figure 36 DU Optical Ethernet Interface 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 59 RBS Description DBA 224 IPBH DYCHN VRX 7 RS-232 1 ALM 8 9 ANT 10 10M 8X EVEN 6 HSSL RM1 RM6 PWR IPBH Ge3163B Figure 37 7.3 Optical Ethernet Connection on DBA E1, T1, and J1 (WCDMA only) The E1, T1, or J1 connection is made through terminal blocks without screws on the TM cable inlet, situated at the bottom of the cabinet. The TM cable inlet accepts cables with an area of 0.1–1.5 mm². Two different TM inlet types are available; one for 100–120 , and one for 75 . The transmission cable is routed from the cable inlets to the DU. Note: Not all DUs support E1, T1 and J1 connection. For more information refer to Digital Unit Description. There are two E1, T1, J1 connection interfaces on the front of the DU, as shown in Figure 38. 60 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 ET B ET A Transmission Standards Ge0702C Figure 38 DU E1, J1 and T1 Interface 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 61 RBS Description 7.4 E1 and T1 (GSM only) The E1 and T1 connection interfaces on the DU are equipped with two female RJ-45 connectors, which occupy positions ET A and ET B. ETB ETA Figure 39 shows the E1 and T1 transmission interfaces. ! Ge0901B Figure 39 62 E1 and T1 Transmission Interfaces for GSM 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Transmission Standards 7.5 STM-1 The STM-1 connection interface on the DU is equipped with optical connectors and occupies positions TN B and TN C if available. The optical transmission interface from the DU must be routed through the TM inlet as shown in Section 6.1.1 on page 31. Figure 40 shows the STM-1 transmission interface. Note: Not all DUs support STM-1 connection. For more information refer to Digital Unit Description. When using the DU with optical transmission, one compatible SFP module is needed. Only use SFP modules approved and supplied by Ericsson. These modules fulfill the following: • Compliance with Class 1 laser product safety requirements defined in standard IEC 60825-1. • Certification according to general safety requirements defined in standard IEC 60950-1. • Functionality and performance verified to comply with RBS specifications. TN C TN B Recommended SFP modules are obtained from the product packages of the RBS and the Main Remote Installation products. See Spare Parts Catalog and Main-Remote Installation Products Overview for more information. Ge0701E Figure 40 STM-1 Transmission Interface 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 63 RBS Description 64 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Alarms 8 Alarms This section describes the alarms available when the RBS is connected to an optional SAU. 8.1 Internal Alarms The RBS is equipped with the following internal alarms: • Door alarm • Fan failure alarm • Smoke alarm, optional • Smoke detector failure alarm, optional 8.2 External Alarms This section describes the external alarms. 8.2.1 RRUS (LTE only) LTE provides support for external alarm ports on the RRUS. Information on RRUS external alarm interfaces and installation can be found in Installing Remote Radio Units. 8.2.2 Customer-Specific External Alarms This subsection is not applicable to RBS-TMR. The optional SAU monitors and controls customer equipment. The RBS can handle up to 16 external alarms. An alarm can be generated by two alarm conditions: • Closed loop condition, called Normally Open (NO) NO means that an alarm is triggered when an open switch is closed. • Open loop condition, called Normally Closed (NC) NC means that an alarm is triggered when a closed switch is opened. NC is the default alarm condition. The customer can configure the alarm condition. More information about the SAU can be found in SAU Description. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 65 RBS Description 66 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Acoustic Noise Emission 9 Acoustic Noise Emission This section contains information about acoustic noise emission from an RBS. The values are for a free-standing RBS and an RBS placed against a wall. Note: The acoustic noise emission values for a free-standing RBS and an RBS installed against a wall are tested according to the EN ISO 9614-2 standard. The values are calculated in accordance with the EN ISO 11203 standard. The values may vary depending on the relative sound absorbency of the installation environment. Table 21 and Table 22 show the sound pressure level at different ambient temperatures, directions and distances from the RBS. Note: Sound pressure level values below 1 meter are not shown. All values stated are for the RBS configured up to the design maximum heat load capacity. Values for sub-configured RBSs must be calculated from Table 4. Table 21 Sound Pressure Levels for a Free-Standing RBS – Standard Climate Temperatur e (C) Sound Pressure dB(A) Calculated Distance (m) Front Left Right Back Top 35 12 10 10 10 9 40 7 5 5 5 5 50 2 1 1 1 1 60 <1 <1 <1 <1 <1 20 Table 22 Temperature (C) Sound Pressure Levels for Against-a-Wall RBS – Standard Climate Sound Pressu re Level dB(A) Calculated Distance (m) Front Left Right Top 35 12 13 13 13 40 7 7 7 7 50 2 2 2 2 60 <1 <1 <1 <1 20 Table 23 shows the sound pressure levels in accordance with EN ISO 11201, at a bystander position 1 m from the cabinet and 1.5 m above the floor. The calculations are valid for free field installation. If the RBS is located in a room, the sound pressure level will be higher than indicated in Table 23. The calculations are in accordance with EN ISO 11203. Table 23 shows the values for an RBS configured up to the design maximum heat load capacity with standard climate. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 67 RBS Description Table 23 Design Maximum Operating Condition Temperature in C 68 Sound Pressure Level at Bystander Position of 1 meter dB(A) Front Left Right Back 20 54 50 48 51 25 60 51 50 55 30 63 55 57 59 45 72 63 63 66 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Standards, Regulations, and Dependability 10 Standards, Regulations, and Dependability This section presents a brief overview of standards, regulatory product approval, and Declaration of Conformity. Declaration of Conformity "Hereby, Ericsson AB, declares that this RBS is in compliance with the essential requirements and other relevant provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC." 10.1 Regulatory Approval The RBS complies with the following market requirement: • European Economic Area (EEA) market requirements, R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC Alert Mark (Class 2 equipment). Restrictions to use the apparatus may apply in some countries or geographic areas. Individual license to use the specific radio equipment may be required. Apparatus may include Radio Transceivers with support for frequency bands not allowed or not harmonized within the European Community (EC). • North American market requirements • FCC and ETL requirements • Various other market requirements 10.1.1 Safety Standards Compliance In accordance with market requirements, the RBS complies with the following product safety standards and directives: International • IEC 60 950-1 • IEC 60 950-22 • IEC 60 215 and Amd.2 Europe • IEC 60 215 and Amd.1 and 2 • IEC 60 950-1 • IEC 60 950-22 and A11:2008 • EN 60 215:1989 • EN 60 950-1:2006, Ed. 2 North America • UL 60950-1 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 69 RBS Description • • • 10.1.2 CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-1-07 UL 60950-22 CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-22-07 EMC Standards Compliance The RBS complies with the following standards regarding Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): International • 3GPP TS25.113 • 3GPP TS36.113 • 3GPP TS37.113 Europe • ETSI EN 301 489-1 • ETSI EN 301 489-23 North America • FCC CFR 47 Part 15 • IC ICES-003 10.1.3 Radio Standards Compliance The RBS complies with the following radio standards: International • 3GPP TS25.141 • 3GPP TS36.141 • 3GPP TS37.141 Europe • ETSI EN 301 502 • ETSI EN 301 908-1 • ETSI EN 301 908-3 • ETSI EN 301 908-14 North America • FCC CFR 47 Part 2, 22, 24 and 27 (Frequency-dependent) • RSS 131, 132 and 139 and RSS-Gen (Frequency-dependent) 10.1.4 Marking To show compliance with legal requirements, the product is marked with the following: 70 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 Standards, Regulations, and Dependability Europe • CE mark North America • ETL/cETL • FCC ID, IC ID, FCC part 15 statement 10.2 Dependability The RBS is designed for a technical lifetime of 20 years (24-hour operation). The following preventive maintenance condition must be fulfilled to guarantee the availability of the RBS: • Fans The fans must be inspected (and cleaned if necessary) every year. Ericsson recommends replacing the fans every 10 years. 10.3 Spare Parts The RBS adheres to the Ericsson Serviceability and Spare Part Strategy. Information about spare parts can be found in Spare Parts Catalog. 10.4 Vandal Resistance Unauthorized access is not possible without damaging the unit. 10.5 Transportation and Storage Information about transportation and storage of the RBS can be found in Transportation and Storage. 28/1551-LZA 701 6001 Uen AD | 2012-12-17 71